![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
430 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

galley
|

Warship with a sail and oars that was used in ancient times; it disappeared in the 18th century.
|
|
|

trireme
|

Warship used by the Romans with a ram, a sail and three vertical rows of oars.
|
|
|
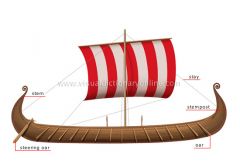
longship
|
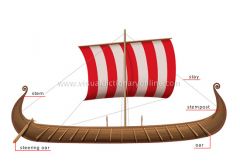
Sailing ship used by the Vikings during the Middle Ages; it had square sails, oars and a prow and stern that were usually sculpted.
|
|
|

galleon
|

Large warship with sails that was used by the Spanish in the 17th and 18th centuries for trading with the colonies.
|
|
|

caravel
|

Fast ship with three or four masts; it was used especially in the 15th and 16th centuries for exploration.
|
|
|

side-wheeler
|

Ship used in the 19th century that was propelled by steam, which turned two paddle wheels.
|
|
|
dugout canoe
|
Light boat used in Africa and Oceania that is made from one piece of wood and is propelled by a paddle or a sail.
|
|
|

outrigger canoe
|

Dugout canoe that is stabilized by one or two outriggers.
|
|
|

junk
|

Boat used in the Far East for fishing and transporting cargo; its sails are made of matting or canvas and are stretched by battens.
|
|
|

felucca
|

A Mediterranean boat of ancient times that was propelled by a sail or an oar; it is still found today on the Nile.
|
|
|

gondola
|

Venetian boat characterized by raised curved ends and steered by an oar.
|
|
|

canoe
|

Light boat used by Native Americans; it is propelled by a paddle and is used for transporting people and cargo.
|
|
|
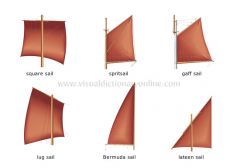
sails
|
sections of durable fabric that are sewn together and mounted on a mast; they create a surface that causes a boat to move when the wind blows against it.
|
|
|

rigs
|

Various combinations of sails that distinguish one sailboat from another.
|
|
|

masting and rigging
|

Masts, yards, ropes and other movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|
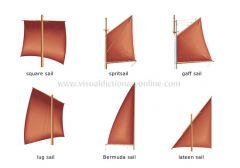
sails
|
A sailboat’s sails that are rigged on the bowsprit, the foremast, the main masts, the jiggermast and between these masts.
|
|
|

container ship
|

Ship that is designed for transporting cargo in containers in its hold and on its deck.
|
|
|

bulk carrier
|

Ship for transporting raw dry materials, such as grain, coal and ore.
|
|
|
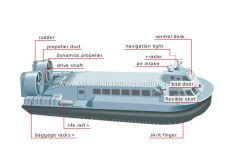
hovercraft
|
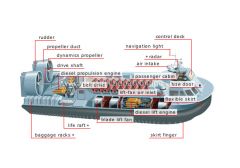
Propeller vehicle that moves above water (or land) by gliding on a cushion of air it creates by blowing downward.
|
|
|

drill ship
|

Ship for drilling for oil in deep water (half mile or more); it is more mobile but less stable than a drilling rig.
|
|
|

tug
|

Boat propelled by powerful engines that is used to tow boats and other floating craft to help them maneuver or to rescue them.
|
|
|

ice breaker
|

Boat that opens up a navigable passage through ice.
|
|
|
tanker
|
Ship with large reservoirs for transporting liquid petroleum products.
|
|
|

trawler
|

Fishing boat that tows a large funnel-shaped net (trawl).
|
|
|

cabin cruiser
|

Pleasure boat of various sizes and speeds with a cabin fit to live in; it can navigate the sea and inland waterways.
|
|
|

motorboat
|

Part of the deck for relaxation; it is surrounded by a handrail.
|
|
|

houseboat
|

Motorized pleasure boat for navigating inland waterways; it is characterized by a long deck and a cabin fit to live in.
|
|
|

ferry boat
|
Compartment from which the pilot operates the boat.
|
|
|
passenger liner
|
Large cruise ship, fitted like a luxury hotel and with diverse recreation facilities for passengers.
|
|
|

hydrofoil boat
|

Fast boat with foils, which lift and support the hull above water when cruising speed is reached.
|
|
|
Hydrochlorothiazide
|
HydroDiuril®; Microzide
|
Diuretic
|
|

examples of anchors
|

The weight and the shape of the arms of anchors are designed to hook onto various bottoms (such as firm, loose or reedy).
|
|
|

life-saving equipment [1]
|

Instruments and equipment for signaling a boat’s presence and for saving people from drowning.
|
|
|

life-saving equipment [1]
|

Instruments and equipment for signaling a boat’s presence and for saving people from drowning.
|
|
|

life-saving equipment [3]
|

Instruments and equipment for signaling a boat’s presence and for saving people from drowning.
|
|
|
sextant
|
Optical instrument for measuring the angle between a heavenly body and the horizon to determine the ship’s position.
|
|
|

liquid compass
|

Instrument with magnets that floats on a liquid; it indicates magnetic north.
|
|
|
depth finder
|
Device that uses a sonic pulse to measure the depth of water below the boat.
|
|
|

satellite navigation system
|

Device that uses radio signals transmitted by a network of satellites to plot a boat’s position and course on a chart.
|
|
|

lighthouse
|

Tower with a powerful lamp at the top for guiding ships.
|
|
|

lighthouse lantern
|

Powerful lamp that projects an encoded beam.
|
|
|

pillar buoy
|

Floating beacon with a pylon-shaped superstructure.
|
|
|
cylindrical buoy
|
Floating beacon with a cylindrical superstructure.
|
|
|

high focal plane buoy
|

Floating beacon whose light is especially high above the surface of the water.
|
|
|

high focal plane buoy
|

Floating beacon whose light is especially high above the surface of the water.
|
|
|

buoyage regions
|

The color of the buoys that indicate starboard and port is the opposite in various parts of the world.
|
|
|
cardinal marks
|
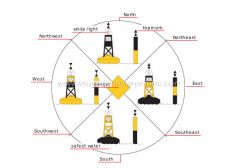
Buoys of standardized colors, topmarks and lights whose placement alone or in a pattern corresponds to the divisions of a compass.
|
|
|
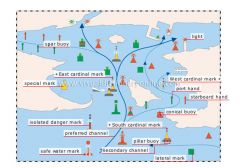
daymarks (region B)
|
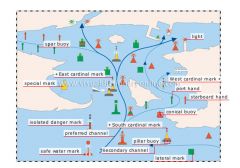
System B combines lateral and cardinal marks. It is the opposite of system A, in which starboard marks are red and port marks are green.
|
|
|
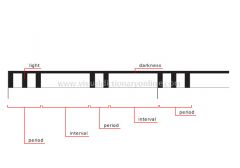
rhythm of marks by night
|
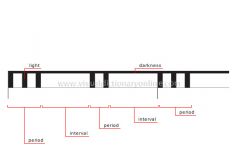
Lights that shine at night; their color and the frequency of their flashing signal various meanings, including the source of the light.
|
|
|

