![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Transitional epithelium -- diagnostic for urinary tract. The surface cells are characteristically dome-shaped and puffy.
|
Name this tissue type & where it's found
|
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium from a distended urinary bladder; compare with the contracted wall in the preceding slide. When stretched, the epithelium becomes very thin, with fewer layers of cells, and the surface cells tend to be flattened. There's only the one layer of flatter cells, however, which is quite different from the appearance of stratifi ed squamous epithelium
|
what is this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized) for comparison. Note that there are many layers of flattened cells, and, in fact, the whole epithelium is quite thick. (from kidney???)
|
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
Papilla (right) projecting into calyx (left) lined with transitional epithelium. kidney/ureter
|
what's this & where's it found?
|
|
|
|
Junction of esophagus (left) and cardiac stomach (right). There is a sudden change in epithelium, from stratified squamous to simple columnar.
|
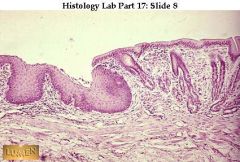
what 2 things do you/where are they found/what's the sudden change/organs?
|
|
|
|
Low power view of stomach through two folds in the wall. Dark pink represents mucosa, with many glands in it.
|
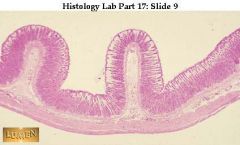
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
Trachea at higher magnification, showing pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lining the lumen. A wide blood vessel lies in the lamina propria below. Hyaline cartilage is at the bottom of the picture.
|
what's this & where is it found? what's tissue below?
|
THIS WILL BE ON EXAM!
|
|
|
Detail of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lining the trachea. Note the presence of pale goblet cells. Foreign particles are trapped in mucus secreted by goblet cells and then moved up (and out of) the respiratory tract by the beating cilia. A pale and quite thick basement membrane underlies this epithelium.
|
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
The trachealis muscle (smooth muscle) is the bright pink band in the middle of the field. Notice how cellular the c.t. under the epithelial layer is. pseudostratified ciliated columnar. Respiratory Tract. Wandering blood cells, especially lymphocytes and eosinophils, are usually found here.
|
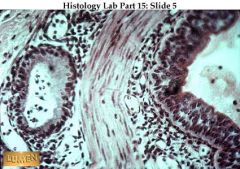
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
pseudo strat ciliated columnar. Also shown are: large chondrocytes of the cartilage. The epithelium lining the lumen looks pseudostratified still. A layer of pink smooth muscle lies between it and the cartilage. Considerable elastic tissue lies in the respiratory wall as well
|
what's this & where is it found? what 's tissue below it?
|
|
|
|
simple squamous, respiratory tract.
alveoli, capillary lumens. fine collagenous and elastic fibers also accompan y the capillaries. As you can see, especially in the capillaries, capillary endothelium = simple squamous alveolar epithelium separating blood from air, is extremely thin. |
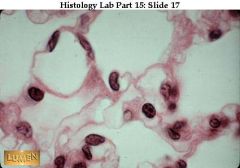
what's thsi & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
simple squamous epithelium lining blood vessels.
Endothelium = the simple squamous epithelium lining blood vessels. -endothelial cells lining a small blood vessel cut in cross-section. |

what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
circumference = simple squamous epithelium
- endothelial nuclei lining the lumen -yellowish cells filling each vessel's lumen are blood cells. |
what's in the circumference, what's the yellow circle?
|
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium lining a tubule
|
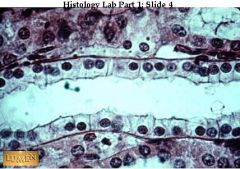
what's this & where can it be found?
|
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium Underneath the epithelium lies a small blood vessel filled with orange-colored blood cells.
|
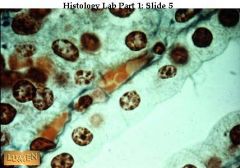
what's this & where can it be found? what's the orange stuff underneath? (what kind of cells is it?0
|
|
|
|
The smaller ones clustered in the center and upper left are lined by simple squamous epithelium. The larger pink tubules have simple cuboidal epithelium.
|
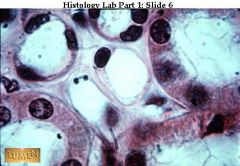
Identify 2 types here & where they can be found.
|
|
|
|
A tubule stained to show the pink basement membrane underlying the base of the simple cuboidal epithelium.
