![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
302 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When did the early renaissance take place? |
1350-1494, with the end of the Medici Rule in Florence |
|
|
What is Classical Humanism? |
Reinvigoration of classical learning based on literary/philosophical works of Greeks and Romans |
|
|
List 3 reasons why the Renaissance began in Florence |
1. Independent states in Italy gave political stability 2. Rome's close ties (due to debt) to the Medici
3. Economic expansion encouraged urbanization
|
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of humanism |
1. Interest in antiquity 2. Interest in life on earth, rather than after death 3. Belief in the worth of humans 4. Importance of the individual 5. Interest in nature and the physical world |
|
|
Who is Petrarch? |
called "Father of Humanism", believed life's quest should be for eternal truth |
|
|
What is a Sonnet and who invented it? |
Invented by Petrarch, consists of 14 lines of iambic pentameter |
|
|
Who invented the Printing Press and when? |
Invented in 1455 by Johannes Gutenberg |
|
|
What is Neoplatonism? |
“New Platonism” which sought to revive Platonic ideals in contemporary culture |
|
|
Name 3 things guilds did/affected |
1. Controlled competition and prices 2. Provided Education to artists 3. Affected innovation
|
|
|
What is a court artist? |
Artists that painted exclusively for the royal family |
|
|
Who created the Dome of the Florence Cathedral and when? |
Filippo Brunelleschi in 1436 |
|
|
What is Linear Perspective? |
A technique used by artists, in which the relative size, shape, and position of objects is determined by drawn or imagined lines converging at a point on the horizon. |
|
|
Who was Michelozzo di Bartolommeo? |
Architect who designed the Palazzo de Medici |
|
|
What is Continuous Narration? |
the simultaneous presentation of events that took place sequentially |
|
|
What is Contrapposto? |
Posture in which the weight of the body rests on one leg, elevating the hip and the opposite shoulder, putting the spine into an S curve |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
David, 1430, Donatello
First large nude since antiquity, uses continuative narration, uses contrapposto |
|

Title, Date, Artist, relevance |
The Trinity with the Virgin, St. John the evangelist and Donors, 1428, Massaccio
Uses, linear perspective, references antiquity with roman arches and columns, gives donors equal importance in painting
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, relevance |
Frederico da Montefeltro, 1473, Francesca
Uses naturalism: depicts Montefeltro with imperfections, shows rising interest in portraiture |
|

Title, Date, Artist, relevance |
Annunciation, 1445, Fra Angelico
shows symbolic perspective |
|

Title, Date, Artist, relevance |
Birth of Venus, 1486, Boticelli
shows interest in mythology of antiquity, Accepted by the church by equating Venus to Mary on the grounds that both were sources of love |
|
|
When did the High Renaissance take place? |
1494 with the end of the Medici Rule until 1527 with the sack of Rome |
|
|
What is Chiaroscuro? |
technique for modelling forms by contrasting light and dark |
|
|
What is Sfumato? |
technique in which outlines are made hazy, as if in a smoky atmosphere |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
Mona Lisa, 1503, Da Vinci
Lisa di Antonio Maria Gherardini, wife of Florentine official Francesco del Gioconda
Shaved/plucked forehead shows fashion of the time |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
School of Athens, 1505, Raphael
shows humanist’s interest in classical learning and truth
Portrays Plato and Aristotle, and greek gods
Includes himself in the image, demonstrates growing self-confidence of artists |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
David, 1504, Michelangelo
Shows naturalism, contrapposto, Symbolizes freedom of Florence Symbolizes battle between good and evil |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
Sistine Chapel: Creation of Adam, 1512, Michelangelo Commissioned by Pope Sixtus IV Portrays god and man almost as equals, representing humanist ideals of man |
|

Title, Date, Author, Define: peristyle and drum |
Tempietto, 1511, Bramante
Peristyle: a continuous row of columns Drum: circular wall, on which Bramante set a hemispheric dome
|
|
|
What is oil paint? |
Painting material created by mixing pigment with linseed oil |
|
|
What is impasto? |
* thick paint made by mixing the pigment with beeswax |
|
|
When did Mannerism take place? |
Begins in 1520 with death of Raphael/1527 with sack of Rome
Ends in 1600 |
|
|
Name 4 characteristics of mannerism |
* obscure subject matter
* unbalanced compositions * distorted proportions in bodies and spacial constructions * preference for secondary and acidic colours |
|

Title, Date, Author |
Last Supper, 1594, Tintoretto
|
|

Title, Date, Author, |
Burial of Count Orgaz, 1586, El Greco |
|

Why is this Mannerist? |
Use of classical design elements (such as columns, scroll brackets) in such a way that they are not functional and impractical |
|
|
Name 4 similarities between the Northern Renaissance and the Italian Renaissance |
* study/influence of antiquity (more prevalent in literature than art)
* Humanism and critical thinking * Publications in local languages (vernaculars) * Naturalism |
|
|
Name Name 4 differences between the Northern Renaissance and the Italian Renaissance |
* Naturalism: Northern Europe focused on detail, Italian Renaissance focused on balance, proportions |
|
|
What is Egg tempera? |
Painting material made by mixing pigment with egg yolk |
|
|
What is Atmospheric Perspective? |
the blurring of objects and colours in the background to create an appearance of perspective |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
Ghent Altarpiece, 1432, Jan van Eyck * Use of intense symbolism * Use of atmospheric perspective * Adam and Eve in painting are earliest large scale nudes in European Renaissance painting * Focus on naturalism |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
Arnolfini wedding, 1434, Jan van Eyck
* Idea that god’s presence on earth could be found in everyday objects |
|

