![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
153 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 2 things pass through Anterior Ethmoidal Foramen? |
1. anterior ethmoidal nerves 2. vessels
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Carotid Canal?
|
1. internal carotid artery 2. deep petrosal nerve
|
|
|
What passes through Cribiform plate?
|
olfactory nerves
|
|
|
What passes through Facial Canal?
|
facial nerve proper
|
|
|
What passes through Foramen Cecum and where does it come from and go to?
|
emissary vein from nasal cavity to superior sagittal sinus
|
|
|
What 4 things pass through Foramen Lacerum? (artery, vein, 2 nerves)
|
1. meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery2. emissary vein from pterygoid venous plexus 3. greater superficial petrosal nerve4. deep petrosal nerve from carotid plexus
|
|
|
What 5 things pass through Foramen Magnum?
|
1. anterior and posterior spinal arteries and veins 2. alar ligaments, 3. tectorial membrane, 4. apical ligament 5. spinal accessory nerve.
|
|
|
What 3 things pass through Foramen Ovale?
|
1. mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (V3) 2. accessory meningeal artery 3. lesser petrosal nerve
|
|
|
What passes through Foramen Rotundum?
|
maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve (V2)
|
|
|
What pass through Foramen Spinosum?
|
1. middle meningeal artery 2. recurrent branch of mandibular nerve
|
|
|
What passes through Foramen Vesalii?
|
emissary vein from pterygoid venous plexus
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Greater Palatine Foramen?
|
1. anterior (greater) palatine nerves and vessels, 2. posterior (lesser) palatine nerves and vessels. These are branches of pterygopalatine or descending palatine nerves and vessels.
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Hiatus of the Facial (greater superficial petrosal) canal?
|
1. greater superficial petrosal nerve 2. petrosal branches of middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Hypoglossal Canal?
|
1. hypoglossal nerve 2. meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Incisive (Nasopalatine) Canal?
|
1. nasopalatine branches of descending palatine nerves 2. nasopalatine branches of descending palatine vessels
|
|
|
What 3 things pass through Inferior Orbital (Sphenomaxillary) Fissure?
|
1. maxillary nerve branches 2. zygomatic infraorbital,lacrimal branch of greater petrosal nerve 3. Infraorbital vessels.
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through (Inferior) Tympanic Canaliculus?
|
1. tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve (will become lesser petrosal) , 2. tympanic branch of ascending pharyngeal artery
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Infraorbital foramen?
|
1. infraorbital branch of maxillary nerve 2. infraorbital vessels.
|
|
|
What 3 things pass through Internal Acoustic Meatus?
|
1. vestibulocochlear nerve2. facial nerve3. internal auditory branch of basilar artery
|
|
|
What 4 things pass through Jugular Foramen?
|
1. internal jugular vein2. glossopharyngeal nerve 3. vagus nerve4. spinal accessory nerve
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Lesser Palatine Foramen?
|
1. posterior (lesser) palatine nerves 2. posterior (lesser palatine vessels These are branches of pterygopalatine or descending palatine nerves and vessels.
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Mandibular (Inferior Alveolar) Foramen?
|
1. inferior alveolar nerve 2. vessels.
|
|
|
What passes through Mastoid Canaliculus (Tympanomastoid Fissure)?
|
1. auricular branch of vagus nerve
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Mastoid Foramen?
|
1. mastoid branch of occipital artery 2. emissary vein
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Mental Foramen?
|
1. mental nerve 2. vessels
|
|
|
What is another name for Nasolacrimal Canal?
|
tear duct
|
|
|
What 3 things pass through Optic Foramen?
|
1. optic nerve2. ophthalmic artery3. central retinal artery
|
|
|
What passes through Parietal Foramen?
|
emissary vein
|
|
|
What passes through Petrotympanic (Squamotympanic) Fissure?
|
chorda tympanic branch of the facial nerve
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Pharyngeal Canals (along with vomerovaginal canals)?
|
1. pharyngeal branch of maxillary artery2. pharyngeal branchess of greater petrosal nerve
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Posterior Condylar Canal?
|
1. emissary vein2. meningeal branches of occipital artery
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Posterior Ethmoidal Foramen?
|
1. posterior ethmoidal nerve2. vessels
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Posterior Superior Alveolar (Maxillary) Foramen?
|
1. posterior superior alveolar nerve2. vessels
|
|
|
What passes through Pterygoid (Vidian) Canal?
|
nerve of pterygoid canal (combined sympathetic postganglionics of deep petrosal nerve and parasympathetic preganglionics from greater petrosal nerve.)
