![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the four types of tissues? |
Epithelial tissue connective tissue muscle tissue neural tissue |
ET, CT... |
|
|
What does epithelial tissue do? |
Covers expose services
Lines internal passageways
Forms glands |
Three things |
|
|
What does connective tissue do? |
Fills internal spaces
Supports other tissues (bones, cartilage)
Transports materials (blood, lymph)
Stores energy (adipose) |
Example: Cartilage |
|
|
What is muscle tissue? |
Specialized for contraction
Skeletal muscle heart muscle walls of hollow organs |
|
|
|
What does neural tissue due? |
Specialized for communication and control
Carries electrical signals from one part of the body to another |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue includes... |
Epithelia - layers of cells Glands - structures that secrete |
|
|
|
What are the four main functions of ET? |
Provide physical protection
control permeability
provide sensation
produce specialize secretions |
|
|
|
Tissue that is thin and flat ? |
Squamous epithelial |
|
|
|
Tissue that is square shaped? |
Cuboidal epithelia |
|
|
|
Tissue that is tall and has slender rectangles? |
Columnar epithelia |
|
|
|
Tissues with a single layer of cells is known as? |
Simple epithelium |
|
|
|
Tissues with several layers of cells are known as? |
Stratified epithelium |
|
|
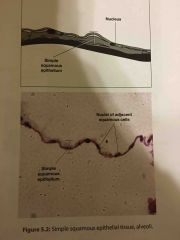
What are the locations and functions of simple squamous epithelium? |
LOCATIONS serous membrane's kidney glomeruli Alveoli of lungs lining of heart blood vessels lymphatic vessels
FUNCTIONS Allows for easy movement of molecules across the membrane through osmosis and diffusion |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium? |
LOCATIONS Epidermis of the skin
FUNCTIONS protection against pathogens abrasion and chemicals
Drying out agent |
Example: only one to have hair (keratin) |
|
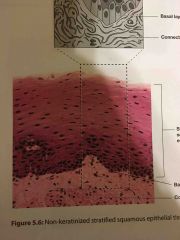
What are the locations and functions of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium? |
LOCATIONS Vagina Anus Rectum Mouth Esophagus
FUNCTIONS protects underlying tissues |
|
|
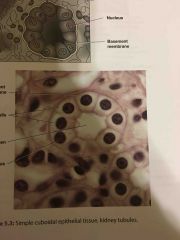
What are the locations and functions a simple cuboidal epithelium? |
LOCATIONS Kidney tubules small ducts and glands thyroid gland covering ovary uterine tubes
FUNCTIONS capable of secretion and absorption |
|
|
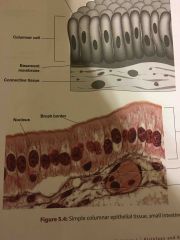
What are the locations and functions of simple columnar epithelium? |
LOCATIONS lining the stomach intestines Gall bladder ducts of large glands small bronchi
FUNCTIONS Capable of absorption, secretion and protection |
Made of cartilage or bone |
|
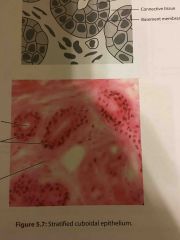
What are the locations and functions of stratified cuboidal epithelium? |
LOCATIONS Ducts of sweat glands
FUNCTIONS absorption, secretion and protection |
|
|
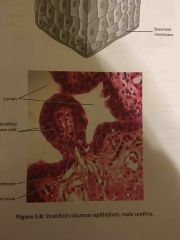
What are the locations and functions of stratified columnar epithelium? |
LOCATIONS large ducts of mammary and salivary gland's
FUNCTIONS protects and select portions of the urethra, anus, epiglottis and pharynx |
Contains: Mesenchymal cells Mesenchymal fibers |
|

What are the locations and functions of pseudostratified columnar epithelium? |
LOCATIONS lined the trachea male reproductive ducts ducts of large glands
FUNCTIONS secrete mucus and possess Cillia that beat to sweep up the mucus and out airways |
Contains: Fibroblasts mass cells macrophages collagen fibers elastic fibers |
|
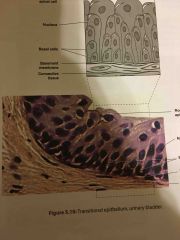
What are the locations and functions of transitional epithelium? |
LOCATIONS line urinary bladder
FUNCTIONS allow stretching to change from the rounded shape to a flattened shape |
Contains: Adipocytes |
|

What are the locations and functions of skeletal muscle? |
LOCATIONS Attached to bones
FUNCTIONS Movement of the skeleton |
Contains: Reticular cells lymphocytes reticular fibers |
|