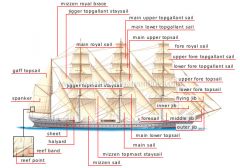
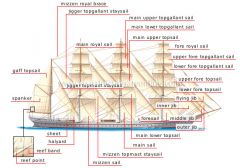
masting and rigging [1]
|

masts, yards, ropes and other Movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|

masting and rigging [2]
|

Masts, yards, ropes and other movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|
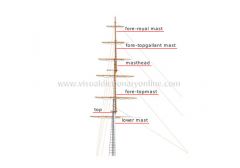
masting and rigging [3]
|
Masts, yards, ropes and other movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|
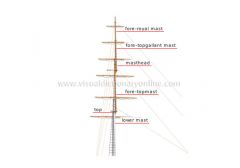
masting and rigging [4]
|
Masts, yards, ropes and other movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|
masting and rigging [5]
|
Masts, yards, ropes and other movable sailing equipment that support and manipulate the rigging.
|
|
|
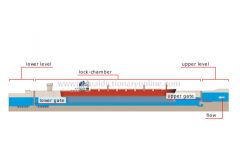
canal lock
|
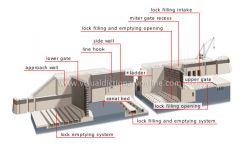
Structure with a lock-chamber that can be filled with water or emptied to raise or lower a ship from one water level to another.
|
canal lock: side view
|
|
harbor
|
Site for refueling and repairing ships, loading and unloading cargo and embarking and disembarking passengers.
|
|
|
|
poop
|
Structure above the aft deck that extends athwartships; it usually serves as officers’ quarters.
|
|
|
|
gaff sail boom
|
Horizontal yard articulating on a mast; it keeps the bottom edge of a sail taut.
|
|
|
|
lift
|
Rope connecting two yards of a sail and used to maneuver them.
|
|
|
|
gaff
|
Diagonal yard aft of a mast and supporting the top part of a gaff sail.
|
|
|
|
oar
|
Long piece of wood that is broad and flat at one end; it is mounted on the boat and pulled by one or more people to propel the boat.
|
|
|
|
topping lift
|
Rope that holds the sail’s gaff loosely in place.
|
|
|
|
steering oar
|
Oar at the back of the ship acting as rudder.
|
|
|
|
jiggermast
|
Mast located aft on the four-masted bark.
|
|
|
|
figurehead
|
Sculpted timber on the prow of a ship in ancient times that depicted a human, a god or a mythical creature.
|
|
|
|
pole
|
Tapered top end of a mast.
|
|
|
|
stempost
|
Main timber reinforcing the prow.
|
|
|
|
yard
|
Long pole that is supported by the mast and holds up the edge of a sail.
|
|
|
|
funnel
|
Tall pipe atop the engine that evacuates the steam and the combustion smoke.
|
|
|
|
footrope
|
Rope hanging along the entire length of a yard that is used by sailors to trim the sails.
|
|
|
|
paddle wheel
|
Wheel with blades that propels the boat; it is driven by a steam engine.
|
|
|
|
fore-topmast
|
Mast that is immediately above a lower mast and carries a topsail.
|
|
|
|
lateen yard
|
Long inclined pole that is supported by the mast and rigged with a triangular sail.
|
|
|
|
masthead
|
Topmost section of a mast that is sometimes doubled with the lower section of the mast supporting it; the stays and shrouds are attached to it.
|
|
|
|
mast
|
Tall pole that is sometimes slightly inclined; it supports the lateen yard.
|
|
|
|
fore-topgallant mast
|
Mast above the fore-topmast that carries a topgallant sail.
|
|
|
|
mizzenmast
|
Mast on the stern of the boat.
|
|
|
|
fore-royal mast
|
Mast above the fore-topgallant mast that carries a royal sail.
|
|
|
|
mainmast
|
Principal mast that is fixed approximately in the center of the boat.
|
|
|
|
lower mast
|
Bottom section of a mast that is solid and thick so it can support the upper sections.
|
|
|
|
foremast
|
Mast nearest the prow of the boat.
|
|
|
|
top
|
Platform at the top of the lower mast from which the upper rigging can be manipulated.
|
|
|
|
batten
|
Rigid pole inserted into the sail’s batten pockets to maintain its shape.
|
|
|
|
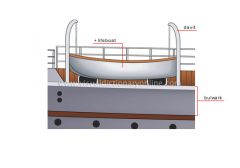
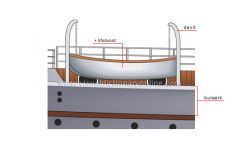
davit
|
Skid hanging over the edge of the ship that supports a boat and is used to lower and raise it.
|
|
|
|
rudder
|
Submerged component that pivots on a vertical axle and is used to steer the boat.
|
|
|
|
lifeboat
|
Boat for transporting passengers and crew in the event of shipwreck.
|
|
|
|
outrigger boom
|
Wooden pole connecting the outrigger to the hull.
|
|
|
|
bulwark
|
Part of the hull above deck level that protects against waves and serves as a parapet.
|
|
|
|
outrigger
|
Piece of wood parallel to the hull that stabilizes the boat.
|
|
|
|
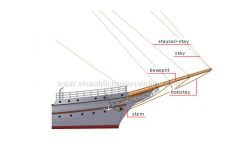
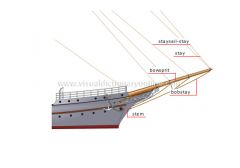
bobstay
|
Rope counterbalancing the tension caused by the stays and the staysail-stays on the bowsprit.
|
|
|
|
hull
|
Part of the boat’s structure that forms a watertight vessel.
|
|
|
|
bowsprit
|
Mast extending before the stem; additional jibs can be attached to it.
|
|
|
|
prow ornament
|
The iron prow is characteristic of gondolas; it symbolizes the pointed caps of the doges and the districts of Venice.
|
|
|
|
stem
|
Main timber reinforcing the prow.
|
|
|
|
gaff sail
|
Trapezoidal sail that is rigged entirely aft of the mast; its top edge is supported by a diagonal yard called a gaff.
|
|
|
|
staysail-stay
|
Stay supporting a staysail or jib
|
|
|
|
ram
|
Timber jutting out in front of the prow usually at water level; it was used to punch holes in the hulls of enemy ships.
|
|
|
|
spritsail
|
Trapezoidal sail that is rigged entirely aft of the mast and is supported by a long, diagonal yard, called a sprit; it articulates at the bottom of the mast.
|
|
|
|
stay
|
Taut rope between a mast and another point on the masting; it secures and supports the mast fore of it.
|
|
|
|
stern
|
Rear end of a ship.
|
|
|
|
lug sail
|
Trapezoidal sail that hangs from a yard; it is attached to the mast one-third of the way from its end.