Title, Date, Author, Relevance |
Hay Wain, 1500, Hieronymus Bosch * uses alla prima * commentary on good and evil |
|
|
What is Alla Prima? |
To paint without preliminary drawing |
|
|
What is Iconoclasm? |
* the systematic destruction of religious icons because of their religious connotations
|
|
|
Who was Erasmus? |
* Known for synthesizing the study of classical civilization and Christian faith
* Critical of the abuses of the Catholic Church |
|
|
Name 3 reasons for the protestant reformation |
* Dissatisfaction with the wealth and opulence of the Papacy
* Disagreed with the idea of Sale of Indulgences * Disagreed that the Papacy held supreme authority on faith and morals |
|
|
What are Indulgences? |
Clergy’s acceptance of payment from people for remittance of punishment for sins in the afterlife and to help souls reach heaven |
|
|
Name 3 characteristics of the Protestant reformation |
* Idea that faith, rather than achievement, led to a person’s salvation
* Stripping of nonessential religious practice * Idea that each person should interpret the bible themselves |
|
|
What is the 95 theses, when were they created, and who created them? |
* outline of the issues of the Catholic Church and the Ideals for Reformation
* Created in 1517 * Created by Martin Luther |
|
|
Name 3 reasons for the success of the Protestant Reformation |
Invention of the printing press made bible/propaganda accessible
Prior dissatisfaction with the Catholic church
Rulers used reformation for political means |
|
|
Name 2 effects the protestant reformation had on the arts |
Move from religious to secular painting
Due to Iconoclasm, many works were destroyed
|
|
|
Describe the differences and similarities between Calvin and Luther |
Both believed in the idea of faith, rather than good works, led to salvation
Both believed the bible was the supreme source of knowledge
Calvin was much more radical; condemned the images of saints, condemned feasting and dancing, jewelry, lace, dressing immodestly
Calvin believed in the idea of the elect and the damned |
|
|
Who was Albrecht Durer? |
Artist, most famous for woodcuts and engravings |
|
|
Who was Hans Holbein? |
Court artist to Henry VIII, responsible for painting portraits of Henry's wives |
|
|
What is Genre painting? |
Portrayal of daily life |
|
|
Name 2 of Pieter Bruegel's paintings and explain their importance? |
Harvesters (1565), One of the first paintings to give the landscape prominence rather than use it as a background
Peasant Wedding (1567), depicts genre painting |
|
|
Name 2 famous literary authors of the High Renaissance |
Shakespeare, Michel de Montaigne, Machiavelli |
|
|
When was the Baroque period? |
From 1600 until 1750 |
|
|
Name 3 differences between Mannerism and Baroque |
Baroque artworks contain clear subject matter while Mannerist art is often complex and obscure
Baroque art focused on modern life of everyday citizens while Mannerist art focused on antiquity and royalty
Baroque art focused more on emotion and drama |
|
|
What was the counter-reformation? |
* In response to Luther’s 95 theses, the catholic Church created the counter-reformation to attempt to make Rome the cultural centre of the world |
|
|
What was the purpose of the council of trent? |
To promote Rome and the catholic church to its former power and to theologically justify patronage of the arts |
|
|
Thirty Years War: when did it take place, who did it involve? |
1618-1648, fought between the Hapsburg Holy Roman Empire (Italy, Spain, most of Germany) on one side and France, Denmark, Holland, and Sweden on the other side |
|
|
Name 5 outcomes of the Thirty Years' War |
Decline of Spain, politically
Independence of Holland
Independence of Portugal
Rise of France as political power
Decline in power of the Catholic Church |
|
|
What is Absolutism? |
* monarchical form of government in which the monarch has absolute power
|
|
|
What is a Crescendo of Columns? |
a building increase of columns in architecture |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
David, 1623, Bernini
Shows use of movement, drama, and emotion characteristic of Baroque |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Ecstasy of St. Teresa, 1652, Bernini
Shows use of emotion and drama characteristic of Baroque |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Calling of St. Matthew, 1610, Caravaggio
Shows the portrayal of common people/everyday life Portrays the "moment of action" Use of Tenebrism |
|
|
What is Tenebrism? |
* a dramatic contrast of light with dark
|
|
|
What is the main difference between italian Baroque and Northern European Baroque art? |
Secular painting used in Northern Europe while religious painting used in Italy
|
|
|
Name 3 characteristics of Dutch art during the Baroque period |
Genre painting
Portrait painting
Still lives
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
The night watch, 1642, Rembrandt
Use of Tenebrism, created a "dynamic" group portrait |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
Jolly Topper, 1630, Frans hals
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Woman with Water Pitcher, 1665, Jan Vermeer
Scientific portrayal of light |
|
|
What was Rachel Ruysch most famous for? |
Still life paintings, especially of flowers |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Marie de Medici landing in Marseilles, 1625, Reubens
Glorification of Marie de’ Medici Dramatic composition, and constant movement |
|
|
What is Vanitas? |
* symbolic artwork, often still life, that contains hidden symbols representing mortality. Symbols include skulls, snuffed out candles, hour glasses, dying flowers, decaying/peeled fruits
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Las Meninas, 1656, Diego Valesquez
Both formal and Genre portrait Includes himself painting Reflections in the back wall of the king and queen |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
Rape of the sabine women, 1637, Nicolas Poussin |
|
|
Describe the Poussiniste/Rubeniste debate |
* Poussinistes: Favoured line, felt it appealed to the mind, believed art was for the educated Rubenistes: Favoured colour, believed it was truer to nature, appealed to emotions, believed art should appeal to all
|
|
|
What is the French Academy, when was it established and by whom? |
Established in 1648 by Louis XIV * Purpose was to define standards by which to judge the art of the period |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of the Enlightenment |
Shift to rational, empirical thought
Age of scientific invention and discovery
Re-emergence of antiquity
Emphasis on Liberty and democracy
Emergence of Capitalism |
|
|
Who were the Philosophes? |
* group of intellectuals that believed that humanity could achieve a utopian society through reason |
|
|
What is Rational Humanism? |
* belief that through rational thought, progress (which was considered to everyone’s benefit) is inevitable |
|
|
Who were the founding fathers of the United States? |
Thomas Jefferson, Thomas Paine, George Washington, and Benjamin Franklin |
|
|
Name 4 factors behind the American Revolution |
Increasing importance of liberty
Increasing importance of Democracy
Heavy taxation by Britain
Poor representation in British Parliament
|
|
|
Name 4 things that prompted the French Revolution |
The American Revolution
Enlightenment Ideals
Growing middle-class
Poverty and starvation |
|
|
What was the Estates-General and what was the issue with it? |
An assembly of the three classes, the aristocracy, the clergy, and the bourgeoisie
Although the population of the bourgeoisie vastly outnumbered the other two, they received only one vote at the estates-general |
|
|
What year was the French revolution? |
1789 |
|
|
What was the Reign of Terror? |
A period following the French Revolution in which, headed by Robespierre, the committee of public safety was in charge of winning the war with Austria and executed over 20,000 aristocrats and sympathizers |
|
|
