![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A CBC gives us which pieces of information: (7)
|
Hb, Hct, RBC count, MCV, MCH, MCHC, RDW
|
|
|
What is Hematocrit?
Hct = (mathematically) |
volume of red cells, expressed as a % of the whole blood volume
Hct = RBC x MCV |
|
|
MCV is....
|
...direct measurement of red cell volume in femtoliters.
|
|
|
Anemia is defined as...
Is anemia a final diagnosis or a manifestation of disease? How common is it? |
.... a decreased hemoglobin/hematocrit below the normal range for gender and age.
manifestation. 1/3 of pop worldwide is anemia |
|
|
Clinical manifestations of anemia depend on factors such as...
|
...
Reduction of O2-carrying capacity Change of the whole blood volume Rate of change Ability of the cardiopulmonary system to compensate Manifestations of underlying illness that caused the anemia |
|
|
Most symptoms of acute hemorrhage are related to...
What are some of these symptoms? |
...hypobolemia.
Hypotension, orthostatis, syncope, shock |
|
|
What are symptoms of tissue hypoxia?
|
Fatigue, SOB, cog. difficulties, ischemic pain (angina, claudication)
|
|
|
In response to anemia, cardiac output does what? How, usually?
|
Increase, thru increased HR
|
|
|
How to we get anemia?
|
Bleeding (hemorrhage)
Destroying the red cells too soon (hemolysis) Not producing blood |
|
|
How do we classify anemias? (2)
|
1. by the erythoropoietic response (i.e., the reticulocyte count)
2. By the red cell size (ie, the MCV) and hemoglobin concentration. |
|
|
Define reticulocytes:
On Wright-Giemsa staining they are.... |
Young red cells immediately released by the bone marrow as the end result of erythropoeisis.
...polychromatophilic (gray-ish blue) |
|
|
If retic index < 2% or absolute retic count < 75,000, then this suggests a problem with ....
|
... red cell production (hypoproliferative abnormality)
|
|
|
If retic index > 2% or absolute retic count > 100,000, then this tells us that there is a good ______ reponse, suggesting that the cause of anemia is either ______ _____ or ____ ______.
|
marrow.
hemorrhage, hemolysis |
|
|
What are the two approaches to treating anemia? Which is ideal? When do we do the other?
|
1. Treat the underlying cause
2. Transfusion 1 is ideal. When we don't have time, or something is pushing us. |
|
|
When deciding whether or not to transfuse, we must consider: (3)
|
1. how symtomatic is the patient?
2. can we reverse the underlying cause? 3. Do we have enough time to treat the underlying cause? |
|
|
Is there a Hb value that should be a 'trigger' in every patient --> transfusion?
|
No! No absolute Hb value.
|
|
|
What are some general indications for giving a transfusion?
|
CV compromise
Hypoproliferative anemia w/ no or prolonged recovery Surgery |
|
|
Acute blood loss and hypovolemia trigger vaso...
|
vasoconstriction.
|
|
|
What could transfusion of a patient with chronic anemai lead to? Why is this?
|
Volume overload!
The kidneys respond to anemai by retaining salt and water to expand intravascular volume. |
|
|
What does the body to with RBC 2.3 DPG in response to anemia? What does this accomplish?
|
increases it. It right shifts the O2 dissociation curve, which favors increased Oxygen delivery to tissues
|
|
|
What do renal mesangial cells do when they sense hypoxia?
|
increase erythoropoietin synthesis.
|
|
|
When dealing with anemia, which part of the body increases erythoropoietin synthesis?
|
renal mesangial cells.
|
|
|
On supravital staining, what is characteristic of Reticulocytes?
|
RNA remnants... they are 'reticulated'
|
|
|
Retic index = ?
|
retic. count x Hct/ideal Hct x 0.5
|
|
|
Absolute retic count =
|
absolute retic count = retic (%) x RBC
|
|
|
What does increased erythropoietin synthesis cause an increase in?
|
Reticulocyte production
|
|
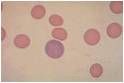
What cells are seen here on Wright-Giemsa staining?
|
polychromatiophilic cells --> Reticulocytes!
|
|
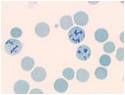
On this supravital stain, what do we see?
|
RNA remnants in the reticulocytes! Woo!
|
|
|
What are the 3 classifications of anemia by RBC size?
|
Microcytic anemia, macrocytic anemia, normocytic anemia
|
|
|
Define Megaloblastic anemia:
What are the most common causes? |
group of disorders characterized by a defect in DNA synthesis leading to a characteristic morphology of bone marrow cells
B12 and folate deficienty |
|
|
What do parietal cells do re: B12 absorption?
