![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
epithelium |
tissue that covers outer surfaces and lines inner surfaces |
|
|
properties of epithelium |
-highly cellular -very little intercellular matrix -rest upon a basement membrane -avascular |
|
|
membranous epithelium |
epithelium organized into flattened sheets classified by number of cell layers and shape of cells |
|
|
glands |
irregular-shaped masses of epithelium that secrete proteins |
|
|
basement membrane |
forms an attachment mechanism between the epithelium and the underlying connective tissue |
|
|
hemidesosome |
serve as additional binding of the cells to the underlying connective tissue |
|
|
basal lamina |
superficial part of basal membrane contains adhesive glycoproteins and type IV collagen fibers that bind to the cell |
|
|
reticular lamina |
deep part of basal membrane contains its own specific fibers and adhesive glycoproteins that bind the basal lamina to the connective tissue |
|
|
simple epithelium |
membranous epithelium with one layer of cells |
|
|
stratified epithelium |
membranous epithelium with more than one layer of cells |
|
|
fusiform |
tapered on each end |
|
|
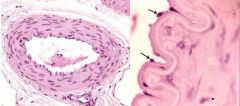
Simple Squamous Epithelium |
composed of a single layer of fusiformtext annotation indicator cells resting on a basement membrane. This type of epithelium is generally found in locations where there is a need for rapid transport across membranes and where is a need for a smooth, non-sticking surface -endothelium lining of blood vessels |
|
|
endothelium |
the simple squamous lining of all blood vessels |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
composed of a single layered sheet of cuboidal-shaped cellstext annotation indicator resting on a basement membrane. This epithelium forms the secretory and excretorytext annotation indicator portions of many glands. The functions of this epithelium are to synthesize a secretory product (such as amylase in salivary glands) and to line passageways (ducts) that transport the product. |
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |
a single layer of columnar cells resting on a basement membrane. This type of epithelium lines most of the gastro-intestinal tracttext annotation indicator, lines ducts of salivary glands, and forms the ameloblaststext annotation indicator (enamel forming cells) of the developing tooth. The epithelium is involved in the synthesis of secretory products in both the GI tract and developing tooth, absorption in the GI tract, and lining passageways that carry a secretory product in the salivary glands. |
|
|
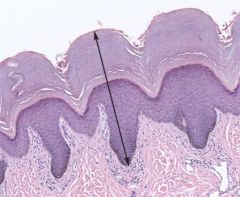
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
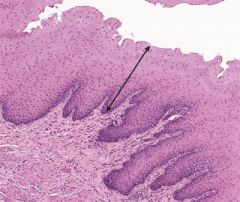
made of several layers of cells with only a single layer resting on the basement membrane. Although the intermediate layers of cells vary in shape, the surface cells are fusiform (squamous). The basal layer of cells (resting on the basement membrane) undergoes mitosis and migrates toward the surface. The cells will change shape and become the squamous surface cells. The function of this epithelium is to protect against friction. can be keratinized (skin) or non-keratinized (inner lining of cheeks) |
|
|
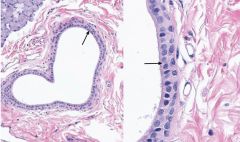
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |
only two cell layers thick, forms portions of the duct system of the salivary glands, and thus functions to carry secretory products to the oral cavity. cuboidal cells |
|
|
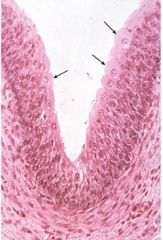
Transitional Epithelium |
a specialized stratified epithelium found in the urinary system and sometimes is referred to as the "urinary epithelium". This epithelium is characterized by large surface cells, which are 2-4 times the size of the underlying cells. allows for expansion |
|
|
dome cells |
convex shaped cells on the surface of transitional epithelium |
|
|
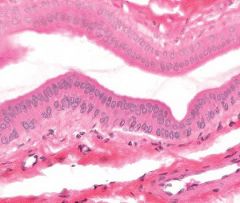
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
