![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cartilage |
-firm but flexible connective tissue -provides some structural rigidity in nose, ears, larynx, airway -cushions joints -has few cells surrounded by abundance of extracellular matrix -avascular -covered by connective tissue called perichondrium |
|
|
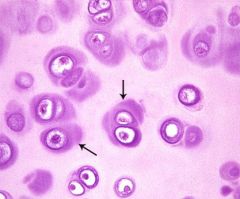
chondrocytes |
-the cells that secrete and are surrounded by the cartilage matrix -maintain cartilage by secreting collagen and glycosaminoglycans -live in lacuna within the matrix |
|
|
cartilage matrix |
-extracellular substance composed of fibers and amporphous ground substance -has mostly type II collagen, some cartilage also has type I and elastic -GAGS: chondroitiin sulfate and keratin sulfate (firmness) -GAG proteoglycans bind water |
|
|
territorial matrix |
-cartilage matrix directly surrounding chondrocytes -stains darker than remaining matrix due to greater concentration of GAGS |
|
|
interterritorial matrix |
matrix not directly surrounding chondrocytes, more abundant |
|
|
perichondrium |
-connective tissue covering of cartilage -covers all surfaces except articular surface -anchor for ligaments and tendons -nutritional sournce -source of stem cells for future growth and repair -outer fibrous layer: mostly collagen, fibroblasts, blood vessels -inner chondrogenic layer: contains chrondroblasts |
|
|
chondroblasts |
cells that secrete cartilage matrix, when surrounded by matric become chondrocytes |
|
|
appositional growth |
-the enlargement of a tissue by the addition of cells and matrix in layers -growth via chrondroblasts |
|
|
interstitial growth |
-growth via mitosis of cells within the matrix -from chondrocytes |
|
|
cell nests |
clusters of daughter cells in matrix formed by mitosis of a parent cell |
|
|
calcification of cartilage |
-loss of blood supply -cells hypertrophy (enlarge) -cells secrete alkaline phosphatase -enzyme breaks down circulating phosphates that are needed for the formation of hydroxyapatitem cystalline form of calcium -prevents the diffusion of nutrients to chondrocytes resulting in death |
|
|
hyaline cartilage |
-most abundant cartilage -serves as embyonic skeleton until replaced by bone -located on articular surfaces of joints, costal ends of ribs, airways, and growth plate of adults -40% type II collagen -glassy appearance -much chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate |
|
|
elastic cartilage |
-located in ears, Eustachian tube, epiglottis -contains elastic fibers in addition to type II collagen -has chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate -covered by perichondrium |
|
|
fibrocartilage |
-looks like intermediate between cartilage and dense C.T. -choondrocytes in columns separated by bundles of type I and type II collagen -sparse proteoglycans -no true perichondrium -found in intevertebral disks, pubic symphysis, temporomandibular joint |
|
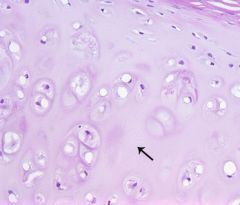
|
cartilage matrix |
|
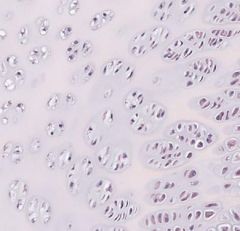
|
cell nest |
|
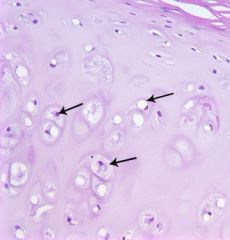
|
chondrocytes |
|
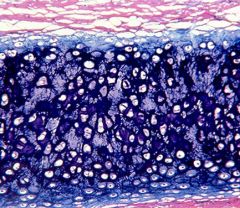
|
elastic cartilage |
|
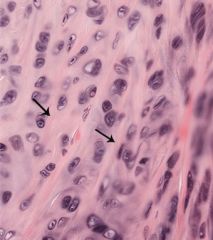
|
fibrocartilage with collagen columns |
|
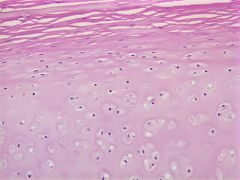
|
hyaline cartilage |
|
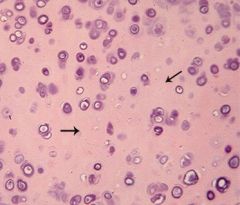
|
interterritorial matrix |
|
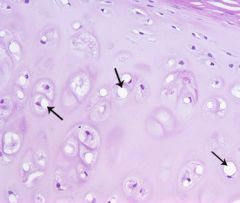
|
lacunae |
|
|
territorial matrix |