|
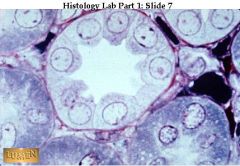
what's the pink circumference called? where can this be found?
|
|
|
|
A tubule stained to show the pink basement membrane underlying the base of the simple cuboidal epithelium.
|
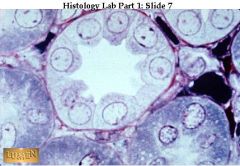
what's the pink circumference called? where can this be found?
|
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium with very regular line-up of nuclei.
|
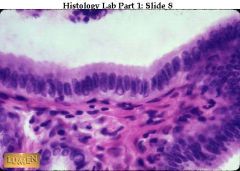
what's this & where is this typically found? (bonus: what're tissues underneath?)
|
|
|
|
simple columnar epithelium w/goblet cell secreting mucus. T
|
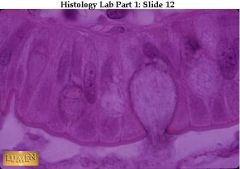
what's this & where is it found? what's that round thing?
|
|
|
|
Four rows of simple columnar epithelium facing each other in pairs (left and right) across a narrow lumen or channel that lies in the middle of each pair.
The goblet cells are filled with blue mucoid secretion which is being poured into the narrow lumens. Notice that in all four rows of epithelium there is a narrow band of striated border next to the lumen. Look at the right hand rows of epithelial cells. The central cavity (middle opening) is a blood vessel with endothelium, surrounded by a very cellular connective tissue. Separating this connective tissue from the epithelium is a thin blue layer of connective tissue fibers. |
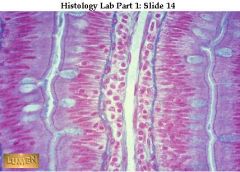
what're 4 rows & where can this be found? where's the cell membrane? How the middle opening different from the L & R one?
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar (Nuclei are at different levels. All cells touch the basement membrane, but only the taller cells reach the lumen).
Trachea. NOtice: cilia are longer and less regular than the microvilli. |
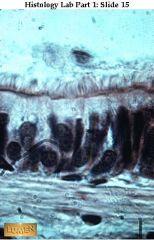
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium with pale goblet cells. The different levels of nuclei are clearer here. Again, notice the wavy-looking cilia.
respiratory tract |
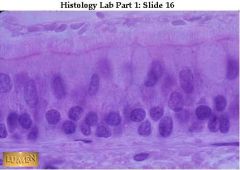
what's this/where is it found?
|
|
|
|
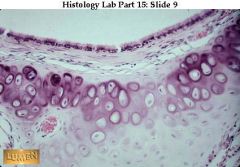
Transitional epithelium of the urinary bladder, low power view. It is a stratified epithelium with several layers of cells.
|
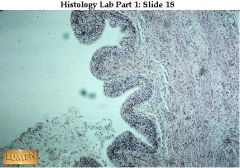
what's this & where it's found? (hint: only 1 place!)
|
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium, (bladder). Notice many layers of cells -- & typically puffy surface cells.
The bladder is contracted so the epithelium is thick. If the bladder were stretched, the epithelium would be thinner!!!! |
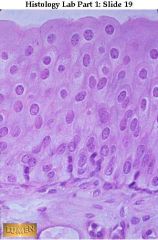
what's this & where can it be found?
|
|
|
|
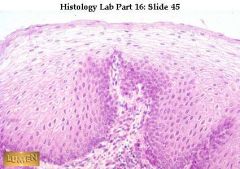
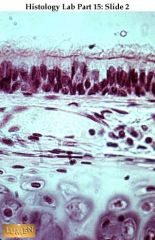
Non-K stratified squamous epithelium -- from esophagus, so the surface is moist and living!
Surface cells are squamous and still nucleated. Basal layer is very distinct; compare this with the less distinct basal layer of the preceding slide of transitional epithelium. |
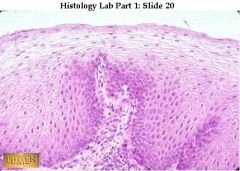
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
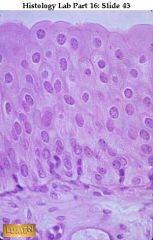
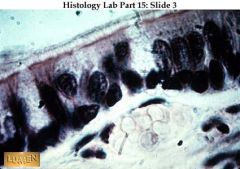
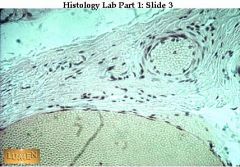
Kratinized STratified Squamous! . Obviously it's from skin-top layer is dead-not moist like esophagus!
|

what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
GI wall - epithelim, Mesiner C, etc.
|
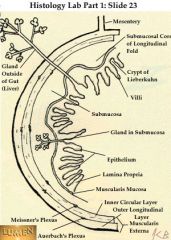
Know this diagram w: see where epithelium is pointed to!! what's the whole structure called?
|
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium
Kidney (Glomerulus) |
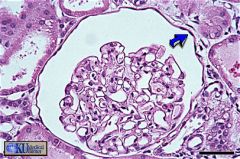
what's this & where can it be found?
|
|
|
|
simple cuboidal epithelium.