|
|
|
|
stay
|
Rope strung tautly from the top of the mast to the planking to stabilize the mast.
|
|
|
|
main sail
|
Lowest square sail on the mainmast.
|
|
|
|
Bermuda sail
|
Triangular sail that is also called a Marconi sail; its longest side is attached directly to a tall mast and its base is attached to a pole called a boom.
|
|
|
|
main lower topsail
|
Square sail above the main sail.
|
|
|
|
lateen sail
|
Triangular sail supported by a long tilted yard called a lateen yard; it is attached to the mast in its middle.
|
|
|
|
foresail
|
Lowest square sail on the foremast.
|
|
|
|
square sail
|
Trapezoidal sail that hangs from a yard; it is attached to the mast in its middle.
|
|
|
|
lower fore topsail
|
Square sail above the foresail.
|
|
|
|
rigs
|
Various combinations of sails that distinguish one sailboat from another.
|
|
|
|
inner jib
|
Very heavy triangular staysail that lies farthest aft on the bowsprit.
|
|
|
|
square sail
|
Trapezoidal sail that hangs from a yard; it is attached to the mast in its middle.
|
|
|
|
middle jib
|
Triangular staysail that lies between the outer jib and the inner jib.
|
|
|
|
brig
|
Two-masted ship with a foremast and a mainmast and square sails; a spanker can be added to the mainmast and three jibs to a bowsprit.
|
|
|
|
outer jib
|
Triangular staysail that lies between the flying jib and the middle jib.
|
|
|
|
brigantine
|
Two-masted ship that is lighter than the brig and rigged differently.
|
|
|
|
flying jib
|
Very light triangular staysail that is foremost on the bowsprit.
|
|
|
|
mainmast
|
One of the principal parts of the ship; it is located closest to the center of gravity.
|
|
|
|
upper fore topsail
|
Square sail between the lower fore topgallant sail and the lower fore topsail.
|
|
|
|
foremast
|
Mast nearest the prow of the boat.
|
|
|
|
lower fore topgallant sail
|
Square sail between the upper fore topgallant sail and the upper fore topsail.
|
|
|
|
backstay
|
Long taut rope between the mast and the deck; it secures and supports the mast athwartships and aft.
|
|
|
|
upper fore topgallant sail
|
Square sail below the fore royal sail.
|
|
|
|
shroud
|
Heavy taut rope between a mast and the side of the ship; it secures and supports the mast on the sides.
|
|
|
|
fore royal sail
|
Small square sail at the top of the foremast above the fore topgallant sail.
|
|
|
|
side
|
Longitudinal surface of the ship.
|
|
|
|
main upper topsail
|
Square sail between the main lower topgallant sail and the main lower topsail.
|
|
|
|
schooner
|
Two-masted ship with a foremast and a mainmast; it has gaff sails and topsails and sometimes a staysail.
|
|
|
|
main lower topgallant sail
|
Square sail between the main upper topgallant sail and the main upper topsail.
|
|
|
|
Marconi cutter
|
Fishing boat with a tall mast and one gaff or Bermuda sail; it has two jibs and a small mast aft of the tiller.
|
|
|
|
main upper topgallant sail
|
Square sail under the main royal sail.
|
|
|
|
ketch
|
Two-masted pleasure sailboat; it has a mainmast and a mizzenmast fore of the tiller, which distinguishes it from the cutter.
|
|
|
|
main royal sail
|
Small square sail above the topgallant sail at the top of the mainmast.
|
|
|
|
whale boat
|
Fishing boat propelled mainly by oars but sometimes fitted with one or two lug sails and a jib.
|
|
|
|
halyard
|
Rope for hoisting a sail or a yard.
|
|
|
|
sheet
|
Rope extending from the lower corner of a sail for trimming it with respect to the wind direction.
|
|
|
|
mizzen sail
|
The lowest square sail supported by the mizzenmast.
|
|
|
|
spanker
|
Gaff sail for the mizzenmast.
|
|
|
|
gaff topsail
|
Sail above a gaff sail and between the gaff and the top of the mast.
|
|
|
|
jigger topmast staysail
|
Triangular sail below the jigger topgallant staysail.
|
|
|
|
jigger topgallant staysail
|
Highest triangular sail among the sails rigged between the mizzenmast and the jiggermast.
|
|
|
|
mizzen royal brace
|
Rope that causes the yard supporting the royal sail to pivot around the mizzenmast.
|
|
|
|
mizzen topmast staysail
|
Triangular sail on the stay supporting the aft fore-topmast.
|
|
|
|
reef point
|
One of several short ropes attached along the reef band on both sides of the sail for tying up the reefed sail.
|
|
|
|
reef band
|
Reinforced horizontal strip of canvas; a part of the sail can be gathered and tied to it to reduce the sail’s wind surface.
|
|
|
|
crew quarters
|
Compartments for housing crew members.
|
|
|
|
chart room
|
Office in which charts and other navigation documents are kept.
|
|
|
|
radio antenna
|
Metal conductor that emits and receives radio waves for communications.
|
|
|
|
lifeboat
|
Boat used for evacuating people from the ship in case of emergency.
|
|
|
|
compass bridge
|
Covered glassed-in platform from which officers and crew navigate the vessel.
|
|
|
|
radar
|
Detection device that emits radio waves and receives their echo; it is used to avoid collisions and to navigate when visibility is reduced.
|
|
|
|
stack
|
Tall pipe atop the engine that evacuates the steam and the combustion smoke.
|
|
|
|
anchor-windlass room
|
Opening made in a ship’s bulwark or deck for the anchor chains and lashings.
|
|
|
|
forecastle
|
Section of the forward deck for storing equipment such as chains and anchors.
|
|
|
|
masthead light
|
Lamp projecting a strong light several miles ahead and to the sides of the ship.
|
|
|
|
container hold
|
Large compartment under the deck where containers are stowed.
|
|
|
|
derrick
|