How did Napoleon Bonaparte come to power? |
Bonaparte staged a coup d'etat and installed himself as leader
|
|
|
Name 5 consequences of the French revolution |
Overthrow of the aristocracy
Increase in democracy, liberty
Royal collections turned into public museums
Increase in capitalism
Rise of Nationalism |
|
|
Name 6 characteristics of the industrial revolution |
Invention of the factory & mass manufacturing
Urbanization
Invention of the steam engine
Emergence of the working class
Rise in poverty
Increased power of capitalists
|
|
|
Name 3 inventions/discoveries that occurred during the scientific revolution |
Isaac Newton's laws of movement & gravity
Francis Bacon's empirical mode of thought
Leuwenhoek's invention of the microscope
Coepernicus' heliocentric model
Galileo's experimentation with telescopes
|
|
|
When did the Rococo art movement take place? |
Between 1700 and 1789 |
|
|
Explain the similarities and differences between Rococo and Baroque |
Both focused on drama, theatre, emotion
Rococo art is considered more intimate
|
|
|
What is a Fête Galante? |
Depiction of an elegant, fantasy, out-door, party |
|
|
With whom is Rococo most closely associated? |
Louis XV |
|
|
What are the New Hotels and why did they become popular? |
After the death of Louis XIV, aristocrats moved from Versailles back into paris into lavish, town houses called New Hotels |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Pilgrimage to Cythera, 1717, Watteau
Depicts a fête galante |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
The Meeting, 1773, Fragonard,
Shows interest in romance/fantasy |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of Rococo art |
Interest in fantasy
Fete Galante
Depiction of the aristocracy
Depiction of Romance
Light, cheerful themes
|
|
|
What was the difference between French Rococo and English Rococo? |
English rococo art was used to satire the aristocracy while French rococo art was made for the aristocracy |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
The Marriage Contract, 1744, Hogarth
Shows English satire of the aristocracy |
|
|
What is a mock epic? |
* A style of writing in which an ordinary event is written as an epic
|
|
|
What does the term Deist mean? |
The belief in a non-intervening god |
|
|
What is a misanthrope? |
Someone who dislikes humanity |
|
|
Name 3 characteristics of Neoclassicism |
Interest in antiquity
Poussiniste
Humanist
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Oath of the Horatii, 1785, David
Represents democratic ideals, reference to antiquity, poussiniste style of painting |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
George Washington, 1792, Houdon
Reference to antiquity, posed contrapposto |
|
|
When and why did the novel become popular? |
The novel was popularized in the 18th century due to rise in literacy and its ability to portray social classes |
|
|
When did Romanticism take place? |
1789-1850 |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of Romanticism |
Interest in the orient & the medieval
Fatalistic view
Interest in Fantasy
Interest in a return to nature |
|
|
What was the shared goal of Romanticism and the Enlightenment? |
* To liberate humanity from strict conventions and to give people more understanding of themselves and the world surrounding them
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
3rd of May 1808, 1814, Goya
Depicts Napoleon forces, portrays good and evil in secular context |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Raft of the Medusa, 1819, Gericault
Shows sympathy with the downtrodden, emphasis on emotion |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Liberty leading the People, 1830, Delacroix
Portrays the middle/working class, emphasis of liberty/democracy |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
La Grande Odalisque, 1814, Ingres
Shows interest in the orient |
|
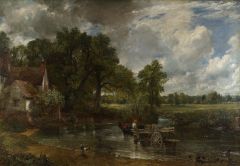
Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Hay wain, 1821, Constable
Shows interest in return to nature, the sublime |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
The Slave Ship, 1840, Turner
Shows portrayal of the sublime |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
The Abbey in the Oakwood, 1810, Friedrich |
|
|
Why was sculpture considered boring during the Romantic era and who proposed this? |
Baudelaire wrote that sculpture was boring because it was too concrete a material to express emotion and allow the viewer to believe the scene |
|
|
What is Neogothic? |
The new gothic style of architecture popular during the romantic era |
|
|
What did Jean-Jacques Rousseau believe? |
Believed that humans possessed an innate sense of morality and compassion |
|
|
Who were the Transcendentalists? |
A group of people who believed in the importance of returning to nature |
|
|
Name 3 characteristics of the civl war |
Abolitionist movement
Emancipation proclamation
Divide between the Industrious North and Agrarian South
|
|
|
What was Emily Bronte's most famous novel and what was its relation to romanticism? |
Wuthering Heights. It portrayed passionate, emotional characters, and a wild and untameable nature at odds with the rational world of the Enlightenment |
|
|
What was the Sturm und Drang movement? |
A german, literary movement focusing on the importance of subjectivity |
|
|
Who wrote Faust, what was it about, and what was it's relation to the enlightenment? |
Written by von Goethe, it tells the story of a man named Faust who sold his soul to the devil for knowledge. Faust represents the rational enlightenment while the devil represents the passionate sensations of Romanticism. |
|
|
When was Realism most prevalent? |
From 1848 until the late 19th century |
|
|
Name 3 characteristics of Realism |
Interest in everyday life
Interest in portraying things realistically
Interest in portraying the brutalities of life |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
Plowing the Nivernais, 1849, Bonheur
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Burial at Ornan, 1849, Courbet
Shows de-romanticized depiction of life |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Dejenur Sur L'herbe, 1863, Manet
|
|
|
What was the Salon de Refuses? |
An alternative salon set up to exhibit the rejected works of the Paris Salon |
|
|
Who was Honore de Balzac and what was the goal in his works? |
A french writer, who attempted to depict the modern world in an encyclopedic manner |
|
|
Who wrote Madame Bovary and what story does it tell? |
Gustave Flaubert. Tells the story of a woman who seeks to reinvent her life in the style of the romantic novel she reads but fails and commits suicide |
|
|
Name 2 of Dostoyevsky's books and describe his goal as a writer |
Brothers Karamazov & Crime and Punishment. His goal was to portray the psychological intentions and inner workings of his characters |
|
|
What is Charles Darwin famous for? |
Theory of evolution |
|
|
When did the impressionist movement take place? |
1850-1900 |
|
|
What is the term Impressionist originally from? |
Named after Monet's painting Impression, Sunrise |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of impressionism |
Importance in the method of painting as well as content
Idea of art for art
Painted from light to dark
Rapid brushstrokes
Interest in portraying the everyday life of the Nouveau Riche, the Belle Epoque
|
|
|
Name 3 inventions that influenced Impressionism |
Premixed paint tubes
Photography
Portable easels
|
|
|
Name 3 ways that photography influenced art |
Artists no longer needed to portray the world realistically
Decrease in employment of artists
Prompted artists to experiment and search for other uses of art |
|
|
What characteristics of Japanese art influenced Impressionism? |
Flat planes
Compressed perspective
Sharp contours
Non-western style of looking at the world |
|
|
What is Avant-Garde? |
A favouring of new and experimental ideas and methods in art |
|

