![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nutrients |
Essential substance for any organism to grow and be healthy. |
1. Plants absorb these from soil
2. Six classes of these: water, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and proteins. |
|
|
Heterotroph |
Digesting other organisms is how they get energy. |
1. Consumers
2. They can eat autotrophs or other forms of themselves. |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Absorbing nonliving things is how they get energy. |
1. Producers
2. They use photosynthesis and chemosynthesis. |
|
|
Photoautotroph |
Autotroph that uses photosynthesis to get energy. |
1. Known as holophytic.
2. Typically they are plants. |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
CO2 and H2O that react to make organic compounds. |
1. Used by plants, a few protistans, and certain bacteria.
2. Base of most food webs. |
|
|
Chemoautotroph |
Autotrophs that uses chemosynthesis for energy. |
1. Most bacteria and archaea.
2. Contrasts photoautotrophs. |
|
|
Chemosynthesis |
The chemical reactions that take place create organic compounds from using chemical energy. |
1. Conversion of one or more carbon molecules.
2. Uses methane as energy in comparison to sunlight. |
|
|
Cell Respiration |
Chemical reactions all organisms use to complete necessary tasks and help organic compounds release energy. |
1. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy
2. Used by heterotrophs, decomposers, and autotrophs. |
|
|
Producers |
Autotrophs |
1. Use photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
2. Energy from sunlight, minerals, and air. |
|
|
Producers |
Autotrophs |
1. Use photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
2. Energy from sunlight, minerals, and air. |
|
|
Consumers |
Heterotrophs |
1. Eat other heterotrophs and autotrophs.
2. Consume living or dead organisms. |
|
|
Decomposers |
Consume already dead organisms to obtain energy. |
1. Considered heterotrophic.
2. Usually fungi and bacteria. |
|
|
Food web |
Relationships between autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers to show energy in an ecosystem. |
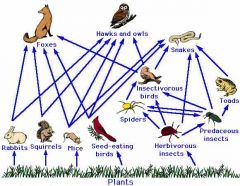
1. Shows energy and nutrient transfer in an ecosystem.
2. |
|
|
Food web |
Relationships between autotrophs, heterotrophs, and decomposers to show energy in an ecosystem. |
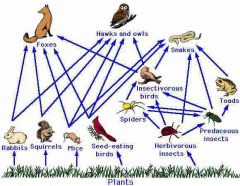
1. Shows energy and nutrient transfer in an ecosystem. |
|
|
Biotic |
Living organisms |

1. Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi |
|
|
Abiotic |
Nonliving organisms |

1. Examples are: rain, sunlight, and fog |
|
|
Ecosystem |
A place where biotic and abiotic organisms live together. |

1. Example: the forest |
|
|
Habitat |
An area where specific organisms live in an ecosystem. |

1. Example: a small pond in a large forest. |
|
|
Biosphere |
The entire Earth and its ecosystems. |
|
|
|
Biosphere |
The entire Earth and its ecosystems. |
|
|
|
Energy |
An object's ability to complete tasks. |
|
|
|
Biosphere |
The entire Earth and its ecosystems. |
|
|
|
Energy |
An object's ability to complete tasks. |
|
|
|
Chemical Energy |
Energy kept in chemical bonds of compounds. |
|
|
|
Biosphere |
The entire Earth and its ecosystems. |

Earth is a sphere with a lot of biology on it. |
|
|
Energy |
An object's ability to complete tasks. |

1. This can be used for anything like creating power or growing. |
|
|
Chemical Energy |
Energy kept in chemical bonds of compounds. |

1. Batteries and natural gas are a stored form of this. |
|
|
Free Energy |
Remaining energy in a cell able to do work. |
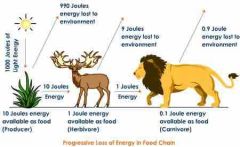
1. A lot of this is lost to the environment in the form of heat. |
|
|
Heat Energy |
Energy transferred between objects because of a difference in temperature and causes a change in entropy. |
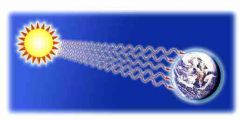
1. Heat is transferred from a high temperature to a lower one. |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can be in different forms but never is destroyed. |
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can be in different forms but never is destroyed. |
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Systems change causing entropy but it will stay the same if not increased. |
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can be in different forms but never is destroyed. |
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Systems change causing entropy but it will stay the same if not increased. |
|
|
|
Entropy |
Disorder that makes energy unable complete tasks. |
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can be in different forms but never is destroyed. |
|
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Systems change causing entropy but it will stay the same if not increased. |
|
|
|
Entropy |
Disorder that makes energy unable complete tasks. |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that make faster chemical reactions because they cause a decrease in activation energy. |
|
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy can be in different forms but never is destroyed. |
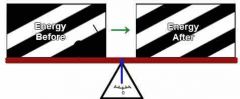
1. Newton assisted in creating it. |
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Systems change causing entropy but it will stay the same if not increased. |

1. 2 of these were created about energy. |
|
|
Entropy |
Disorder that makes energy unable complete tasks. |

1. Commonly known as disorder. |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that make faster chemical reactions because they cause a decrease in activation energy. |
1. They are a form of catalyst. |
|
|
Catalysts |
Speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. |

1. Enzymes are a biological form of this. |
|
|
Active Site |
Part of an enzyme that connects with a protein or substrate during a reaction. |

1. Created to fit with a specific substrate. |
|
|
Substrate |
Connects with the active site in a reactions. Enzymes act on this. |
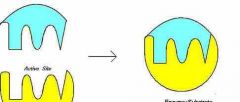
1. Must fit perfectly with an active site to form a correct enzyme. |
|
|
Metabolism |
Chemical reaction in an organism to maintain normal function. |
|
|
|
Metabolism |
Chemical reaction in an organism to maintain normal function. |

1. Specific foods can kickstart this process. |
|
|
Synthesis |
Chemical reactions cause compounds made from smaller parts inside cells and organisms. |
|
|
|
Synthesis |
Combining things to create something new. |

1. Chemical reactions with new products occur from this process. |
|
|
Biosynthesis |
Chemical reactions cause compounds made from smaller parts inside cells and organisms. |
1. A form of synthesis found inside the body. |
|
|
Decomposition |
Decaying of an organism to cause the breakdown of it. |

1. Can be caused by heat, light, or activity chemically or biologically. |
|
|
Oxidation |
Loss of electrons during a chemical reaction. |

1. Rust forming on metal is an example of this. |
|
|
ATP |
Stores energy and kickstarts metabolism. Called adenosine triphosphate. |
|
|
|
ATP |
Stores energy and kickstarts metabolism. Called adenosine triphosphate. |
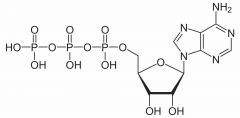
1. If one phosphate group is removed, it becomes adenosine diphosphate. |
|
|
ADP |
Adenosine diphosphate. It is created by removing a phosphate group from ATP. |
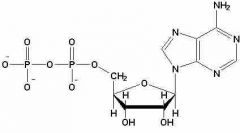
1. It is a nucleotide that helps to transfer energy. |