Metal structure erected over an oil well; tools for drilling through rock are raised and lowered through it.
|
|
|
|
dynamics propeller
|
Device that is made up of blades integrated with a shaft; it pushes air behind the hovercraft thus causing a forward movement.
|
|
|
|
navigation light
|
Lamp that is visible from afar to signal the hovercraft’s presence.
|
|
|
|
air intake
|
Intake opening for the fan.
|
|
|
|
radar
|
Detection device that emits radio waves and receives their echo; it is used to avoid collisions and to navigate when visibility is reduced.
|
|
|
|
bow door
|
Door for passengers to enter and exit the cabin.
|
|
|
|
control deck
|
Compartment from which the pilots operate the hovercraft.
|
|
|
|
skirt finger
|
Flexible and pliable extension to the skirt that adapts to the surface of the water.
|
|
|
|
flexible skirt
|
Rubber flexible side that surrounds the edge of the hull to trap the air blown down by the lift fan; this increases pressure, which in turn causes lift.
|
|
|
|
life raft
|
Inflatable boat that transports passengers and crew in case of emergency.
|
|
|
|
baggage racks
|
Compartment for storing luggage.
|
|
|
|
drive shaft
|
Part transmitting the engine’s rotational movement to the propellers.
|
|
|
|
rudder
|
Pivoting part behind the propeller blast for steering the hovercraft.
|
|
|
|
propeller duct
|
Metal part that surrounds the propeller and increases its power by concentrating its air intake.
|
|
|
|
blade lift fan
|
Device blowing air downward under the hovercraft to keep it levitated.
|
|
|
|
passenger cabin
|
Compartment where the passengers sit during the trip.
|
|
|
|
belt drive
|
Flexible link transmitting the engine’s rotational movement to the propellers.
|
|
|
|
lift-fan air inlet
|
Duct through which air enters, which is then blown downward under the hovercraft by the blade lift fan.
|
|
|
|
diesel lift engine
|
Power source using the combustion of an air/fuel mixture to drive the blade lift fan.
|
|
|
|
diesel propulsion engine
|
Power source using the combustion of an air/fuel mixture to drive the propellers.
|
|
|
|
propeller
|
Device with blades integrated onto a shaft that is driven by the engine to provide thrust and thus impel the ship.
|
|
|
|
rudder blade
|
Part of the rudder that receives the thrust from the propeller in order to steer the boat.
|
|
|
|
wheelhouse
|
Cabin that houses the pilot and the navigation instruments.
|
|
|
|
rear propeller
|
Screw driven by a powerful engine to propel the ice breaker.
|
|
|
|
stem propeller
|
Screw that pulls up water from under the ice sheet to weaken its support thus making it easier to break and move.
|
|
|
|
stem
|
Reinforced part of the boat’s prow that crushes the ice with its weight and then pushes it aside to open a channel.
|
|
|
|
trawler
|
Fishing boat that tows a large funnel-shaped net (trawl).
|
|
|
|
rear propeller
|
Screw driven by a powerful engine to propel the ice breaker.
|
|
|
|
stem propeller
|
Screw that pulls up water from under the ice sheet to weaken its support thus making it easier to break and move.
|
|
|
|
stem
|
Reinforced part of the boat’s prow that crushes the ice with its weight and then pushes it aside to open a channel.
|
|
|
|
davit
|
Winch that manipulates the anchors.
|
|
|
|
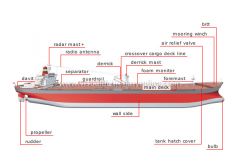
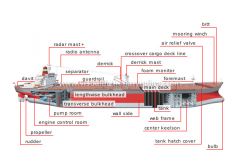
radar mast
|
Mast with a radio-wave detection device (radar set) used to prevent collisions when visibility is reduced.
|
|
|
|
guardrail
|
Railing along a ship’s deck that protects crew from falling overboard.
|
|
|
|
separator
|
Device that removes any water that might contaminate the oil tanks.
|
|
|
|
radio antenna
|
Metal conductor that emits and receives radio waves for communications.
|
|
|
|
mooring winch
|
Motorized spool around which a mooring cable is wound.
|
|
|
|
crossover cargo deck line
|
Thick pipe that runs transversally and is used to fill and empty the tanks.
|
|
|
|
bitt
|
Metal cylindrical fittings attached to the deck for fastening mooring ropes and tow lines.
|
|
|
|
air relief valve
|
Device that allows air to escape as oil fills the tanks to displace it.
|
|
|
|
tank hatch cover
|
Watertight door that provides access to a tank.
|
|
|
|
foremast
|
Mast located near the bow of the deck that supports the navigation lights.
|
|
|
|
main deck
|
Flat top that seals the hull and protects the cargo; it provides space for crew to circulate and for auxiliary equipment.
|
|
|
|
wall side
|
Vertical part of the hull below the water line.
|
|
|
|
foam monitor
|
Pressurized mechanism that produces foam for extinguishing fires.
|
|
|
|
derrick mast
|
Short thick mast that supports the derrick.
|
|
|
|
bulb
|
Bulge in the bottom part of the stem that reduces the hull’s water resistance.
|
|
|
|
transverse bulkhead
|
Wall that divides the hold across the width thus demarcating the tanks.
|
|
|
|
lengthwise bulkhead
|
Wall that divides the hold along the length to demarcate the tanks.
|
|
|
|
engine control room
|
Compartment housing the instruments that monitor the ship’s movement and control the engines and other machinery.
|
|
|
|
pump room
|
Compartment housing the machinery that pumps the oil in and out of the tanks.
|
|
|
|
center keelson
|
Metal girder that runs along the ship’s longitudinal axis to reinforce the bottom of the hull.
|
|
|
|
web frame
|
Metal reinforcement that spans the hull transversally.
|
|
|
|
tank
|
Watertight reservoir; the hold is divided into several tanks to prevent sloshing.
|
|
|
|
handrail
|
Railing serving as support for the passengers.
