![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where in the BODY is the THYROID LOCATED? |
BASE of the THROAT |
|
|
Describe the STRUCTURE of the THYROID |
BI-LOBED Divided into LOBULES Divided into FOLLICLES |
|
|
Describe the FOLLICLES of the THYROID |
hollow SPHERES of SIMPLE CUBOIDALEPITHELIUM Inside: COLLOID:: STORES HORMONES Surrounded by CAPILLARIES |
|
|
What CELLS make up the FOLLICLE? |
PRINCIPAL CELLS/FOLLICULAR CELLS (Simple Cuboidal) |
|
|
What MAKES UP the COLLOID? |
THYROGLOBULIN |
|
|
Describe the THYROGLOSSAL DUCT |
MIGRATES from BACK of TONUGE to the BOTTOM of NECK BIFURCATES into the BILOBED THYROID DUCT then undergoes APOPTOSIS |
|
|
Describe the FORAMEN CECUM |
HOLE in TONGUE left from THYROGLOSSAL DUCT migration |
|
|
Describe a PYRAMIDAL LOBE |
Pointed REMNANT of THYROGLOSSAL DUCT at TOP of THYROID (1/3 of people) |
|
|
What is a Lingual Thyroid? |
Remnants of T. duct at the BACK of TONGUE |
|
|
What TYPE of EPITHELIUM are FOLLICULAR CELLS of HYPERACTIVE THYROIDS? |
SIMPLE COLUMNAR
|
|
|
What TYPE of EPITHELIUM are FOLLICULAR CELLS of an UNDERACTIVE THYROID?
|
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS |
|
|
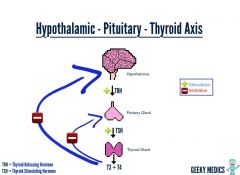
Describe the PATHWAY of HORMONES for THYROID ACTIVITY? |
HYPOTHALAMUS releases THYROID RELEASING HORMONE (TRH) -> TRH targets THYROTROPHS, releasing THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) -> TSH targets THYROID, releasing T3 + T4 |
|
|
Describe the NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP of T3 +T4 |
T3/T4 inhibit PITUITARY release of TSH & inhibit HYPOTHALAMUS release of TRH |
|
|
|
|
|
What is MORE ACTIVE, T3 or T4, and by HOW MUCH? |
T3 is 4x MORE ACTIVE
|
|
|
What PERCENTAGE of T3 + T4 are SYNTHESIZED by the THYROID? |
80% T4 20% T3 |
|
|
Where does T4 travel to be CONVERTED to T3? |
LIVER |
|
|
Describe the T3+T4 PATHWAY from TSH BINDING to FOLLICULAR CELLS |
1. TSH Binds to FOLLICULAR CELL RECEPTOR 2. THYROGLOBULIN produced & stored in Colloid 3. IODINE symported into COLLOID 4. IODINE in COLLOID binds to THYROGLOBULIN producing T3+T4 5. T3+T4 is DUMPED out of cell |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of T3 + T4? |
CONTROL METABOLISM |
|
|
What is HYPOTHYROIDISM? |
LOW Production of T3 + T4 |
|
|
What is HYPERTHYROIDISM? |
HIGH Production of T3 + T4 |
|
|
Describe CRETINISM |
HYPOTHYROIDISM as a CHILD <10 yr old Mental Ability |
|
|
Describe MYXEDIMA |
HYPOTHYROIDISM as an ADULT due to LOW IODINE -> GOITER |
|
|
Describe HASHIMOTO'S DISEASE |
HYPOTHYROIDISM AUTOIMMUNE RESPONSE to THYROGLOBULIN GOITER due to INFLAMMATION |
|
|
Describe GRAVE'S DISEASE |
HYPERTHYROIDISM AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE: ANTIBODY fits into TSH RECEPTORS |
|
|
What are PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS? |
Cells AROUND the FOLLICULAR CELLS |
|
|
What do PARAFOLLICULAR CELLS produce? |
THYROCALCITONIN (calcitonin) |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of THYROCALCITONIN? |
LOWER BLOOD CA++ |
|
|
How many PARATHYROIDS are there, and WHERE are they located? |
FOUR 2 per THYROID LOBE (Within Thyroid C.T.) |
|
|
What HORMONE do PRINCIPAL/CHIEF CELLS produce? |
PARATHYROID HORMONE: Raises Blood Ca++ |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of PARATHYROID HORMONE? |
RAISE BLOOD CA++ by Stimulating OSTEOCLASTS (Ca++ retrieval) & conserving Ca++ from URINE |
|
|
What are the TWO TYPES of CELLS in the PARATHYROID? |
PRINCIPAL/CHIEF CELLS OXYPHIL CELLS |
|
|
What do OXYPHIL CELLS do? |
We have no ******* idea. (OXYphil - OXYMORON - We're MORONS) |
|
|
What is ANOTHER name for the SUPRARENAL GLANDS? |
ADRENAL GLAND |
|
|
Where are the SUPRARENAL GLANDS located? |
ONTOP of the KIDNEYS |
|
|
What are the TWO SEGMENTS of the SUPRARENAL GLANDS? |
CORTEX & MEDULLA |
|
|
Describe the size of the CORTEX of the SUPRARENAL GLAND |
8-9X Larger than Medulla |
|
|
Where is the CORTEX of the SUPRARENAL GLAND DERIVED? |
MESOTHELIUM |
|
|
Where is the MEDULLA of the SUPRARENAL GLAND DERIVED? |
NEURAL CREST CELLS |
|
|
What are the THREE ZONES of the ADRENAL CORTEX? |
ZONA GLOMERULOSA ZONA FASCICULAE ZONA RETICULARIS |
|
|
Describe how BLOOD FLOWS through the SUPRARENAL GLAND |
DRAIN thru the CORTEX and taken out via VEINS in the MEDULLA From OUTSIDE -> IN |
|
|
Describe the ZONA GLOMERULOSA |
TOP LAYER of ADRENAL CORTEX w/SPHERICAL STRUCTURES |
|
|
What CLASS of HORMONES is PRODUCED by the ZONA GLOMERULOSA?