Title, Date, Artist, |
Impression, Sunrise, 1872, Monet
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Haystacks at Giverny, 1891, Monet * Portrayed the effects of changes in light and weather |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Dance at the Moulin de la Galette, 1876, Renoir
Portrayal of the Belle Epoque |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
The Dance Class, 1874, Degas
|
|
|
Who were the symbolists? |
A group of poets, headed by Mallarmé, that attempted to convey reality by impression and sensation |
|
|
When did Post-Impressionism begin and end? |
It began in the 1880's and ended at the first world war |
|
|
Name 5 characteristics of Post-impressionism |
Attempt to improve impressionism
Desire for more control in paintings
Greater Emphasis on composition and form
Emphasis on psychological depth
Questioning of conventional behaviour |
|
|
What was The Great Binge? |
An era of increased use of new drugs such as morphine and opium and increased alcohol consumption |
|
|
Name 4 famous inventors/scientists/philosophers from the Impressionist era |
Einstein, Nietzsche, Freud, Thomson |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
Mount Sainte-Victoire, 1887, Cezanne
|
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Sunday Afternoon on the island of la Grande Jatte, 188, Seurat
Use of Pointillism, Colour Theory |
|
|
What is colour theory? |
the idea that multiple colours placed next to each other could create the appearance of a different colour |
|
|
What is Pointillism? |
Precise application of small dots of paint, uniform in size, onto the canvas |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
Starry Night, 1889, van Gogh
|
|
|
What is the symbolist movement? |
an artistic movement characterized by heightened colour, flattened forms, and heavy outlines |
|