|
|
|
|
sundeck
|
Part of the deck for relaxation; it is surrounded by a handrail.
|
|
|
|
outboard engine
|
Detachable engine mounted on the boat’s stern.
|
|
|
|
steering whee
|
Wheel for steering the engine and hence the boat.
|
|
|
|
windshield
|
Front sheet of glass and plastic protecting the pilot from the wind and splashing.
|
|
|
|
handrail
|
Railing serving as support for the passengers.
|
|
|
|
fore and aft passage
|
Passageway on the deck that connects the bow and the stern.
|
|
|
|
pilot house
|
Compartment from which the pilot operates the boat.
|
|
|
|
compass bridge
|
Covered glassed-in platform from which officers and crew navigate the vessel.
|
|
|
|
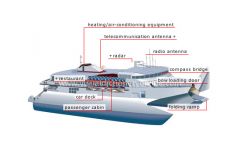
heating/air-conditioning equipment
|
Machinery that regulates the cabin’s temperature and humidity.
|
|
|
|
telecommunication antenna
|
Multipurpose antenna that receives and transmits various signals such as video, telephone and digital.
|
|
|
|
car deck
|
Compartment where the vehicles are parked in such a way as to keep the ferry balanced.
|
|
|
|
restaurant
|
Compartment where meals are prepared and eaten.
|
|
|
|
folding ramp
|
Retractable door that lowers onto the quay to load and unload vehicles.
|
|
|
|
bow loading door
|
Door for loading vehicles; another is located aft for unloading cars.
|
|
|
|
stabilizer fin
|
Small pivoting winglike flaps on each side of the hull to reduce the rolling motion.
|
|
|
|
porthole
|
Waterproof glassed-in opening in the hull that lets natural light and air into the ship.
|
|
|
|
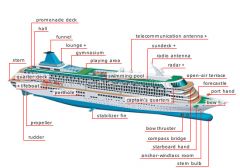
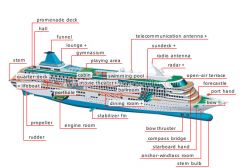
promenade deck
|
Open deck for strolling that is sometimes glassed in.
|
|
|
|
quarter-deck
|
Open part of the main deck at the aft end.
|
|
|
|
stern
|
Rear end of a ship.
|
|
|
|
lounge
|
Area with a counter and tables where alcoholic drinks are sold.
|
|
|
|
gymnasium
|
Large room for playing indoor sports.
|
|
|
|
playing area
|
Fenced-in area for playing ball sports.
|
|
|
|
swimming pool
|
Large basin designed for swimming.
|
|
|
|
hall
|
Large basin designed for swimming.
|
|
|
|
bow thruster
|
Propeller on each side of the stem bulb for maneuvering the ship to port or starboard at slow speeds.
|
|
|
|
starboard hand
|
Right side of the ship when looking forward
|
|
|
|
anchor-windlass room
|
Opening in the hull for the ship’s anchor chains and towropes.
|
|
|
|
stem bulb
|
Bulge in the bottom part of the stem that reduces the hull’s water resistance.
|
|
|
|
captain's quarters
|
Lodgings for the captain located aft of the bridge on the starboard side.
|
|
|
|
bow
|
Foremost part of the ship.
|
|
|
|
port hand
|
Left side of the ship when looking forward.
|
|
|
|
compass bridge
|
Covered glassed-in platform from which officers and crew navigate the vessel.
|
|
|
|
open-air terrace
|
Outdoor platform that is formed from the roof of the deck below and is protected by a guardrail.
|
|
|
|
sundeck
|
Usually the highest and sunniest deck with a pool and lounge chairs.
|
|
|
|
funnel
|
Long vertical pipe above the machinery evacuating exhaust gases from the engines, with filters for absorbing carbon particles.
|
|
|
|
open-air terrace
|
Outdoor platform that is formed from the roof of the deck below and is protected by a guardrail.
|
|
|
|
dining room
|
Hall for eating meals.
|
|
|
|
movie theater
|
Room for screening films.
|
|
|
|
cabin
|
Room that accommodates one or several passengers.
|
|
|
|
engine room
|
Room housing the engines, turbines and related machinery that propel the ship.
|
|
|
|
funnel
|
Long vertical pipe above the machinery evacuating exhaust gases from the engines, with filters for absorbing carbon particles.
|
|
|
|
open-air terrace
|
Outdoor platform that is formed from the roof of the deck below and is protected by a guardrail.
|
|
|
|
dining room
|
Hall for eating meals.
|
|
|
|
movie theater
|
Room for screening films.
|
|
|
|
cabin
|
Room that accommodates one or several passengers.
|
|
|
|
engine room
|
Room housing the engines, turbines and related machinery that propel the ship.
|
|
|
|
ballroom
|
Large hall with a dance floor for holding dances and balls.
|
|
|
|
front foil
|
Wing on each side of the prow.
|
|
|
|
propeller shaft
|
Long metal rod that transmits the motor’s rotational movement to the propeller.
|
|
|
|
strut
|
Vertical support that connects each foil to the boat’s hull.
|
|
|
|
surface-piercing foils
|
Parts that lift the boat when cruising speed has been reached; they also stabilize the boat.
|
|
|
|
life buoy
|
Ring made of buoyant material that is thrown to anyone who has fallen overboard to help them float.
|
|
|
|
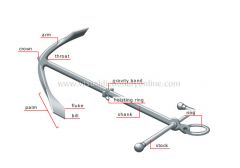
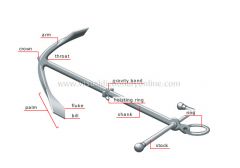
stock
|
Transverse rod perpendicular to the shank; it positions the anchor so that its two arms grip the bottom of the water.
|
|
|
|
shank
|
Long straight rod forming the body of the anchor.
|
|
|
|
bill
|
Tip of the palm.
|
|
|
|
palm
|
Flat pointed part at the end of the arm; it sinks into the bottom of the water to grip it.
|
|
|
|
fluke
|
Broad part of the palm.
|
|
|
|
ring
|
Heavy ring through the eye at the end of the shank; the anchor’s cable or rope is attached to it.
|
|
|
|
hoisting ring
|
Small ring at the anchor’s center of gravity; a rope is attached to it, which is pulled to dislodge the anchor from the bottom of the water.
|
|
|
|
gravity band
|
Anchor’s center of gravity.
|
|
|
|
throat
|
Point where the arms meet the shank.
|
|
|
|
crown
|
Point at the end of the shank.
|
|
|
|
