![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is histology the study of?
|
tissues
|
|
|
What are the 4 principal tissues?
|
1. epithelial tissue
2. connective and supporting tissue 3. muscle tissue 4. nervous tissue |
|
|
where is epithelial tissue located?
|
it covers the surface
|
|
|
What is this kind of tissue?
|
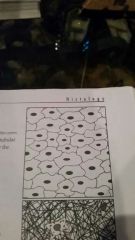
epithelial tissue
|
|

What kind of tissue is this?
|
connective and supporting tissue
|
|
|
What kind of tissue has few cells with lots of extracellular material; numerous functions?
|
connective and supporting tissue
|
|
|
What kind of tissue has elongated cells that are specialized to shorten?
|
muscle tissue
|
|
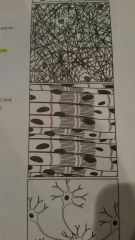
What kind of tissue is this?
|
muscle tissue
|
|
|
What kind of tissue consists of cells specialized for initiation and transmission of electrical signals?
|
nervous tissue
|
|
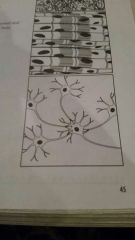
What kind of tissue is this?
|
nervous tissue
|
|
|
What are the 3 cell shapes of epithelial tissue?
|
1. squamous
2. cuboidal 3. columnar |
|
|
What are the 2 types of layers of epithelial tissue?
|
1. simple
2. stratified |
|
|
What are the 4 functions of epithelial tissue?
|
1. secretion
2. absorbtion 3. excretion 4. protection |
|
|
What are the 3 primary ways that epithelial tissues function?
|
1. as selective barriers that limit or aid the transfer of substances in and out of the body.
2. as secretory structures that release products produced by the cells onto their free surfaces. 3. as protective surfaces that resist the abrasive influences of the environment, protect against chemical and bacterial invasion, and temper the harmful rays of the sun. |
|
|
What type of tissue consists of many tightly packed cells with little extracellular material?
|
epithelial tissue
|
|
|
What type of tissue forms numerous specialized cell junctions?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissue form sheets comprised of either a single layer or multiple layers of cells?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissues are always surface tissues?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissues are a vascular, meaning they lack blood vessels?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissues have nerve endings and sensory receptors?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissues are mitotically active tissues that are capable of regenerating?
|
epithelial
|
|
|
What type of tissue is located inside lining of the blood vessel?
|
simple epithelial tissue
|
|
|
What type of tissue has a function of diffusion?
|
epithelial tissue
|
|
|
What type of tissue lines the cardiovascular lining and body cavities?
|
simple squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What type of tissue is in the lining of many glands of the body?
|
simple cuboidal epithelium
|
|
|
What kinds of tissue are found as the inner lining surface of the digestive tract, from the beginning of the stomach to the anus or lining the bronchi of the lungs and the uterine tubes?
|
simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What tissue lines the upper respiratory tract and the apical surface which is covered with cilia?
|
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What kind of tissue has many layers?
|
stratified
|
|
|
What type of tissue is the thickest epithelial tissue in the body, it is the epidermis layer of the skin and it can also be found lining the inside of the mouth and nose, lining the esophagus and anus, and covering the surface of the eye?
|
stratified squamous epithelium
|
|
|
What tissue is not a common tissue in the body?
|
stratified columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What tissue in the body can be found in certain regions of the larynx (voice box) and pharynx (throat) as well as lining the large excretory ducts of some glands?
|
stratified columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What tissue lines the urinary system from the large urinary tubules of the kidney through the ureter, bladder, and urethra?
|
transitional (stratified cuboidal) epithelium
|
|
|
What tissue interconnects and fills the space between other tissues and organs; protects, cushions and provides structural support for other tissues and organs; stores energy reserves in the form of neutral fats; transports substances throughout the body?
|
connective and supporting tissue
|
|
|
What are the 4 basic types of connective tissue?
|
1. general connective tissue-soft connective tissue
2. cartilage 3. bone 4. blood |
|
|
What kind of connective tissue has a greater ratio of extracellular material to cells?
|
general connective tissue
|
|
|
What connective tissue has the following two major categories of cells: those that are permanent residents of the tissue and responsible for the characteristics of the extracellular content, transient cells that enter the tissue from the blood?
|
general connective tissue
|
|
|
What are the 3 categories of general connective tissue?
|
1. connective tissue proper
2. reticular tissue 3. adipose tissue |