Title, Date, Artist, Relevance |
Manao Tupapao, 1892, Gauguin
shows symbolist movement |
|

Title, Date, Artist |
The Thinker, 1889, Rodin |
|
|
Describe the change in architecture during the Impressionist era |
Change in material: use of concrete, steel, iron, glass
Height more easily added to buildings, invention of the skyscraper |
|
|
What is Art Nouveau? |
* a style of architecture, art, clothing etc. characterized by curvilinear decoration and patterns, based on the forms of nature
|
|
|
When was Art Nouveau popular? |
Between 1890's to early 1900's |
|
|
Name 3 different styles of abstraction and explain them |
* Expressionism: Emotional, gestural, art with free use of colours
* Formalism: Art concerned with structure and order * Fantasy: Art concerned with imagination and the unconscious |
|
|
What is Fauvism? |
* Fauvism: Art with use of seemingly arbitrary use of colour (Critic Louis Vauxcelles labeled the artists Les Fauves, meaning Wild Beasts because of their violent use of colour)
|
|

Title, Artist, Movement |
Femme au Chapeau, Henri Matisse, fauvism |
|
|
Name the characteristics of Cubism |
* Inspired by Cézanne’s work
* Emphasis on depiction of reduced, geometric forms * More interested in form, less interested in colour (unlike fauvists) * Simultaneous representation of multiple view points |
|

Title, Artist, Movement |
les demoiselles d'Avignon, picasso, cubism |
|
|
Name the characteristics of Futurism |
* Founded by Filippo Marinetti (1876-1944):
* Importance of speed, steel, modernity * Focus on movement * Destruction of formalized institutions * Glorification of war * Dynamic use of cubist forms * Use of simultaneous perspective of objects in motion |
|
|
Characteristics of Die Brucke |
* German expressionist movement, characterized by crude technique, un-naturalistic colours, interest in primitivism, and often sexually charged content
|
|

Title, Date, Movement |
Dancing around the golden calf, Emile Nolde, Die Brucke |
|
|
Characteristics of Der Blaue Reiter |
* German expressionist movement, characterized by prismatic colours, interest in art as spirituality
|
|

Title, Date, Movement |
Improvisation 30, Kandinsky, Der Blaue Reiter |
|
|
Characteristics of Dadaism |
* Derived from the nonsensical word “Da” often uttered by children, meaning “yes, yes”
* Disillusioned by the first world war * Search for an 'elementary art that would save mankind' |
|

Title, Artist, Movement |
Fountain, Duchamp, Dadaism |
|
|
Ready-made |
Art made by taking already made objects and placing them in an artistic context |
|
|
Characteristics of Surrealism |
* Interest in the irrational
* Combination of ordinary objects in an extraordinary manner * Interest in the unconscious and subconscious: interest in Freud * Interest in Automatism: Drawing blindly without plan |
|

Title, Artist, Movement |
Persistence of memory, Dali, Surrealism |
|
|
Characteristics of De Stijl |
* Founded in 1917 in Holland
* hopeful response to the war * Sought to integrate painting, sculpture, architecture, and industrial design * Interested in ‘pure’ abstraction |
|
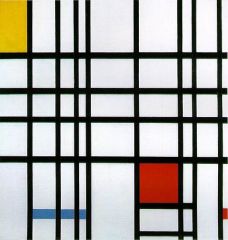
|
Composition with Yellow, Blue, and Red, Mondrian, De Stijl |
|
|
Bauhaus Architecture |
* Architectural movement that sought to integrate art, science, and technology
* Use of purely geometric shapes, and clean lines |
|
|
Le Corbusier |
Bauhaus architect, idea of houses as "machines for living" |
|

Title, Artist, movement |
Yellow Calla lily, georgia o'keefe, American Modernism |
|
|
Ezra Pound & T.S. Eliot |
* Relied on use of rapidly shifting images, presented without explanation
* Believed Poetry should be difficult to read/understand * T.S. Eliot wrote The Waste Land (1922) |
|
|
James Joyce |
* Modernist writers
* Used Stream of Consciousness * Shifted abruptly between characters * Wrote Ulysses (1922) |
|
|
Stream of Consciousness |
A modernist literary technique that records the free flow of a character’s thoughts/impressions |
|
|
Virginia Woolf |
* Modernist writer
* Interested in portraying a character’s inner personality through thoughts and emotions * Wrote Mrs. Dalloway (1925) and To the Lighthouse (1927) |
|
|
Ernest Hemmingway |
* Modernist writer
* Used plain language * Complexity of his work is due to its suggestiveness and implications, the unspoken |
|
|
Frans Kafka |
* Modernist writer
* Style of writing that combines the ordinary and fantastic * Created an existential universe |
|
|
Name 7 important political/economic/social/technological events that occurred during the Modernist period |
* Second Industrial Revolution (advent of phones, automobile, electricity, new weapons)
* First world war * Scientific Advancements (theory of relativity, psychoanalysis) * Increase in Nationalism * Russian Revolution * European Fascism/Second World War * Stock Market Crash |
|

Artist, Title, Relevance |
* Dorothea Lange
* FSA (Farm Security Agency) photographer * Migrant Mother, Nipomo, California (1936) * Depicts the plight of the farmers from the dustbowl during the great depression |
|

Artist, Title, Relevance |
* Margaret Bourke * FSA photographer * At the time of the Louisville Flood * Depicts the plight of black americans during the great depression |
|
|
Regionalism |
* American style of painting, prevalent in the midwest, rejecting abstraction and interested instead in portraying American experiences through regional scenes
|
|