|
secrete IF (intrinsic factor)
|
|
|
What does IF do?
|
binds free b12
|
|
|
Can TRUE vegans get b12 in their diet?
|
no! only in animal stuff.
|
|
|
How can B12 absorption be messed up?
|
Inadequate dietary intake
- Vegan diet Inadequate absorption - Lack of gastric acid - Destruction/removal of parietal cells (pernicious anemia) Reduced B12 absorption in the ileum - Crohn’s disease - Sprue (celiac or tropical) Pancreatic insufficiency Competition for B12 - fish tapeworm, bacterial overgrowth Non-functional TCII Inactivation of cobalamine (via nitrous oxide) |
|
|
"I can't feel my feet in space."
"I fall in the dark." Suggests what type of deficiency? |
B12
|
|
|
Can Neruopsych manifestations of b12 deficiency reverse?
|
yes, if it is caught early.
|
|
|
Does b12 deficiency develop quickly?
|
no, it takes years to develop.
|
|
|
If you treat a b12 deficient person w/ folate alone, what happens?
|
precipitates the neuropsychiatric manifestations.
|
|
|
What should we do, treat the cause or supplement w/ b12?
|
cause if we can, supplements (intramuscular shots) if not.
|
|
|
Iron uptake is influenced primarily by...
Direct or Inverse relationship? What is the most efficient way to absorb iron? Are the other ways even close to as good? |
...iron stores. Inverse: decreased stores will increase absorption.
As heme - absorbed intact from meat. No, vegetable like beets, etc. suck. |
|
|
Does Hb fall early or later on in iron deficiency?
Why? |
Later.
The body in early iron deficiency will use iron stores before dropping the hemoglobin. |
|
|
What are 4 hematologic features of the clinical presentation of megaloblastic anemia caused by both folate and b12 deficiency?
2 non-hematologic deficiencies? Are both seen with all etiologies? |
Most important:
Elevated MCV, Hypersegmented PMNs Less important: Anemia, elevated RDW Beefy, red smooth tongue Neuro/psychaiatric features (ONLY w/ B12 deficiency) |
|
|
Symptomatically speaking, how can we differentiate b/t megaloblastic anemia caused by B12 deficiency vs. Folate deficiency?
|
B12 def. has neuro/psychiatric features.
|
|
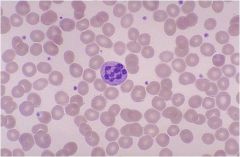
What is seen in this picture? In which type of anemia is it seen?
|
Hypersegmented PMN
Megaloblastic anemia |
|
|
Answer the following with (a) folate, (b) B12, or (c) both:
1. DNA synthesis requires.... 2. Myelin synthesis requires... |
1. (c) both
2. (b) only B12 |
|
|
Which cells secrete intrinsic factor (IF)?
|
parietal cells
|
|
|
Where in the GI tract is the B12-IF complex taken up?
|
distal ileum
|
|
|
Are pancreatic enzymes necessary for B12 absorption? Why or why not?
|
Yes. B12 in diet binds to salivary R protein in acid environment; pancreatic enzymes degrade R protein --> free B12.
IF *only* binds free B12 |
|
|
Vegan diet, destruction/removal of parietal cells, Crohn's disease, fish tapeworm, and/or bacterial overgrowth can all cause a deficiency in what?
|
B12
|
|
|
What is pernicious anemia?
|
destruction/removal of parietal cells
|
|
|
Whippits can inactivate cobalamine, causing what?
|
B12 deficiency
|
|
|
Can neuropsychological manifestations of B12 deficiency be present in the absence of anemia?
|
Yes.
|
|
|
What are some of the neuropsych symptoms of B12 deficiency?
|
Loss of position/vibration sense (especially in feet)
Dementia, personality change, psychosis less important: optic nerve atrophy |
|
|
How quickly do we see reversal of the following Sx of B12 deficiency following Rx initiation?
Megaloblastic changes in BM Lowered retic count Anemia Hypersegmented PMNs Neuro manifestations |
12-48hrs
2-8 days 2 months 10-14 days 6 months if ever |
|
|
When should you get more folate than normal?
|
pregnant/lactating, if you have a lot of active cell turnover
|
|
|
Where in the GI tract is folic acid absorbed?
Is the liver important? |
small intestine
yes, enterohepatic circulation is important for folate absorption. |
|
|
What is the major source of folate?