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Pterygomaxillary Fissure?
|
1. maxillary artery 2. posterior superior alveolar nerve
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Pterygopalatine (Descending Palatine) Canal?
|
1. descending palatine nerves 2. vessels.
|
|
|
What 5 things pass through Pterygopalatine (Sphenopalatine) Foramen?
|
1. pterygopalatine vessels 2. nasopalatine nerve3. posterior nasal nerves4. pharyngeal nerves 5. vessels.
|
|
|
What passes through Stylomastoid Foramen?
|
facial nerve proper
|
|
|
What is the Sulcus Tubae Auditivae?
|
groove for cartilaginous portion of auditory tube
|
|
|
What 5 things pass through Superior Orbital Fissure?
|
1. occulomotor nerve2. ophthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve (V1)3. trochlear nerve4. abducens nerve 5. ophthalamic vein
|
|
|
What 2 things pass through Supraorbital Fissure?
|
1. supraorbital nerve 2. vessels
|
|
|
What passes through Zygomaticofacial Foramen?
|
1. zygomaticofacial branch of zygomatic nerve of zygomatic branch of maxillary
|
|
|
What passes through Zygomatico-orbital Foramen?
|
zygomatic nerve of V2
|
|
|
What passes through Zygomaticotemporal Foramen?
|
zygomaticotemporal branch of zygomatic branch of maxillary
|
|
|
Name CNI
|
Olfactory
|
|
|
Name CNII
|
Optic
|
|
|
Name CNIII
|
Occulomotor
|
|
|
Name CNIV
|
Trochlear
|
|
|
Name CNV
|
Trigeminal
|
|
|
Name CNVI
|
Abducens
|
|
|
Name CNVII
|
Facial
|
|
|
Name CNVIII
|
Vestibulococchlear (auditory)
|
|
|
Name CNIX
|
Glossopharyngeal
|
|
|
Name CNX
|
Vagus
|
|
|
Name CNXI
|
Spinal Accessory
|
|
|
Name CNXII
|
Hypoglossal
|
|
|
Pneumonic for relating CNs to their names
|
On old Olympus' towering top, a frenchman and german viewed and hopped.
|
|
|
What CN provides special sense of smell?
|
CNI (olfactory)
|
|
|
What CN provides special sense of vision?
|
CNII (optic)
|
|
|
Which CN provides motor function to superior, inferior and medal rectus, inferior oblique and levator palpebrae muscles and muscles of the iris and ciliary body?
|
CNIII (occulomotor)
|
|
|
What CN provides motor function of superior oblique muscle, the only muscle innervated by this CN?
|
CNIV (trochlear)
|
|
|
What CN provides sensory function to head, face (except ear and angle of mandible), teeth, mucous membranes (except post oral cavity and pharynx)?
|
CNV (trigeminal)
|
|
|
What CN provides motor function to muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, digastric (anterior belly), tensor veli palatini and tensor tympani muscles?
|
CNV (trigeminal)
|
|
|
What CN provides motor function to lateral rectus muscle?
|
CNVI (abducens)
|
|
|
What CN provides mostly motor function to the face (muscles of facial expression), digastric(posterior belly), stylohyoid and stapedius muscles?
|
CNVII (facial)
|
|
|
What CN provides secretory motor function to lacrimal, palatal, submandibular & sublingualglands?
|
CNVII (facial)
|
|
|
What CN provides special sense of taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue)?
|
CNVII (facial)
|
|
|
What CN provides special sense of hearing and special sense of balance?