Title, Artist, Movement |
Nighthawks, Edward Hopper, American Regionalism |
|
|
American Regionalism in Literature |
* Style of American writing, prevalent in the south, used south’s traditional “tall-tale”, enhanced with colourful dialect, and memory of the civil war
|
|
|
William Faulkner |
* American Regionalist writer
* Chronicled the American South and the decline of local families * Use of multiple points of view * Use of Stream of Consciousness technique |
|
|
Name 4important feature of the mid twentieth century |
* Cold War
* Vietnam War * Existentialism * Consumerism |
|
|
Existentialism |
* Fueled by the shock of World War II and the Holocaust
* Emphasis on subjectivity, individualism * Interest in responsibility * Moral relativism * Emphasis on the absurd |
|
|
Name 3 existentialist writers |
Kierkegaard Sartre Beauvoir Camus |
|
|
Abstract Expressionism |
* Inspired by existentialism
* Emphasis on personal, subjective painting * Rejected the idea of art as representation |
|
|
What is Action Painting and name an artist who used it |
* style of art focused on conveying the artist’s physical actions
* Jackson Pollock |
|
|
Mark Rothko |
* Created fuzzy, rectangles of colour
* Considered his paintings a backdrop for viewers to experience feelings and emotions |
|
|
* Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
|
* Bauhaus member
* Famous motto “less is more” * Considered responsible for the modern skyscraper |
|

Title, Architect, relevance |
LakeShore Drive apartments, Mies van der Rohe, example of the modern skyscraper |
|
|
Waiting for Godot: playwright, relevance |
Samuel Becket, example of existentialist, absurdist theatre |
|
|
Consumerism |
* Growth of the automobile industry * Advent of fast food chains * Increase in television sets * First Shopping mall * Sexual revolution, including the invention of the oral contraceptive |
|
|
John Cage |
Musical composer, composed "4 minutes 30 seconds", composition consisting of 4 minutes and 30 seconds of silence |
|
|
Andy Warhol |
* Pop artist
* Turned his studio into the “factory” * Created large prints * Raised everyday objects to artistic status |
|
|
Pop Art |
* Artists, like Dadaists believed anything could be art
* Raises everyday objects to artistic status * Use of ready-mades * Both criticizes and embraces consumerism |
|
|
Roy Liechtenstein |
* Pop artist
* Painted large-scale imitations of both war and romance comic strips * Used the “printer’s dot” * Raises everyday objects to artistic status |
|
|
Beat Movement |
* literary movement
* Believed material wealth lead to conformity |
|
|
Jack Kerouac |
* Beat writer
* Interested in reviving the “lost American type”, that had founded the country * Depicts the American-archetype as main character |
|
|
Alan Ginsberg |
* Beat writer
* Writes against conformity * Rushed, abstract language |
|
|
Postmodernism |
* Skeptical, critical
* Interest in the nontraditional, anti-conventional, anti-authority, and anti-establishment * Dominance of the signifier over the signified (the symbol becomes more important that the object it represents) |
|
|
Jean-Francois Lyotard |
* Abundance of information created a crisis of legitimization: ambiguity with which information is correct
* Rejection of Meta-narratives: overarching narratives for society (-isms) * Emphasis on Pluralism * Rejects objective reality/universal truth |
|
|
* Jacques Derrida (1930-2004)
|
Philosopher, intersted in intertextuality and deconstructionsim |
|
|
Intertextuality |
* Belief that anything that conveys a message is a text
* Belief that nothing is truly original; all texts refer to other texts |
|
|
Deconstructionism |
* rejection of universals
* Freedom to interpret texts subjectively * Emphasis on content that is left out of works * Death of the author |
|
|
Roland Barthes |
Philosopher interested in semiotics |
|
|
Explain 4 differences between modernism and postmodernism |
* Distinction between high and low art vs. blurring of high and low art
* Autonomous arts vs. Disappearance of autonomy and creation of all encompassing cultural industry * Stylistic purity, formalism vs. stylistic impurity, eclecticism * Absolute truths vs. plurality of perspectives |
|
|
Cindy Sherman |
* Photographer
* Created film stills in which she assumed the role of archetypal/stereotypical females * Multiple interpretations of her Feminist commentary |
|