only two cell layers thick, forms portions of the duct system of the salivary glands. Thus, it functions to carry secretory products to the oral cavity. columnar cells |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |
composed of three different cells of varying heights. The basal cell is a small pyramidal shaped cell whose nucleus is located nearest to the basement membrane. The tallest is columnar with its nucleus located near the surface, whereas the third type, the fusiform cell, has a nucleus intermediate in location. Because of the cells' sizes, the nuclei are layered in the epithelium. However, each of the cells rests upon the basement membrane making it a simple epithelium. found in respiratory system, ciliated |
|
|
exocrine gland |
product of gland is carried to its site of fucntion by a system of epithelial lined ducts |
|
|
endocrine glands |
product of gland is released into the blood for transport |
|
|
development of glands |
develop as a down growth of the surface epithelium into the underlying connective tissue. In the case of the developing exocrine glands, the cluster of cells of that form secretory cells maintain their attachment to the surface of the epithelium by excretory ducts. On the other hand, the cells of the endocrine glands lose their attachment with the surface and are invaded by blood vessels. |
|
|
unicellular gland |
Goblet cell found in the epithelial lining of many respiratory organs and digestive system organs and secretes a protective layer of mucous. |
|
|
Tubular gland |
the secretory cells are organized in the shape of an elongated hollow tube. |
|
|
Alveolar gland |
the secretory cells form a sac-like structure around a central lumen. |
|
|
tubuloaveolar gland |
a combination of a tube and alveolus, which resemble a saccular dilation at the end of a tube. |
|
|
mucous cells |
secrete a thick, viscous mucoprotein called mucinogen roughly pyramidal in shape with a flattened nucleus located next to the basement membrane. |
|
|
serous cells |
secrete a watery product usually containing enzymes The nucleus is usually spherical and tiny secretory granules can be seen in the apical cytoplasm (near the luminal surface). |
|
|
serous demilune |
secrete both serous and mucous products a cluster of serous cells called a serous demilune forms a half-moon shaped structure on the surface of mucous cells. |
|
|
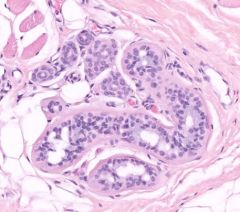
sweat glands |
secrete a watery product that contains waste products and can cool the body by the evaporation of the fluid |
|
|
sebaceous glands |
secrete an "oily substance" along the shaft of hair in the hair follicle |
|
|
merocrine secretion |
secretion characterized by the fusion of the membrane of the secretory to the plasma membrane. the plasma membrane degenerates and releases the protein without any loss of cytoplasm. salivary glands |
|
|
apocrine secretion |
secretion is a similar process in which the membranes of the secretory granules fuse to membrane; however cytoplasm is lost during the process. mammary glands |
|
|
holocrine secretion |
secretion in which the entire cell becomes so filled with secretory product that the cell dies and the entire cell is released from the gland. sebaceous glands |
|
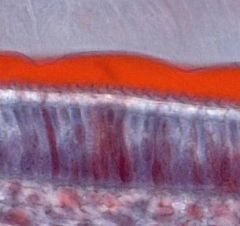
|
ameloblasts |
|
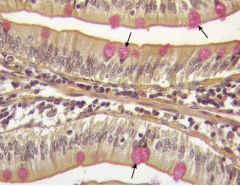
|
Goblet cells |
|
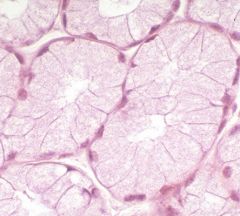
|
mucous cells |
|
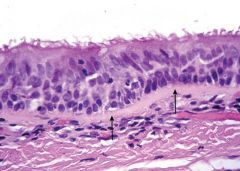
|
pseudostratified epithelium |
|
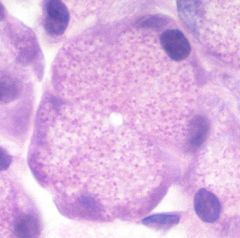
|
serous cells |
|
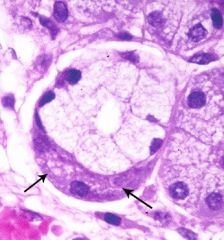
|
serous demilune |
|
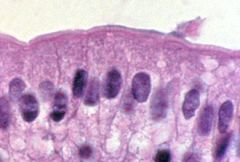
|
simple columnar epithelium |
|
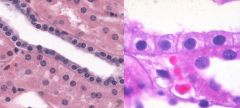
|
simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
stratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
stratified cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
keritinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
sweat gland |
|
|
transitional epithelium |