Thyroid Gland |
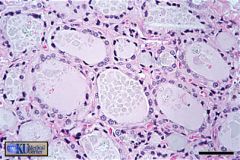
name tissue type & where it can be found
|
|
|
|
Collecting Duct (Kidney)
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in several structures in the kidney, including the collecting duct. |
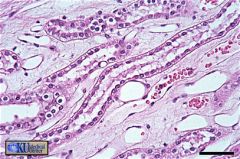
what's this & where is it found?
|
|
|
|
Slide 5: Gall Bladder
Simple columnar epithelium lines the gall bladder. Note the underlying connective tissue with blood vessels. |
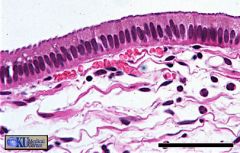
what's this & where can it be found?
|
|
|
|
Uterine Gland
Simple columnar epithelium forms the glands which are surrounded by connective tissue. |
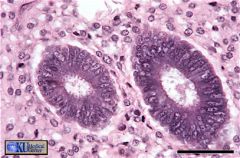
what's this /where can it be found?
|
|
|
|
Male Urethra
A pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines most of the penile urethra. |
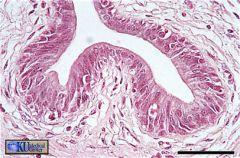
name this & where found
|
|
|
|
Trachea
The pseudostratified columnar epithelium of the trachea is ciliated and has goblet cells. |
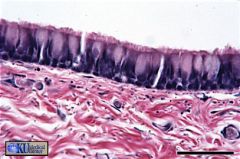
name this & where found
|
|
|
|
Trachea
The pseudostratified columnar epithelium of the trachea is ciliated and has goblet cells. |
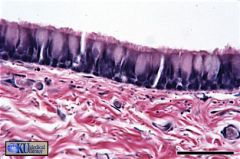
what's this /where found
|
|
|
|
transitional epithelium.
Urinary Bladder The expandible stratified epithelium of the bladder. transitional epithelium. Note that its surface cells are large rather than flattened as in stratified squamous epithelium. |

what's this & where found?
|
|
|
|
Transitional
Urinary Bladder -The expandible stratified epithelium of the bladder is referred to as transitional epithelium. Surface cells of the bladder are sometimes binucleate (black arrow). Note the presence of occasional lymphocytes (blue arrows) in both connective tissue and epithelium. |
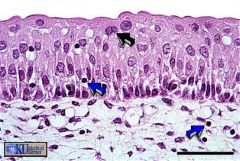
what's this & where found?
|
|
|
|
Stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium covers the lip. Note the thin flat shape of surface cells. The keratin layer is very thin, and is not visible on this section.
|
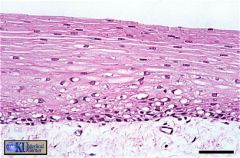
what's this & where found?
|
|
|
|
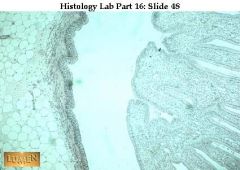
Stratified squamous non-keratinizing epithelium lines the vagina. Note that the surface is to the upper right and that the underlying connective tissue is not visible in this field
|
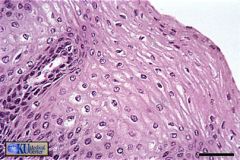
what's this & where found?
|
|
|
|
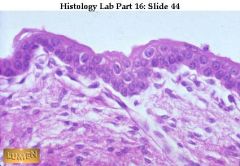
e stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium of thin skin has thin layers of keratin on the upper surface. Note that the epithelium rests on connective tissue below (light pink). Thin Skin
|
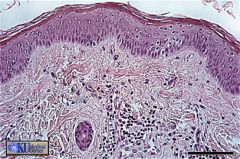
name this & where found
|
|