title, artist, relevance |
The Dinner Party, Judy Chicago, celebration of influential women |
|
|
Guerilla Girls |
* Dressed in Gorilla masks: undermined modernist idea of individuality/subjectivity
* Used mass media billboards and posters to address Feminist issues |
|
|
Jean-Michel Basquiat |
* Originated as graffiti artist “Samo”
* Art protests against exploitation of black heroes |
|
|
Banksy |
* Uses stencils to create graffiti on walls
* Humorous, satirical, political, morally charged messages * Stencils animals, especially rats to convey ideas |
|
|
Swoon |
* Uses block printing for street art
* Inspired by people seen on the streets * Interest in combining traditional mediums in modern contexts |
|
|
Globalization |
* Precipitated by the fall of the Berlin wall
* Enabled by advances in technology and communication * Mass availability of information via the internet * Emergence of global corporations * Economic globalization * Rise of Asian economies |
|
|
Postmodern Architecture |
* Abandonment of functionalism and minimalism
* Eclectic style * Importance of the experience of the building * Combines past styles * Function follows form: many buildings built representing the function * Las Vegas: Hyperreal representations of previous styles |
|
|
Postmodern Muisc |
* Conglomeration of different styles, cultural music etc, Use of dissonant sound |
|
|
What did orchids and bamboo represent in chinese culture? |
* Bamboo in paintings represented the Chinese people, bending but unbreakable.
* Orchids in paintings represented the Chinese people, able to maintain themselves without soil surrounding their roots |
|
|
What European time period roughly corresponds with the Ming dynasty? |
early Renaissance - Mannerism |
|
|
4 traditional styles of chinese painting formats |
hand scroll, vertical hanging scroll, album leaves, fans |
|
|
Chinese hand scrolls |
* Viewed while lying flat, slowly unrolled to reveal one section at a time
* Ideal for narratives |
|
|
Chinese Vertical hanging scroll |
* Viewed all at once, hung on a wall
* Increased in popularity due to increased interest in landscape painting |
|
|
ChineseAlbum leaves |
* Collection of small paintings
* Viewed close up |
|
|
Chinese Fans |
* Originally used for function
* Became important personal accessory * Eventually fan shape was used to paint without original function * Viewed close up * Often gifts of friendship, dedicated to an event/journey/meeting etc. |
|
|
Most important subject in Chinese painting? |
Landscapes |
|
|
Characteristics of Chinese paintings |
* Multiple focal points
* Strong use of diagonals * Large portion of the composition is often left empty * Used ink and colour |
|
|
What are the 4 treasures used for? |
* Four materials used for caligraphy
* Paper * Brush * Ink-stick * Ink-stone |
|
|
Literati |
* Scholars, also trained in artistic, poetic mediums
|
|
|
Wet-Brush Technique Name an artist who used this technique |
* fuzzy merging of ink and colours on paper * Shi Tao |
|
|
Calligraphy |
* Considered the highest form of art
* Multiple style of scripts * Written fro top to bottom and right to left |
|
|
2 types of porcelains |
* Blue and White Porcelains: Specialty style of Chinese porcelains, most popular during the Ming dynasty, created with a cobalt blue painting on a white background
* Polychrome Enamel Painting: porcelain painting technique using multiple colours, and both underglazes and overglazes |
|
|
What does the dragon represent in Chinese culture? |
* Dragon is considered symbol of strength, power, good luck; 5 clawed dragon denotes an imperial dragon
|
|
|
What does the fish symbolize in Chinese culture? |
* Fish is the symbol of the desire for wealth
|
|
|
Characteristics of Chinese architecture |
* Architecture was used to represent the connection between the rule of the emperor and the universe
* Used a grid system to construct cities * Ruler’s palace was placed at the north of the city, facing south (towards the people, protecting them) with the back towards the north (from which evil was thought to come) |
|
|
Famous example of Chinese architecture |
Forbidden city |
|
|
Dream of the Red Chamber |
* 120 chapter, 3 volume tome depicting the decline of a family
* Love triangle tragedy * Closely related to the life of the author |
|
|
Shogun |
Military ruler |
|
|
Tokugawa Dynasty |
* Tokugawa family ruled Japan from 1600-1868
* Isolated Japan from the world, only the Dutch were allowed to trade with the Japanese * Confucian influences ordered ruling class into Samurai (who became government officials during peacetime), farmers, artisans, and merchants * American military expedition forced Japan to open trade to the Western world |
|
|
Shinto |
* Indigenous, Japanese religious belief system involving ritual veneration of Kami: local deities
* Importance of Japanese landscape * Importance of the superiority of Japan over other cultures |
|
|
Momoyama Period |
* Momoyama period Warlords should be both adept in battle but also cultured in art and architecture
* Considered an artistic renaissance in Japan |
|
|
Zazen |
* Seated meditation focused on posture
|
|
|
Characteristics of Ukiyo-e |
* means “ pictures of the floating world/transcient world”
* Style of woodblock art popular during the 17th and 18th century * Portrayal of everyday life, especially theatre, music, dance, travel * Portrayal of courtesans * Prints of Kabuki theatre actors were extremely popular * Greatly admired by European artists |
|
|
Lacquerware |
* object made of wood, covered in lacquer which dries as a hard, clear, durable surface
* Use of extremely asymmetrical design on both lacquerware and ceramics |
|

|
Hokusai, The Great Wave * Depiction of the power of nature* Mount Fuji in the background, symbolizing Japan’s enduring beauty |
|

Artist, Title |
Hiroshige, One hundred view of Edo |
|
|
Characteristics of Japanese Gardens |
* asymmetry
* balance * proportion * overall unity and visual harmony * Design specific for contemplation, meandering etc. * Microcosm * Often included carefully raked pebbles punctuated by rocks, used to suggest water and islands |
|
|
Haiku |
* Three line, poems consisting of 17 syllables, 5 in the first and last line, 7 in the middle line
* Should portray a momentary, spiritual insight * Must use imagery from nature * Usually includes reference to a season * Does not rhyme |
|
|
Kabuki |
* Form of theatre consisting of short, dramatic dances with song and percussion celebrating the exploits of heroes, especially Samurai
* Originally included both male and female actresses but scandals led to all male casts |
|
|
Geisha |
* Female entertainers, skilled in art, music, dance, storytelling, and entertainment (such as juggling)
* A small number of Geisha were also prostitutes |
|
|
Causes of Colonialism |
* Invention of Breech-loading cartridge-firing rifles: Guns were more reliable, especially in wet environments, and allowed faster firing making even small numbers of soldiers more effective
* Development of Steam Powered and Metal-hull boats: Allowed rapid transport of European troops, and transport of perviously unnavigable rivers * Forced labour in Colonies allowed cheap production of materials |
|
|
2 Types of Colonial rule |
* Practiced mainly by the French, Belgians, and Portuguese
* Important positions in the country are held directly by French nationals * Laws, and practices, including language, were according to French systems * Use of Assimilation: the idea that the more French/Belgian/Portuguese that Africans acted, the more civilized they were considered * Influence on dress, music, etiquette, etc. * Practiced mainly by the British * Ruled through existing African political systems, incorporating rulers into colonial governments * Considered less culturally disruptive * British colonial officers were required to learn local languages, rather than vice versa |
|
|
Effects of Colonialism |
* Africans created independent forms of christianity
* Rapid expansion of Islam: colonialism facilitated the spread of Islam * Created a single African identity |
|
|
Characteristics of African Art |
* African art is interwoven with multiple areas of life (unlike the western autonomous view of life)
* Expression of life through music, and dance * Woodcarving, poetry are on a lower lever than music * Importance of storytelling * Importance of Ubuntu * Artists are anonymous |
|
|
Ubuntu |
* the balance of life forces, importance of people as part of a community
|
|
|
Tourist Art |
* african art created for tourists that conforms to the international expectations of buyers
|
|
|
Colialism in Latin America |
* Significant cultural and economic divide between the upperclass (namely the heirs of colonists) and the lower-class (the indigenous peoples)
* Destruction of native populations in Argentina and Uruguay due to European diseases * Large influence of Roman Catholicism |
|
|
* Frida Kahlo (1910-1954):
|
* Tumultuous marriage to Diego Rivera
* Commentary on race/heritage * Most famous for self-portraits * Painted The Two Fridas (1939): |
|