Clopidogrel Bisulfate
|
Plavix®
|
Hematological Agent
|
|
|
mushroom anchor
|
Anchor with a large crown instead of arms.
|
|
|
|
grapnel
|
Small anchor with four, sometimes folding, cruciform arms.
|
|
|
|
plow anchor
|
Anchor with a plow-shaped arm that pivots on the shank and hooks onto most bottoms.
|
|
|
|
sea anchor
|
Solid cone-shaped canvas sack that is dragged behind a boat to counter heaving and strong winds.
|
|
|
|
stockless anchor
|
Relatively light anchor with a pair of pivoting palms that fold along the shank.
|
|
|
|
stocked anchor
|
Relatively heavy and bulky anchor with a stock and two arms ending in palms.
|
|
|
|
life raft
|
Inflatable boat where passengers can take refuge in case of emergency.
|
|
|
|
buoyancy tube
|
Inflatable tube that serves as a hull to make the raft float.
|
|
|
|
inflation system
|
Device containing pressurized air that automatically inflates the buoyancy tubes when the life raft is launched.
|
|
|
|
canopy
|
Covering that automatically deploys to protect against wind, rain and spray.
|
|
|
|
boarding ladder
|
Nylon straps that form steps for climbing into the life raft.
|
|
|
|
life buoy
|
Ring made of buoyant material that is thrown to anyone who has fallen overboard to help them float.
|
|
|
|
retro-reflective tape
|
Tape that reflects light, making it easier to find a person in the water.
|
|
|
|
rope
|
Nylon rope that can be caught with the boat hook to hoist a person out of the water.
|
|
|
|
ring
|
Rigid buoyant circle that a person in the water slips under the arms.
|
|
|
|
life jacket
|
Buoyant vest filled with air or plastic foam that is used to keep a person afloat.
|
|
|
|
leg strap
|
Adjustable nylon belt that goes between the legs to prevent the life jacket from riding up.
|
|
|
|
belt
|
Nylon strap that adjusts to the wearer’s size to keep the life jacket in place.
|
|
|
|
buckle
|
Fastener with two elements that hook together and unfasten when pressed.
|
|
|
|
boat hook
|
Usually telescopic pole with a tip and a hook; it is used to maneuver a boat alongside quays, to hook an object and to fathom the bottom.
|
|
|
|
hook
|
Curved end for hooking a rope or fishing an object out of the water.
|
|
|
|
distress beacon
|
Device that automatically transmits a radio distress signal giving its precise position.
|
|
|
|
strobe
|
Lamp that produces an intense light from a gas, which glows between two electrodes.
|
|
|
|
antenna
|
Metal rod that emits the radio signal into the atmosphere.
|
|
|
|
fog horn
|
Instrument that makes a regulation sound when visibility is reduced to indicate the presence of a boat.
|
|
|
|
trumpet
|
trumpet
Bell mouth that amplifies the sound emitted by a diaphragm when compressed air passes over it. |
|
|
|
canister
|
Small container of compressed air.
|
|
|
|
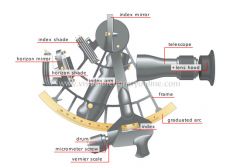
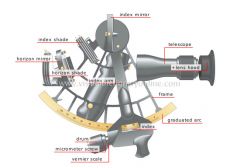
drum
|
Thumbnail for turning the micrometer screw.
|
|
|
|
horizon shade
|
Colored glass that blocks certain rays in the light spectrum to filter out ambient light.
|
|
|
|
micrometer screw
|
Screw with a head graduated in minutes that is turned to set the index arm precisely.
|
|
|
|
vernier scale
|
Small graduated rule that slides along the ruler and is used to read very precise measurements.
|
|
|
|
graduated arc
|
Arc graduated in degrees; the observed angle measurement is read from it.
|
|
|
|
frame
|
Support for the various components of the sextant.
|
|
|
|
horizon mirror
|
Fixed mirror in front of the telescope; it is aimed at the horizon and the image of the Sun is projected on it.
|
|
|
|
index shade
|
Colored glass that blocks certain rays in the light spectrum to filter out ambient light.
|
|
|
|
telescope
|
Optical instrument that magnifies an observed object.
|
|
|
|
lens hood
|
Device attached to the telescope’s eyepiece that shields the eye from light coming from the source and from strong ambient light.
|
|
|
|
index arm
|
Moving arm on the sextant that measures the displacement angle on the graduated arc to determine the height of the observed heavenly body.
|
|
|
|
index mirror
|
Mirror integrated with the index arm that is positioned so that the Sun reflects on the horizon mirror.
|
|
|
|
index
|
Guide mark that helps to read the graduation marks on the arc.
|
|
|
|
pivot
|
Axle around which the compass card rotates.
|
|
|
|
sliding cover
|
Retractable cover that protects the glass dome from scratches when not in use.
|
|
|
|
bowl
|
Watertight case containing the magnetic elements, which float in a liquid (oil or alcohol) to reduce oscillations.
|
|
|
|
compass card
|
Rotating disk graduated from 0° to 360° and integrated with two magnets; it shows the cardinal points and the points in between.
|
|
|
|
glass dome
|
Transparent nondistorting hemispherical cover for the bowl containing the liquid.
|
|
|
|
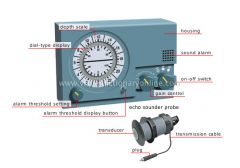
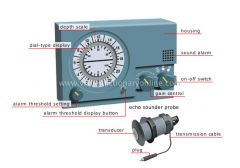
alarm threshold setting
|
Knob for setting the maximum depth considered to be dangerous.
|
|
|
|
alarm threshold display button
|
Button that is pushed to display the alarm threshold value.
|
|
|
|
gain control
|
Knob for adjusting the amplification of the signal.
|
|
|
|
on-off switch
|
Button for activating the sounder and for selecting the scale.
|
|
|
|
sound alarm
|
Audible signal activated when the alarm threshold is reached.
|
|
|
|
dial-type display
|
Display surface where an illuminated dot appears at the point on the scale that corresponds to the depth.
|
|
|
|
depth scale
|
Line graduated in feet or meters for reading the distance to the bottom.