|
MINERALOCORTICOIDS |
|
|
Where are MINERALOCORTICOIDS produced? |
ZONA GLOMERULOSA of the SUPRARENAL GLAND |
|
|
What are the TWO MINERALOCORTICOID HORMONES? |
ALDOSTERONE & DOCA |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of ALDOSTERONE? |
CONSERVE Na+ (and WATER) INCREASES BP |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of DOCA? |
Dump K+ out |
|
|
What would a TUMOR of the ZONA GLOMERULOSA cause? |
HIGH BP LOW K+ |
|
|
Describe the ZONA FASCICULATA |
Largest Zone of the ADRENAL CORTEX Btwn GLOMERULOSA & RETICULARIS |
|
|
What are the CELLS of the ZONA FASCICULATA? |
SPONGOCYTES |
|
|
What CLASS of HORMONE is produced by the ZONA FASCICULATA? |
GLUCOCORTICOIDS |
|
|
What are the TWO GLUCOCORTICOID HORMONES? |
CORTISONE HYDROCORTISONE |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of GLUCOCORTICOIDS? |
INCREASE BLOOD SUGAR LEVELS |
|
|
What is CORTISOL? |
MIXTURE of Cortisone & Hydrocortisone |
|
|
What type of PITUITARY (HYPOPHYSIS) CELL controls GLUCOCORTICOID production? |
CORTICOTROPHS
|
|
|
What would a TUMOR of the CORTICOTROPHS cause? |
High ACTH -> High CORTISOL 0> |
|
|
Describe the ZONA RETICULARIS |
BOTTOM/THIN LAYER of the ADRENAL CORTEX |
|
|
What CLASS of HORMONES does the ZONA RETICULARIS produce? |
ANDROGENS (sex hormones) |
|
|
What is the ANDROGEN HORMONE produced by the ZONA RETICULARIS? |
DHEA |
|
|
What is the FUNCTION of DHEA? |
Modification INTO TESTOSTERONE/ESTROGEN |
|
|
Describe the ADRENAL MEDULLA |
VENOUS are of the ADRENAL GLAND |
|
|
What TYPE of STRESS does the ADRENAL CORTEX respond to? |
LONG TERM STRESS |
|
|
What TYPE of STRESS does the ADRENAL MEDULA respond to? |
SHORT TERM STRESS |
|
|
What are the TWO HORMONES produced by the ADRENAL MEDULLA? |
EPINEPHRINE & NOREPINEPHRINE |
|
|
What are the CELLS in the ADRENAL MEDULLA? |
CHROMAFFIN CELLS
|
|
|
From WHERE do ADRENAL MEDULLA CELLS ORIGINATE?
|
NEURAL CREST CELLS |
|
|
From WHERE do ADRENAL CORTEX CELLS ORIGINATE? |
MESOTHELIUM |
|
|
What is HYPOADRENALCORTICOLISM |
UNDERACTIVITY of ADRENAL CORTEX |
|
|
What is ADDISON'S DISEASE? |
HYPOADRENALCORTICOLISM (Underactivity of Adrenal Cortex) AUTOIMMUNE attack of Adrenal Cortex 20% due to Tuberculosis (JFK) |
|
|
What is HYPERADRENALCORTICOLISM? |
OVER PRODUCTION of the ADRENAL CORTEX |
|
|
What is CUSHING'S SYNDROME? |
HYPERADRENALCORTICOLISM (big hairy lady) |