|
Mona Lisa at the age of 12, Fernando Botero, Satire of the Latin American elite, Depicts three images: Mona Lisa, Velasquz’s Maids of Honour, and Alice in Wonderland |
|
|
Magic Realism |
* the convincing blending of realist events with imaginary and fantastical events
|
|
|
Motet |
* a multi-voiced composition, based on a latin text sung A-capella
|
|
|
A-capella |
* without instrumental accompaniment
|
|
|
Gregorian Chanting |
Monophonic chant |
|
|
Monophonic vs. Polyphonic |
* Monophonic: use of one voice
* Polyphonic: simultaneous playing or singing of several independent musical lines |
|
|
Melismatic chant |
melismatic chant: a syllable sung to 2 or more notes (more reflective and celebratory) |
|
|
Syllabic chant |
each syllable is one tone |
|
|
Characteristics of Renaissance Music |
* Musicians employed by churches and courts
* Increase in secular themed music * All educated people were musically trained * Evolution of instruments recognizable to today’s instruments * Placement of the main melody in the highest voice, unlike in medieval times when it was placed in the lowest voice |
|
|
Word Painting |
* style of musical composition which underlines the words of the music
|
|
|
Guillame Dufay |
* Renaissance composer
* Composed Parody Masses: masses in which a popular song was inserted into the mass * Use of word painting |
|
|
Madrigal |
Vocal composition for a small group of singers, usually a-capella, with each singer singing a different text (unlike motets which used the same texts) |
|
|
Name 4 Renaissance composers |
Thomas Weelkes, Thomas Morley, Josquin de Pres, Guillame Dufay |
|
|
Characteristics of Baroque music |
* Advent of the Opera
* Advent of Oratoris * Theatricality and drama of the baroque age evident in the opera |
|
|
Opera |
staged drama sung to the accompaniment of an orchestra |
|
|
Oratorios |
* religious opera sung without costume or acting
|
|
|
Name 4 Baroque Composers |
Monteverdi, Vivaldi, Handel, Bach |
|
|
Characteristics of 18th century music |
* Popularization of the public concert
* Large, open audience * Construction of public opera houses * Creation of the Symphony |
|
|
Symphony |
* large musical composition consisting (usually) of four movements
|
|
|
Name 3 18th century Composers |
Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven |
|
|
Characteristics of Romantic Music |
* Romantic music did not break with classical ideals but expanded on technique and emotion in symphonies
* Expression of individuality and emotion in music * International popularity of opera due to rise of the middle class * Shift from Absolute music (music that refers to nothing outside music) to Program Music (music that conveys a scene/story/event/emotion) |
|
|
Name 3 Romantic Composers |
Berlioz, Wagner, Chopin, Verdi, Schubert |
|
|
Characteristics of early 20th century music |
* Shift from dramatic dynamics of romantic era to greater tonal variety * Advent of jazz, blues |
|
|
Characteristics of Jazz/blues Music |
* Originated from African rhythms and songs
* Use of Riffs: short improvised phrase * Use of Scat: improvised vocalization of nonsense syllables on a melody * Pentatonic scale * Syncopation |
|
|
Characteristics of Chinese Music & Beijing Opera |
* Chinese music was associated with drama
* Uses traditional styles of acting * Lively, colourful, fast-paced * Based on Chinse myths, legends, and fables * movements are symbolic and suggestive, rather than realistic * Use of masks to symbolize character and character traits |
|
|
Pentatonic scale |
* Pentatonic Scale: 5 note scale, 3rd note is often flat
|
|
|
Koto Music |
* Form of Japanese music, using a Koto: a string instrument
* Form of entertainment * Koto is used for solos, vocal accompaniments, and duets, often with a bamboo flute |
|
|
Characteristics African Music |
* Music styles carried by slaves to America greatly influenced future music, including blues and jazz
* Minor Pentatonic Scale * Use of bent notes * Use of Call-and-response format * Use of Polyrhythms |
|
|
Call-and-response-Format |
Call-and-response Format: Style of music in which lines are called out by a leader and sung back by the band, choir, or audience |
|
|
Samba |
* Latin American music
* Urban music style from the slums of Rio de Janeiro * African Influence * Strongly associated with dance * Common use of the guitar, which has a long history in Spanish culture |