|
|
|
|
echo sounder probe
|
Part of the sounder that is submerged to send the ultrasound to the bottom; it receives the echo and converts it into sound.
|
|
|
|
transmission cable
|
Electric wire that relays the electric signals between the housing and the echo sounder probe.
|
|
|
|
plug
|
Metal prong that plugs into the housing.
|
|
|
|
transducer
|
Part of the echo sounder probe that emits the ultrasound and receives its ech
|
|
|
|
bracket
|
Support fixed onto a surface that holds the display.
|
|
|
|
display
|
Liquid crystal display screen on which graphics or text data are displayed.
|
|
|
|
GPS receiver-antenna
|
External antenna and GPS receiver that receive radio waves from satellites to calculate the boat’s position.
|
|
|
|
tower
|
Concrete structure that forms the lighthouse’s body; it is resistant to waves and very strong winds.
|
|
|
|
gallery
|
Narrow platform with a guardrail that provides a panoramic view from the lighthouse.
|
|
|
|
lantern pane
|
Framed panes of glass that protect the lantern and support the cupola.
|
|
|
|
lantern
|
Powerful lamp that projects an encoded beam.
|
|
|
|
cupola
|
Roof protecting the lantern; it is equipped with a lightning rod.
|
|
|
|
housing
|
Case enclosing and protecting the device’s mechanism.
|
|
|
|
lamp base
|
Metal end of a lightbulb inserted into a socket to connect it to the electric circuit.
|
|
|
|
dioptric ring
|
Concentric glass rings surrounding the lantern that refract its rays to intensify them.
|
|
|
|
incandescent lamp
|
Lamp in which a filament heated by an electric current produces light rays.
|
|
|
|
ventilation hood
|
Part that allows excess heat to escape from the lantern.
|
|
|
|
conical buoy
|
Floating beacon with a cone-shaped superstructure.
|
|
|
|
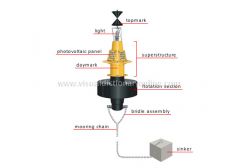
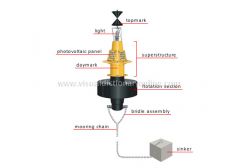
light
|
Encoded light beam that serves as a navigation aid at night.
|
|
|
|
photovoltaic panel
|
Device that converts solar energy into electricity to power the light.
|
|
|
|
daymark
|
Navigation aid that is visible by day only; it displays various colors and signage.
|
|
|
|
mooring chain
|
Long, very sturdy chain that links the buoy to the sinker.
|
|
|
|
sinker
|
Heavy object often made of concrete; it rests on the bottom of the waterway to keep the buoy in place.
|
|
|
|
bridle assembly
|
Two chains that link the flotation section to the mooring chain.
|
|
|
|
flotation section
|
Lightweight base that keeps the buoy afloat and upright.
|
|
|
|
superstructure
|
Metal frame that forms the buoy’s body and contains all its elements.
|
|
|
|
topmark
|
Metal cone-shaped part atop a buoy that serves as a navigation aid during the day; its position signifies various meanings.
|
|
|
|
ladder
|
For accessing the components at the top of the tubular structure.
|
|
|
|
tubular structure
|
Columnar part of the superstructure that supports the day- and nightmarks and keeps them above the water.
|
|
|
|
daymark
|
Navigation aid that is visible by day only; it displays various colors and signage.
|
|
|
|
ladder
|
For accessing the components at the top of the tubular structure.
|
|
|
|
tubular structure
|
Columnar part of the superstructure that supports the day- and nightmarks and keeps them above the water.
|
|
|
|
daymark
|
Navigation aid that is visible by day only; it displays various colors and signage.
|
|
|
|
radar reflector
|
Metal part that reflects ships’ radar signals so they can locate the buoy.
|
|
|
|
starboard hand
|
Right side of the ship when looking forward.
|
|
|
|
port hands
|
Left side of the ship when looking forward.
|
|
|
|
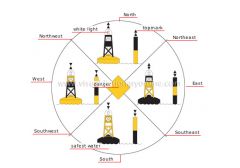
North
|
The north cardinal mark is composed of two topmarks with both tips pointing upward.
|
|
|
|
white light
|
White flashing light whose flash pattern serves as a cardinal mark at night.
|
|
|
|
West
|
The west cardinal mark is composed of two topmarks placed tip to tip.
|
|
|
|
safest water
|
Navigable water is deep enough that it is safe to proceed.
|
|
|
|
South
|
The south cardinal mark is composed of two topmarks with both tips pointing downward.
|
|
|
|
danger
|
Buoys signal shallow waters, a submerged object or an object posing a hazard to a boat or a ship.
|
|
|
|
East
|
The east cardinal mark is composed of two topmarks placed base to base.
|
|
|
|
topmark
|
Metal cone-shaped part atop a buoy that serves as a navigation aid during the day; its position signifies various meanings.
|
|
|
|
lateral mark
|
Red or green buoy that indicates the port or starboard limits of the channel.
|
|
|
|
safe water mark
|
Buoy signaling that the water is navigable.
|
|
|
|
secondary channel
|
Navigation lane with beacons that is longer or more difficult than the preferred channel.
|
|
|
|
preferred channel
|
Navigation lane with beacons; it is the shortest and safest way to a harbor or for navigating near a coast or through a waterway.
|
|
|
|
isolated danger mark
|
Buoy marking an isolated danger zone beyond which the waters are navigable.
|
|
|
|
East cardinal mark
|
Buoy with two base-to-base topmarks that is placed to the east of a danger zone.
|
|
|
|
South cardinal mark
|
Buoy with two topmarks pointing downward that is placed to the south of a danger zone.
|
|
|
|
pillar buoy
|
Floating beacon with a pylon-shaped superstructure.
|
|
|
|
conical buoy
|
Floating beacon with a cone-shaped superstructure.
|
|
|
|
spar buoy
|
Long tubular buoy used in harbors and in waters that have no tides.
|
|
|
|
part hand
|