|
CNVIII (auditory, vestibulocochlear)
|
|
|
What CN is the sensory nerve to the posterior tongue, palate, & pharynx and has motor function to palatal muscles, parotid gland (secretion) &gag reflex?
|
CNIX (glossopharyngeal)
|
|
|
What CN provides special sense of taste (posterior 1/3 tongue, soft palate)?
|
CNIX (glossopharyngeal)
|
|
|
What CN has overlapping motor function with IX, gag reflex and is the only motor innervation to laryngeal muscles (voice); it also has sensory innervation of ear (pinna) and parasympathetic to heart and other viscera?
|
CNX (vagus)
|
|
|
What CN provides motor function to trapezius & sternocleidomastoid muscles?
|
CNXI (spinal accessory)
|
|
|
What 2 muscles are innervated by motor CNXI?
|
trapezius, sternocleidomastoid
|
|
|
What CN provides motor function to tongue?
|
CNXII (hypoglossal)
|
|
|
What CN is the only motor innervation to laryngeal muscles (voice)?
|
CNX (vagus)
|
|
|
What CN has motor function to palatal muscles, parotid gland (secretion) &gag reflex?
|
CNIX (glossopharyngeal)
|
|
|
What does the olfactory nerve attach to, which attaches to what CN?
|
olfactory nerve attaches to olfactory bulb, which attaches to CNI (olfactory)
|
|
|
What CN has the most anatomically distinct chiasm (crossover)?
|
CNII (optic)
|
|
|
What does olfactory nerve go through?
|
cribiform plate
|
|
|
What is the only CN to enter through one foramen and leave through another?What foramen?
|
CNXI (spinal accessory) enters through foramen magnum and leaves through ?
|
|
|
What is a nerve nucleus?
|
when cell bodies are in CNS and aggregated
|
|
|
What is a nerve ganglion?
|
when cell bodies are in PNS and aggregated
|
|
|
What 3 things comprise the CNS?
|
1. brain2. brainstem3. gray matter of spinal cord
|
|
|
The posterior alar plate cells of the brainstem are what?
|
sensory cells (afferent)
|
|
|
The anterior basal plate cells of the brainstem are what?
|
motor cells (efferent)
|
|
|
What fold in the spinal cord separates alar from basal plates? (afferent from efferent)
|
sulcus limitans
|
|
|
What is the difference between "special" and "general"?
|
Special - only associated with CNsGeneral - found in CNs AND/OR spinal nerves
|
|
|
What is the difference between "somatic" and visceral"?
|
Somatic - body as a wholeVisceral - linked to a tubular organ
|
|
|
What 3 CNs are SSA (special somatic afferent)?
|
olfactory, optic, vestibulococchlear
|
|
|
Are most CNs GSA (9 of them)? (general somatic afferent) Which is the most important one?
|
Yes. CNV is most important general somatic sensory.
|
|
|
What 4 CNs are SVA (special visceral afferent)? What are they related to?
|
related to smell or tastesmell: olfactorytaste: facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
|
|
|
What 2 CNs are GVA? (general visceral afferent)
|
glossopharyngeal, vagus
|
|
|
What are the 2 visceral organs in the head?
|
nasal cavityoral cavity
|
|
|
What 4 CNs are GVE? (general visceral efferent)
|
occulomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus
|
|
|
What 5 CNs are SVE and associated with muscles that developed from branchial arches? (special visceral efferent)
|
trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, spinal accessory
|
|
|
What 4 CNs are GSE (general somatic efferent)?
|
occulomotor, trochlear, abducens, hypoglossal
|
|
|
What is the largest ganglion in the body and is ONLY GSA?
|
CNV ganglion
|
|
|
The only motor ganglia in the body are what?
|
autonomic
|
|
|
What is the pneumonic for sensory, motor, or both of CNs?
|
Some say marry money but my brother says big boobs marry money.S- sensoryM- motorB- both
|
|
|
What is the component of CN I?`
|
SVA
|
|
|
What is the component of CN II?
|
SSA
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of CN III?
|
GSE, GVE, GSA
|
|
|
What are the 2 components of CN IV?
