![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
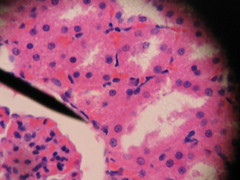
Simple Squamous: Allows passage of molecules through diffusion and filtration. |
|
|
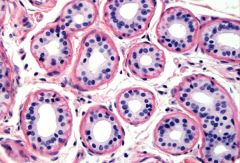
Simple Cuboidal: Performs secretion and absorption in ducts and tubules. |
|
|
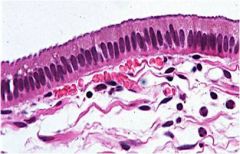
Simple Columnar: Performs absorption and secretion of mucus enzymes. |
|
|
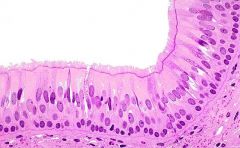
Psuedostratified Columnar: Secretion of mucus and propulsion of mucus through ciliary action. |
|
|
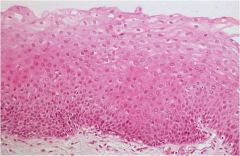
Stratified Squamous: Works to protect underlying tissue. |
|
|
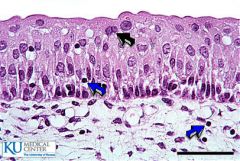
Transitional: Can distend or shrink based on contents, mainly found in urinary bladders. |
|

|
Bone: Helps support body and gives it structure.
|
|
|
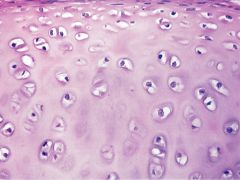
Hyaline Cartilage: Supports and reinforces the body and bones. Has resilient properties. |
|
|
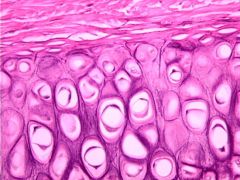
Elastic Cartilage: Maintains the shape of structures, but is very flexible. An example would be the ear. |
|
|
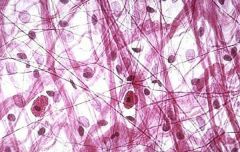
Areolar: Wraps, and cushions organs |
|
|
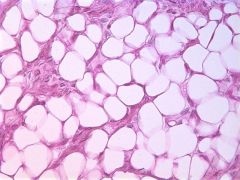
Adipose: Provides space to hold long term energy and triglycerides in the shape of fat droplets. Very small nuclei with large vacuole. |
|
|
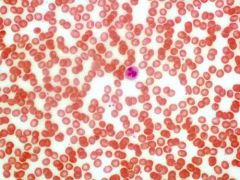
Blood: Provides transport of respiratory gasses, nutrients, and hormones. |
|
|
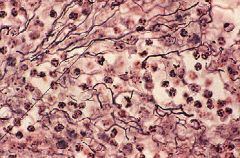
Reticular: Uses fibers to form soft, internal skeleton. |
|
|
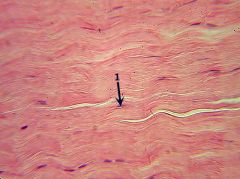
Dense Fibrous: Used in parts of body under lots of tension. Able to withstand lots of tension. |
|

|
Skeletal Muscle: Works to preform voluntary movement and manipulation of environment. Can have multiple nuclei and visible striations. |
|
|
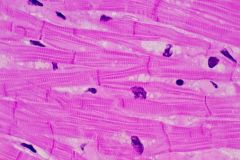
Cardiac Muscle: Contracts and releases the heart, pumps blood into circulatory system. Has only one nuclei per cell and has striations as well as intercolated discs. |
|
|
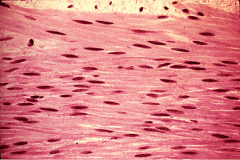
Smooth Muscle: Propels items along internal structures. Has only one nuclei per cell and has striations. |
|
|
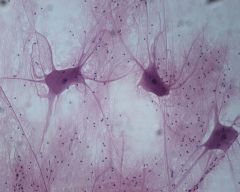
Neuron: Transports action potentials and neurotransmitters to brain and spine. |

