![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
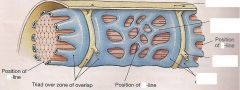
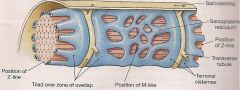
Where do skeletal and cardiac muscle cells get their calcium from?
|
Skeletal - the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Cardica - extracellular space |
|
|
|
|
|
What determines the strength of a muscle contraction?
|
The number of motor-units rectuited.
|
|
|
How is a muscle stimulated to contract? ( steps)
1. AP arrives in terminal knob 2. 3. ACth causes... 4. DHP 5. ..... = contraction |
1. AP arrives causing influx of Ca
2. Influx of Ca stimulated exocytosis of Acetylcholine which diffuses across the cleft 3. ACth causes a depolarization of the muscle cell that travels down the T-tubules 4. The DHP receptor (in T-tubule membrane) is voltage sensitive and will open the Ryanodine recepto (in SR membrane), a passive Ca channel 5. The Ryanodine receptor of the SR opens, releasing Ca into the cytoplasm and this Ca causes a contraction |
|
|
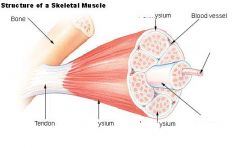
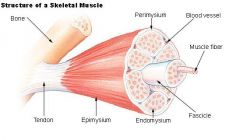
Define endomysium
|
delicate connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle cells
|
|
|
Define epimysium
|
a dense investment of collagen fibers that surrounds a skeletal muscle, and is continuous with the tendon/aponeurosis of the muscle (also continuous with the perimysium
|
|
|
|
|
|
Describe smooth muscle (shape of cell & nucleus)
|
Spindle shaped cells with long oval nuclei. Cytoplasm is homogenous (ie no striations)
|
|
|
Describe arrangement of filaments in smooth muscle:
thin thick intermediate |
criss-cross the cytoplasm. The actin (thin) filaments are anchored to "dense bodies" in cytoplasm or cell membrane.
Thick filaments lie between the thin filaments Intermediate filaments anchor the dense bodies in place and align thick and thin. |
|
|
How can you distinguish smooth muscle from connective tissue?
|
Look for the nucleus - in connective tissue the nuclei is beside the pink stuff (ie collagen). In smooth muscle the nuclei (sometimes wrinkled) is inside the pink stuff.
|
|
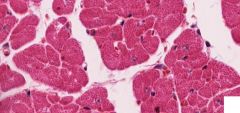
What type of cell is this? How can you tell?
|
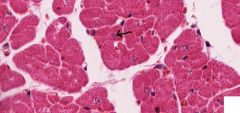
Cardiac muscle - pale central nucleus
|
|
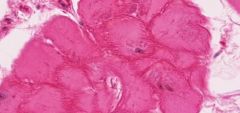
What type of cardiac muscle cell is this? How can you tell?
|
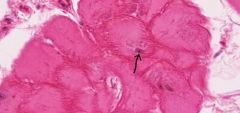
Pirkinje fiber - it is larger and more pale staining. Their myofibrils are concentrated at cell periphery, creating a dark eosinophilic border around the cell
|
|
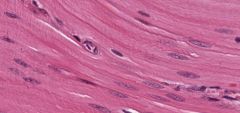
What type of tissue is this? What two cells are present (how can you tell)?
|
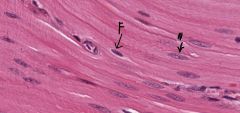
Smooth muscle - long pale oval nucleus. The darker, smaller nuclei (with no obvious cytoplasm) is a fibroblast)
|
|
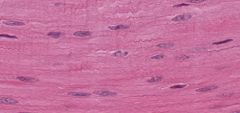
What type of cell is this?
|
Contracted smooth muscle - some cells always contracted and nuclei becomes compressed
|