Mark the ship must keep on the left side of its prow as it navigates a channel.
|
|
|
|
West cardinal mark
|
Buoy with two point-to-point topmarks that is placed to the west of a danger zone.
|
|
|
|
special mark
|
Buoy marking an area that is regulated for a specific use (such as military exercises or fishing) or contains submerged obstacles (such as cables or pipelines).
|
|
|
|
starboard hand
|
Mark the ship must keep on the right side of its prow as it navigates a channel.
|
|
|
|
interval
|
Duration between two periods at which time the light remains dark.
|
|
|
|
period
|
Duration between two intervals at which time the light signals.
|
|
|
|
light
|
The light’s color and brightness vary during the period as a function of the type of light.
|
|
|
|
darkness
|
No light.
|
|
|
|
lock filling and emptying opening
|
Holes through which the water flows in to fill the lock-chamber or out to empty it.
|
|
|
|
upper gate
|
Watertight door or pair of doors made of wood or metal that open when the water levels between the lock-chamber and the upper level are the same.
|
|
|
|
lock filling intake
|
Holes through which the water flows to fill the lock-chamber.
|
|
|
|
ladder
|
Ladder fixed to the side wall for climbing up out of and down into the lock-chamber.
|
|
|
|
miter gate recess
|
Indentation in the side wall into which a gate fits when open.
|
|
|
|
lock filling and emptying system
|
System consisting of a conduit with sluices alongside the side wall and perpendicular conduits on the canal bed that together raise and lower the water level in the lock.
|
|
|
|
canal bed
|
Thick concrete base that makes up the lock’s foundation.
|
|
|
|
lock emptying system
|
Conduit that evacuates the water from the downstream side causing the water level in the lock-chamber to go down.
|
|
|
|
approach wall
|
Wall along the side wall that guides ships into the lock.
|
|
|
|
lower gate
|
Watertight door or pair of doors made of wood or metal that open when the water levels between the lock-chamber and the lower level are the same.
|
|
|
|
line hook
|
Piece of wood or metal attached to the side wall for securing the rope that holds a ship in place while it is in the lock-chamber.
|
|
|
|
side wall
|
Wall forming one side of the lock-chamber and supporting its doors.
|
|
|
|
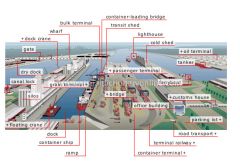
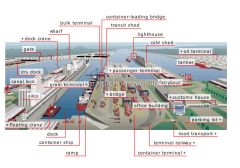
bulk terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment to store, sort and handle bulk items, such as ore and coal.
|
|
|
|
customs house
|
Structure where inspection and legal operations related to imported and exported cargo are carried out.
|
|
|
|
parking lot
|
Area for parking vehicles.
|
|
|
|
office building
|
Structure where personnel who administer the port work.
|
|
|
|
road transport
|
Transportation of cargo by truck on public roads.
|
|
|
|
cold shed
|
Insulated refrigerated structure for storing perishable foodstuffs.
|
|
|
|
bridge
|
Structure consisting of a girder and posts that rolls along tracks moving containers.
|
|
|
|
terminal railway
|
Railroad tracks leading onto a wharf for transshipping containers from a ship to a car or vice versa.
|
|
|
|
ramp
|
Slope leading from the wharf to the level of the water.
|
|
|
|
dock
|
Enclosed basin where ships take on and unload cargo.
|
|
|
|
floating crane
|
Dock crane that is mounted on a floating movable platform and often used for carrying heavy cargo.
|
|
|
|
grain terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment for storing, sorting and handling grain.
|
|
|
|
dry dock
|
Dock where water is pumped out so that a ship’s hull can be repaired, cleaned or painted.
|
|
|
|
dock crane
|
Crane that rolls along rails the length of the wharf and uses a moving arm to load and unload cargo in forms such as container, bulk and break bulk.
|
|
|
|
wharf
|
Structure for docking ships so that passengers can embark and disembark and cargo can be loaded and unloaded.
|
|
|
|
transit shed
|
Warehouse located near the wharf for temporarily storing cargo.
|
|
|
|
gate
|
Waterproof device that closes a dock.
|
|
|
|
silos
|
Very large, usually cylindrical, reservoirs for storing products in bulk, especially grain.
|
|
|
|
canal lock
|
Structure with a lock-chamber that can be filled with water or emptied to raise or lower a ship from one water level to another.
|
|
|
|
container-loading bridge
|
Cantilevered gantry crane along the quay for loading and unloading containers.
|
|
|
|
container ship
|
Ship that is designed for transporting cargo in containers in its hold and on its deck.
|
|
|
|
lighthouse
|
Tower with a powerful lamp at the top for guiding ships.
|
|
|
|
passenger terminal
|
Structures and facilities where passengers embark and disembark ships.
|
|
|
|
tanker
|
Ship with large reservoirs for transporting liquid petroleum products.
|
|
|
|
oil terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment to store petroleum products and load them into tankers.
|
|
|
|
container terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment to store, sort and handle containers.
|
|
|
|
ferryboat
|
Shuttle boat for carrying vehicles with their cargo and passengers.
|
|
|
|
tanker
|
Ship with large reservoirs for transporting liquid petroleum products.
|
|
|
|
oil terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment to store petroleum products and load them into tankers.
|
|
|
|
container terminal
|
Area with installations and equipment to store, sort and handle containers.
|
|
|
|
ferryboat
|
Shuttle boat for carrying vehicles with their cargo and passengers.
|
|

