![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
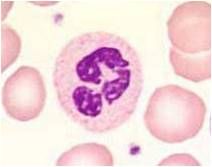
Describe this cell. what is it called?
|
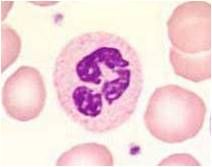
Pale pink granular cytoplasm with condensed, segmented nucleus
PMN |
|
Decribe this cell. What is it?
|
Granulocytes with large, refractile, orange-pink granules.
Nucleus is typically bilobed. Eosinophil |
|
|
What do we call a cell with a curved nucleus that has not yet segmented?
|
Stab / Band form... immature PMN.
|
|
|
What is the most uncommon of all granulocytes?
|
Basophil.
|
|
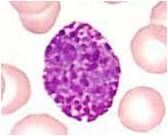
Describe this cell. what is it?
|
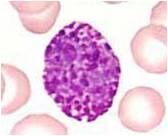
Large, dark blue granules which overlie the nucleus.
Basophil. |
|
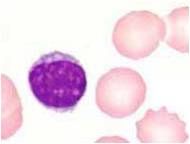
What is this cell?
|
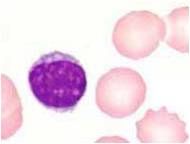
Lymphocyte
|
|
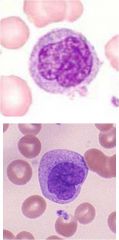
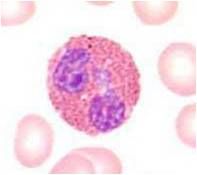
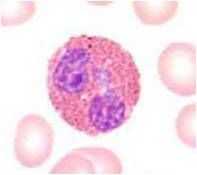
Describe these cells.
What is the top cell? the bottom one? |
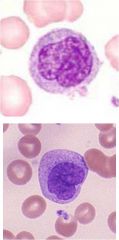
Has a folded nucleus with uneven countour
Slate grey cytoplasm--there may be vacuoles Both are monocytes. |
|
|
What cell's function include chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and killing of phagocytosed bacteria?
|
Neutrophil's functions
|
|
|
What do Eosinophils do?
|
everything PMN does (chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and killing of phagocytosed bacteria)
serve as effector cells for antibody-dependent damage to parasites regulation of immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions: inactv. histamine and leukotrienes released by basophils and mast cells. |
|
|
What cell's functions include mediation of immediate-type hypersensitivity and modulation of inflammatory responses by releasing heparin and proteases?
|
Basophil
|
|
|
what do lymphocytes do?
|
Function in immune regulation and production of hematopoietic growth factors.
|
|
|
What cell's functions include chemotaxis, phagocytosis, killing of some microbes, antigen presentation, release of cytokines which stimulate bone marrow stromal cells to produce growth factors?
|
Monocyte
|
|
|
Which cells are precursors of tissue macrophages?
|
Monocytes
|
|
|
In what physiological situations do we see an elevated neutrophil count?
|
exercise, preg., lactation, neonates
|
|
|
What Pathological situations do we see an elevated PMN count?
Which drugs types (3 main ones) can elevate PMN #? Can splenectomy incite an elevated PMN count? |
acute infections, actue inflammation, Myeloproliferative disorders (CML)
corticosteroids Growth Factors Lithium Yes. |
|
|
What are the genetics of Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency? Pathogenesis?
Lab/Clinical findings? |
autosomal recessive.
g. Neutrophils lack 2 integrins or other molecules necessary for surface adhesion and are thus unable to leave the circulation to gather at sites of infection - Peripheral WBC is markedly elevated. - severe recurrent infections w/o pus formation |
|
|
What can lead to demargination?
|
Epinephrine and corticosteroids
|
|
|
What are the largest of the white cells?
|
Monocytes
|
|
|
Do all of the peripheral neutrophils circulate?
|
No. Half of them adhere to the vessel wall, where they are 'marginated'.
|
|
|
What is the term for an absolute lack of neutrophils?
What can induce it? What are some Sx? |
agraunulocytosis
Almost always drug induced. severe necrotizing ulcers in the mouth and the throat |
|
|
Name some drugs that can induce agranulocytosis.
|
Clozapine (Clozaril, an antipsychotic)
Propythiouracil (an antithyroid) Anti-convulsants sulfa and chloramphenicol (antibiotics) gold salts (given to treat RA) |
|
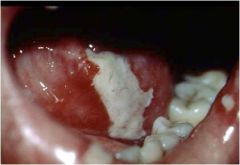
What is this? What can cause this?
|
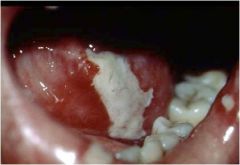
Necrotizing ulcer from a bacterial infection.
Agranulocytosis opens the door. |
|
|
What is the DiffDx for Eosinophilia?
|
NAACP:
Neoplasm, Allergy/asthma, addison's disease, collagen vascular disease parasites (wormz!! omg!) |
|
|
What is addison's disease?
|
(chronic adrenal insufficiency, hypocortisolism or hypocorticism) is a rare endocrine disorder in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough steroid hormones (glucocorticoids and often mineralocorticoids)
|
|
|
What if the chief important cause of Basophilia?
|
Myeloproliferative disorder
|
|
|
What are the big causes of Lymphocytosis?
|
Viral infections
Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) also bacterial infections: whooping cough, TB, syphilis, brucellosis |
|
|
What are 5 causes of Lymphocytopenia?
|
Immunodeficiencies
immunosup. drugs lymphomas granulomatous diseases (sarcoid, TB) Alcoholism/malnutrition/zinc def. |
|
|
What is the most notable cause of monocytosis?
|
Myelodysplastic syndromes
|
|
|
How can you get an acquired defect in neutrophil function?
|
corticosteroid use, alcoholism, leukemias, myelodysplasia, and myeloproliferative disorders
|
|
|
Transplant patient presents with neutropenia. What virus might have caused it?
|
CMV.
|
|
|
Which lineage of cells is sytemic lupus erythematosus associated with?
|
can be assoc. with cytopenias of all lineages.
|
|
|
What is felty's syndrome?
|
Splenomegaly + RA + Neutropenia
|
|
|
What do all myeloproliferative disorders tend to have as a feature?
|
basophilia
|
|
|
What let neutrophils roll along the surface of the endothelium?
How about adhere more tightly? |
selectins
B2 integrins. |
|
|
GCD is...
|
...an inherited defect in the NADPH oxidase complex.
|
|
|
Myeloperoxidase def is...
makes it hard to do what? Why are many cases asymtomatic? |
... problems making hypercholorous acid.
kill bacteria and fungi. b/c there are other ways to kill bacteria, and fungi are rare. Thus, presenting finding can often be a fungal infection. |
|
|
What is Chediak-Higashi Syndrome?
Results? Outcome? |
Autosomal recessive defect in granule fusion with the plasma membrane.
defects in leukocyte function and platelet function, as well as oculocutaneous albinism Death in early childhood. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is concerning white cells is false?
a. Eosinophil levels can be elevated in myeloproliferative diseases b. Felty’s syndrome is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus c. Neutropenia can be caused by antithyroid medications d. Neutrophil dysfunction can result from myelodysplastic syndromes e. Basophils play a role in hypersensitivity reactions |
B.
|
|
|
Which of the following statements concerning neutrophil function is true?
a. Superoxde dismutase converts oxygen into superoxide. b. B2 integrins interact with carbohydrate moieties on Pns to mediate rolling c. Chemotaxis is the process by which neutrophils adhere to the endothelial cell layer d. Myeloperoxidase deficiency may be asymptomatic. |
D.
|