What are the locations and functions of smooth muscle? |
LOCATIONS stomach urinary bladder muscular blood vessels (arteries)
FUNCTIONS moves substances through digestive urinary and reproductive tracts
Regulates blood vessel diameter
Controls diameter of respiratory passageways |
Contains: Fibroblasts collagen fibers |
|

What are the locations and functions of cardiac muscle? |
LOCATIONS only in wall of the heart
FUNCTIONS allows for rapid communication between adjacent cells necessary for fibers to contract as unit |
Contains: Fibroblasts collagen fibers |
|
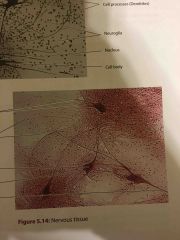
What are the locations and functions of nervous tissue? |
LOCATIONS neuron - generates and conducts an electrical pulse
neuroglial cells - do not carry nerve impulses
FUNCTIONS Protect, support and insulate neurons |
Contains: Elastic fibers |
|
|
What do you connective tissue's do? |
Function to bind, support, protect and fill spaces |
Contains: Chondrocytes collagen fibers |
|
|
What three CT's are known as loose connective tissue proper? |
Areolar CT Adipose CT Reticular CT |
Contains: Chondrocytes collagen fibers
|
|
|
What three CT's are known as dense connective tissue proper? |
Dense regular CT dense irregular CT elastic CT |
Contains: Chondrocytes elastic fibers |
|
|
What are the five supporting connective tissue's? |
Hyaline cartilage fibrocartilage elastic cartilage compact bone cancellous bone |
Contains: Osteocytes collagen fibers |
|
|
What are the two fluid connected tissues? |
Blood lymph |
Contains: Osteocytes |
|

What are the locations and functions of Mesenchyme/embryonic connective tissue? |
LOCATIONS embryo
FUNCTIONS gives rise to all types of adult CT |
Contains: Erythrocytes Leukocytes |
|

What are the locations and functions of Areolar connective tissue? |
Locations Capillary networks
Functions Binds and protects the capillaries |
|
|
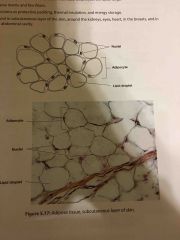
What are the locations and functions of adipose connective tissue? |
Locations Subcutaneous layer of skin around kidneys Heart breasts abdominal cavity
Functions Protective padding Thermal insulation Energy storage |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of reticular connective tissue? |
Locations Lymph nodes spleen bone marrow liver kidney
Functions Forms of flexible internal scaffolding that supports other types of cells |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of dense regular connective tissue? |
Locations Ligaments tendons
Functions Forms ligaments and tendons It is able to anchor bones to each other and muscles to bones |
|
|
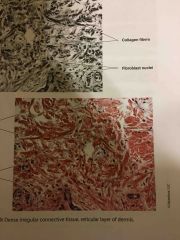
What are the locations and functions of dense irregular connective tissue? |
Locations Reticular layer of dermis Wall of digestive tract Fibrous capsules of organs in joints
Functions Structural strength to resist herring in all directions |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of elastic connective tissue? |
Locations Walls of large arteries walls of the bronchial tubes
Functions Allows for recoil of tissue following stretching |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of hyaline Cartlidge? |
Locations Covering ends of long bones within joints coastal cartilage cartilage of nose Trachea Larynx
Functions Shock absorbency reduce friction between bony surfaces |
|
|
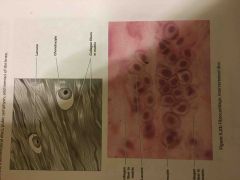
What are the locations and functions of fibrocartilage? |
Locations vertebral disks pubic symphysis Menisci of the knee
functions Shock absorber |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of elastic cartilage? |
Locations Auricle of the outer ear epiglottis
Functions Very flexible Cartlidge |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of compact bone? |
Locations Bones
Functions Support structure forms hard tissue |
|
|

What are the locations and functions of cancellous bone? |
Locations Deep to compact bone
Functions Has trabeculae which form red bone marrow |
|
|
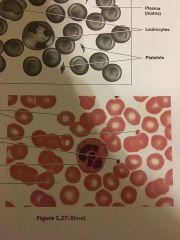
What are the locations and functions of blood? |
Locations Blood vessels
Functions Contains rbc that transport respiratory gases
Contains wbc that participate in the body's defenses
Contains platelets involved in blood clotting |
|
|
|
What are the three epithelial membranes underlying layers of connective tissue? |
Cutaneous membrane - The skin
mucous membranes - line the openings into the body the digestive reproductive urinary and respiratory tracts
serous membranes - line body cavities and cover the surfaces of many internal organs |
|
|
|
Synovial membranes do not contain a true epithelium. They are composed of CT and the line what? |
Cavities surrounding the joints form a smooth surface and a lubricating fluid (synovial fluid) |
|

