![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is the definition of biology? |
the study of life |
|
|
|
what are the 8 characteristics of life? |
1) highly organized DNA 2) growth and development 3) response to enviromental 4) reproduces 5) evolves 6) uses energy 7) homeostasis 8) made of cells |
|
|
|
what are to 7 levels of classification? |
1) kingdom 2) phylum 3) class 4) order 5) family 6) genus 7) species |
|
|
|
what is the monomer of carbohydrates? |
sugar |
|
|
|
what is the monomer of lipids? |
fatty acids |
|
|
|
what is the monomer of proteins? |
amino acids |
|
|
|
what is the monomer of nucleic acids? |
nucleotides |
|
|
|
what elements are found in carbohydrates? in what ratio? |
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen; 1:2:1 |
|
|
|
hydrolysis |
hydro - water lysis - to cut separating molecules by readding water |
|
|
|
dehydration synthesis |
dehydration - to take away water synthesis - to create taking water away to link molecules together |
|
|
|
isomer |
same chemical formula but different structure |
|
|
|
monosaccharide |
simple sugars |
|
|
|
disaccharide |
two monosaccharides joined together |
|
|
|
polysaccharide |
many sugars; more than 3 monosaccharides joined together |
|
|
|
triglyceride |
tri - 3 fatty acids glyceride - glycerol 3 fatty acids and glycerol |
|
|
|
phospholipid |
compose the cell membrane; contain glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group |
|
|
|
what regions on a phospholipid are hydrophilic? hydrophobic? |
head - hydrophilic tail - hydrophobic |
|
|
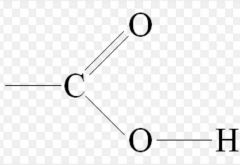
what is this? |
carboxyl group |
on a lipid |
|
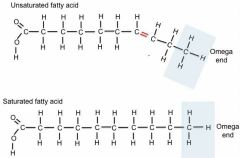
where is the omega end found? |
fatty acids |
|
|
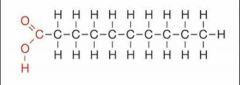
what kind of fat is this? |
saturated fat |
|
|
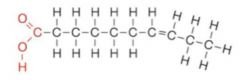
what kind of fat is this? |
unsaturated fat |
|
|
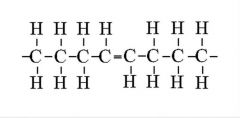
what kind of fat is this? |
trans unsaturated fat |
|
|
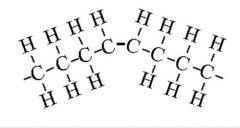
what kind of fat is this? |
cis unsaturated fat |
|
|
|
how do you recognize an omega 3 fatty acid? |
a hydrogen is missing 3 from the omega end |
|
|
|
amino acid |
monomer of proteins |
|
|
|
peptide bond |
a bond formed between two adjacent amino acids |
|
|
|
polypeptide |
multiple amino acids linked together |
|
|
|
structure of amino acids |
contains amino group, carboxlic acid, and a radical (R) group; each is identical except for the R group |
|
|
|
parts of a nucleotide |
sugar, nitrogen base, and phosphate group |
|
|
|
what sugar is found in DNA? RNA? |
deoxyribosnucleic acid; ribonucleic acid |
|
|
|
what bases are found in DNA? RNA? |
DNA - adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine RNA - adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine |
|
|
|
enzymes are...? |
proteins |
|
|
|
catalyst |
a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed 8 |
|
|
|
what is the function of a phospholipid in a cell membrane? |
what goes in and comes out must pass through it somehow |
|
|
|
what is the function of proteins in a cell membrane? |
form many structures in your body; controls what comes in and out |
|
|
|
what is the function of carbohydrates in the cell membrane? |
"markers" to allow your body to recognize your cells from someone else's |
|
|
|
why are phospholipid tails located on the inside of the membrane? |
they're hydrophobic and don't like water |
|

