![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Stimulus |
Any change in the environment that cause a response. |
Environmental change |
|
|
Response |
A change in behavior or physiology as a result of a change in the environment |
Behaviour change |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The maintenance of the internal environment in a constant state despite eternal changes |
Maintainance |
|
|
Negative feedback |
A process that brings about a reversal of any change in conditions.
It maintains optimal metabolism and homeostasis. |
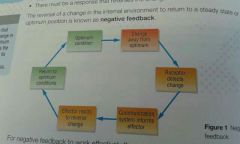
Change to/from optimum conditions |
|
|
Positive feedback |
A process that increases any change detected by the receptors. Often harmful. |
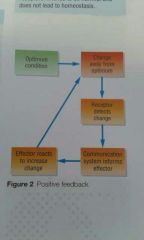
Increase change |
|
|
Beneficial Positive feedback |
During pregnancy the cervix begins to stretch, which stimulates the secretion of oxytocin, which increases uterine contraction, which stretches the cervix more. |
Pregnancy and oxytocin |
|
|
Harmful positive feedback |
When the body gets too cold, enzymes become less active and the body cools further. |
Cold |
|
|
Ectotherm |
An organism that relies on external sources of heat to regulate body temperature. |
Lizard |
|
|
Endotherm |
An organism that can use internal sources of heat, such as heat generated from metabolism in the liver, to maintain its body temperature. |
Humans |
|
|
Ectotherm advantages |
Less food used for respiration. Less food is needed overall. May be able to survive extended periods without food. A greater proportion of energy obtained can be used for growth.
|
Food |
|
|
Ectotherm Disadvantages |
Les active in cooler temperatures - may need to warm up in the morning - more risk of predation. May not be active in the winter - need to have sufficient food supplies to survive without eating.
|
Cold |
|
|
Temperature regulation in ectotherms |
When ecotherms are cold they will change behaviour or physiology to increase heat absorption from the environment.
When they are hot, behaviour or physiology change to decrease heat absorption. |
Hot and cold |
|
|
Temperature regulation in ectotherms |

Adaptations |
Adaptation |