What is the major cause of deficiency? How quickly can you become folate deficient? Why? |
Raw, green, leafy vegetables
Malnutrition as little as a month; stores in liver are only adequate for 2-4 months. |
|
|
What is the only way we can get iron?
|
Intestinal absorption.
|
|
|
What b/ iron in the bloodstream and transports it to cells?
|
Transferrin (Tf)
|
|
|
What happens to the TIBC (total iron b/ capacity) of Tf when the body is iron deficient?
|
it goes up.
|
|
|
What is Tf saturation? Does this increase or decrease with iron deficiency?
|
fraction of available Fe-binding sites which have iron bound to them.
decrease. |
|
|
When does iron leave the body?
|
ONLY when cells are lost. No regulated excretion.
|
|
|
How much iron does one entire pregnancy cause a woman to lose?
What is the normal daily loss in adults? |
500-750mg
1mg/day. |
|
|
Iron deficiency in adults is almost always due to primarily _______ , though there may be a component of malabsorption or dietary insufficiency.
|
blood loss.
|
|
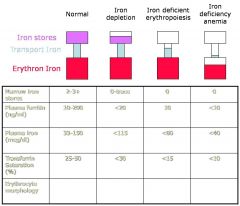
Fill in Normal, microcytic, and/or hyprochromic in each of the blank spaces.
|
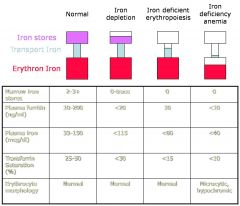
fo' realz.
|
|
|
Describe the Sx of the clinical presentation of iron deficiency.
|
Possible anemia.
Sx of the source of the blood loss. * Koilonychia (nail-spooning) * Pica (eating weird shit w/ no nut. value) * Thrombocytosis: elevated platelet count Glossitis (smooth, shiny tender tongue) Angular cheilitis (sores at the corners of the mouth) |
|
|
Track the changes in CBC lvls seen in progression of iron deficiency:
First sign is ____ of RDW Next is _____ of MCV. ____ (2) fall last. |
First sign is elevation of RDW, followed by falling MCV.
Hemoglobin and Hct fall last |
|
|
In an outpatient, what is the single best test for iron deficiency? What is the cutoff?
Why isn't it as reliable in inpatients? How do iron studies track w/ the development of iron deficiency? (Serium iron, TIBC, Transferrin) What is the gold standard diag. test? |
Ferritin < 15 = iron deficiency
Drugs and other fun stuff might mess with the ferritin lvls. Serum iron falls, TIBC increases, Tf saturation also falls. BM evaluation |
|
|
Describe the pathogenesis of the anemia of chronic disease.
What does hepcidin do? |
cytokines act to sequester iron away from the bloodstream by increasing levels of Hepcidin.
decreases iron abs from gut, decreases iron export out of hepatocytes, decreases Tf and TIBC --> serum lvls fall |
|
|
Patient comes in w/ low serum iron levels and TIBC. Their ferritin is normal to slightly elevated. What might they have?
|
Anemia of Chronic Disease
|
|
|
Patient comes in with elevated TIBC, low serum iron, and low ferritin. What might they have?
|
Iron deficiency anemia.
|
|
|
What are the differences in lab values between someone with Fe-def anemia and someone with AOCD?
|
Fe-def:
v. high TIBC, v. low ferritin AOCD: low TIBC, norm/high ferritin |
|
|
What is the Rx for Fe-def anemia?
Why isn't IV iron considered more strongly? |
Try to treat underlying cause. If not possible/feasible, oral iron is the therapy of choice.
IV iron is not any faster than oral, and it risks anaphylaxis. |
|
|
What is the most accurate and reproducible way (lab value) to describe and monitor anemia?
Why is it more accurate than Hct? |
Hb.
It is a measured, not a derived value. |
|
|
What are the two types of Macrocytic anemias and their respective common causes?
|
Megaloblastic and Non-megaloblastic
B12 and/or folate deficiency anything that elevates reticulocyte counts liver disease, alcohol, hypothyroidism, myelodysplasia. |
|
|
What are some real ABSOLUTE indications for emergent transfusion?
|
CHF, Shock, Angina
|
|
|
What is a a microcytic anemia, characterized by abundant free iron, but the patient is unable to incorporate it into Hb?
What are signs of this disorder? |
Sideroblastic anemia
Sideroblasts are seen in aspirates of bone marrow; these are atypical nucleated erythrocytes with granules of iron accumulated in perinuclear mitochondria |
|
|
What are sideroblasts?
|
atypical nucleated erythrocytes with granules of iron accumulated in perinuclear mitochondria
|