|
GSE, GSA
|
|
|
What are the 2 components of CN V?
|
GSA, SVE
|
|
|
What are the 2 components of CN VI?
|
GSE, GSA
|
|
|
What are the 5 components of CN VII?
|
SVE, GVE, SVA, GSA, GSA
|
|
|
What are the only 2 components not represented by CN VII?
|
SSA, GVA
|
|
|
What is the component of CN VIII?
|
SSA
|
|
|
What are the 5 components of CN IX?
|
SVE, GVE, SVA, GSA, GVA
|
|
|
What are the 5 components of CN X?
|
SVE, GVE, SVA, GSA, GVA
|
|
|
What are the 3 components of CN XI?
|
SVE (?), GSE (?), GSA
|
|
|
What are the 2 components of CN XII?
|
GSE, GSA
|
|
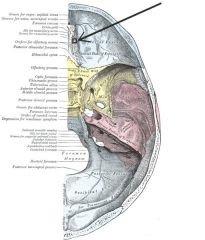
What is it and what does it transmit?
|
Anterior Ethmoidal Foramen - anterior ethmoidal nerves
|
|
10What is it and what does it transmit? (3)
|
Carotid Canal - internal carotid artery, deep petrosal nerve and other Postganglionic sympathetics (carotid plexus).
|
|
6What is it and what does it transmit? (6) What CN?
|
Foramen Magnum - spinal accessory nerve.junction of spinal cord and brainstem, anterior and posterior spinal and veins, alar ligaments, tectorial membrane, apical ligament,
|
|
9 What is it and what does it transmit? (one vein and 3 CNs)
|
Jugular Foramen - internal jugular v., glossopharyngeal n., vagus n., spinal accessory n.
|
|
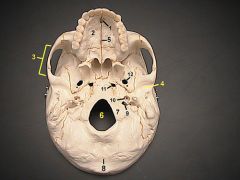
11What is it and what does it transmit? (1 artery, 1 vein, and 2 nerves)
|
Foramen Lacerum - meningeal br. of ascending pharyngeal a., emissary v. from pterygoid venous plexus, greater superficial petrosal n.,deep petrosal n. from carotid plexus.
|
|
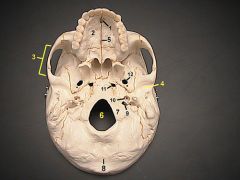
12What is it and what does it transmit? (2 nerves, 1 artery)
|
Foramen Ovale - mandibular br. of trigeminal nerve, accessory meningeal a.,lesser petrosal n.
|
|
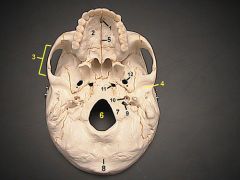
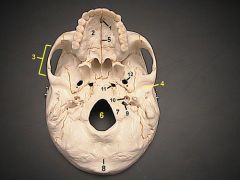
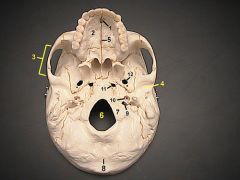
1What is it?What does it transmit?What 2 foramen form the ends that border it?
|
Facial canaltransmits facial nerve properstarts at internal acoustic meatus and ends at stylomastoid foramen
|
|
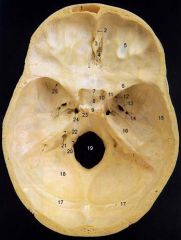
2What is it and what does it transmit? (1 vein)
|
Foramen Cecum - emissary vein from nasal cavity to superior sagital sinus.
|
|
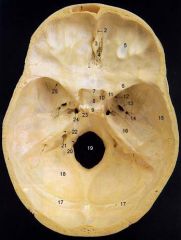
4What is it and what does it transmit?
|
Cribriform Plate - olfactory nerves
|
|
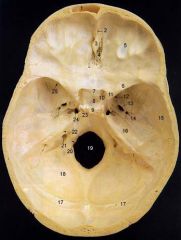
6
|
lesser wing of sphenoid
|
|
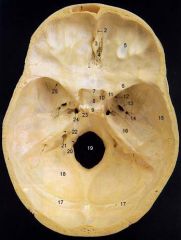
12What is it and what does it transmit?
|
Foramen Rotundum - maxillary br. of trigeminal nerve
|
|
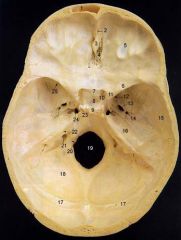
13What is it and what does it transmit? (2 nerves, 1 artery)
|
Foramen Ovale - mandibular br. of trigeminal nerve, accessory meningeal a., lesser petrosal n.
|
|
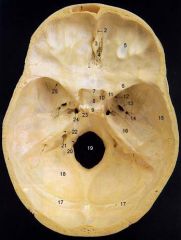
14What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve, 1 artery)
|
Foramen Spinosum - middle meningeal a., recurrent br. of mandibular n.
|
|
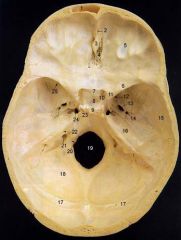
16
|
Petrous Part of Temporal bone
|
|
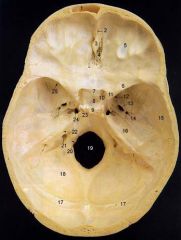
20What is it and what does it transmit?
|
Hypoglossal Canal - hypoglossal nerve meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal a.
|
|
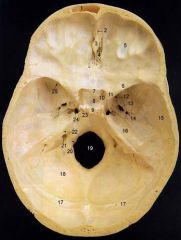
21What is it and what does it transmit? (1 vein, 3 CNs)
|
Jugular Foramen - internal jugular v., glossopharyngeal n., vagus n., spinal accessory n.
|
|
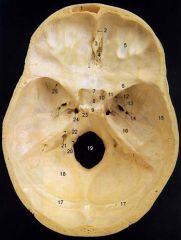
22What is it and what does it transmit? (2 CNs and 1 artery)
|
Internal Acoustic Meatus - vestibulocochlear n., facial n., internal auditory br. of basilar a.
|
|
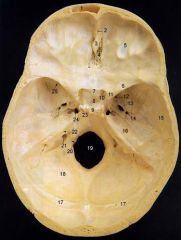
24What is it?
|
Foramen Lacerum
|
|
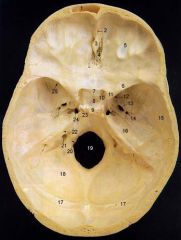
25What is it and what does it transmit? (4 CNs and 1 vein)
|
Superior Orbital Fissure - occulomotor (III)trochlear n. (IV)ophthalmic br. of trigeminal n. (V1)abducent n. (VI)ophthalamic v.
|
|
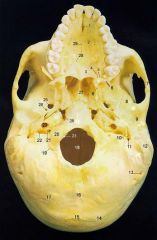
1What is it and what does it transmit? (nerves and vessels)
|
Incisive (Nasopalatine) foramen - nasopalatine branches of descending palatine nerves vessels to the palate
|
|
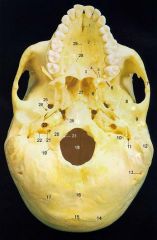
4What is it and what does it transmit? (2 nerves and vessels along with those nerves)
|
Greater Palatine Foramen - anterior (greater) palatine nerves and vessels, posterior (lesser) palatine nerves and vessels.
|
|
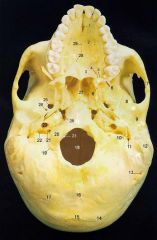
5What is it and what does it transmit? (nerves and vessels along with it)
|
Lesser Palatine Foramen - posterior (lesser) palatine nerves and vessels.
|
|
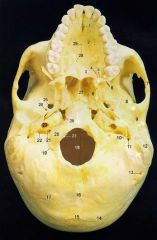
6
|
Pterygoid Processes of Sphenoid
|
|
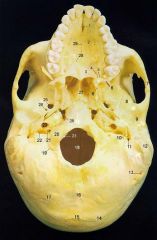
8
|
Squamous Part of Temporal Bone
|
|
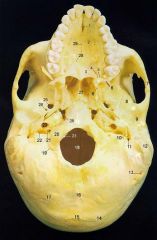
9
|
Mandibular Fossa (glenoid)
|
|
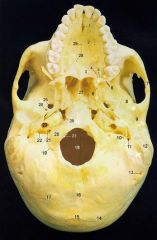
11What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve)
|
Stylomastoid Foramen -facial nerve proper
|
|
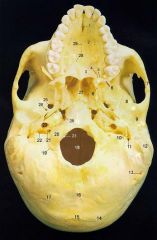
12
|
Mastoid Process
|
|
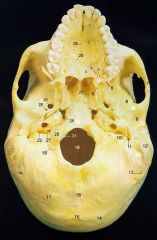
13What is it and what does it transmit? (1 artery, 1 vein)
|
Mastoid Foramen - mastoid branch of occipital a. emissary v.
|
|
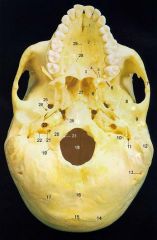
14
|
Superior Nuchal Line
|
|
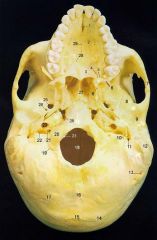
16
|
Median Nuchal Line
|
|
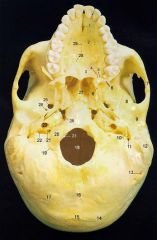
17
|
Inferior Nuchal Line
|
|
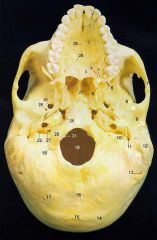
21What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve and 1 artery)
|
Hypoglossal Canal -hypoglossal nervemeningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal a.
|
|
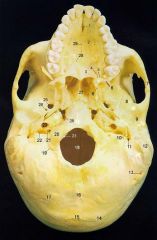
24What is it and what does it transmit? (1 artery and 1 nerve)
|
Foramen Spinosum - middle meningeal a., recurrent br. of mandibular n.
|
|
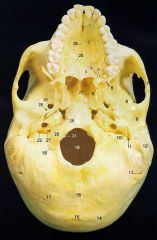
27
|
Vomer
|
|

Circled orifice and what it transmits? (2 nerves, set of vessels)
|
Inferior Orbital (Sphenomaxillary) Fissure 1. maxillary nerve branches 2. zygomatic infraorbital,lacrimal br. of greater petrosal n., 3. Infraorbital vessels.
|
|
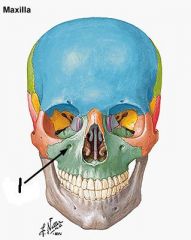
1What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve, 1 set of vessels)
|
infraorbital foramen infraorbital br. of maxillary n., infraorbital vessels.
|
|
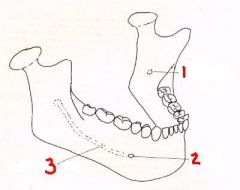
1What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve)
|
Mandibular (Inferior Alveolar) Foramen inferior alveolar n. and vessels.
|
|
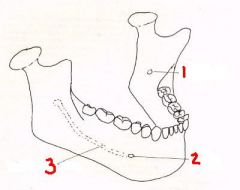
2 What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve)
|
Mental Foramen - mental n. and vessels.
|
|
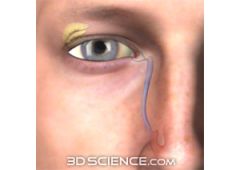
What is it and what does it transmit?
|
nasolacrimal canaltears
|
|
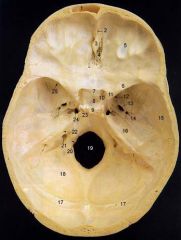
10What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve, 2 arteries)
|
Optic Foramen - optic n., ophthalmic a., central retinal a.
|
|
What is it and what does it transmit? (1 nerve and vessels)
|
Supraorbital Fissure - supraorbital n. and vessels
|

