![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
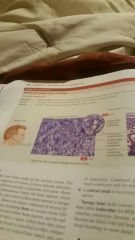
Simple squamous epithelium |
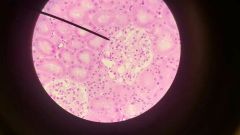
Present at sites of filtration Example: Small intestine |
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |
Funtion: Secretion and absorption Location Example: Kidney |
|
|
|
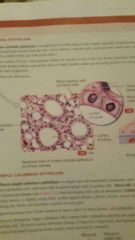
Nonciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium |
Function: Secretion and absorption Location Example: Small intestine |
|
|
|
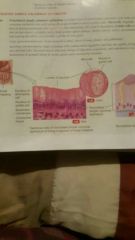
Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium |
Location: Uterine tube |
|
|
|
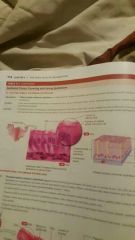
Psuedo Stratified Columnar Epithelium |
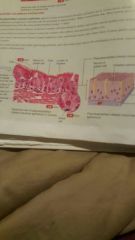
Location Example: Trachea |
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |
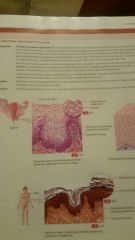
Location Example: Vagina Function: Protection against abrasion, water loss, U.V radiation, and foreign invasion. |
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium |
Function: Allows urinary organ to stretch while holding variable amounts of fluid without rupturing. Location: Urinary bladder |
|
|
|
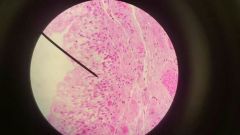
Areolar Connective Tissue |
Function: Strength, Elasticity, Support Location: Subcutaneous Layer |
|
|
|
Adipose Tissue |
Function: Hold fat, fat storage Location: Around Heart, where ever aerolar convective tissue is located. |
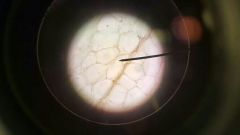
|
|
|
Reticular Connective Tissue |
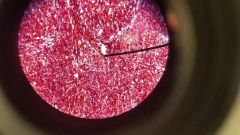
Function: Forms stroma of organs, bonds smooth muscle tissue cells, filters and removes worn-out blood cells in spleen and microbes in lymph nodes. Location: Lymph Node |
|
|
|
Collagenous Connective Tissue |
Function: Forms tendons, most ligaments, and aponeuroses. Location: Tendon |
|
|
|
Elastic Connective Tissue |
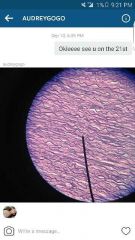
Function: Allows stretching of various organs, can recoil after being stretched Location: Aorta |
|
|
|
Hyaline Connective Tissue |
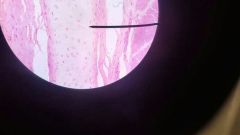
Function: Moat abundant cartilage in the body Location: Fetal skeleton |
|
|
|
Fibro cartilage |
Function: Support and joining structures together Location: Intervertebral Discs |
|
|
|
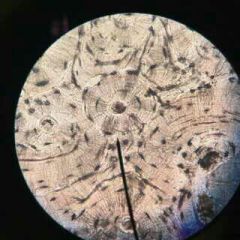
Elastic Cartilage |
Function: Provides strength and elasticity Location: Auricle of the ear |
|
|
|
Bone tissue |
Function: Support, protection, storage, houses blood forming tissue. Location: Femur |
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Tissue |

Function: Motion, protection, heat production, posture. Location: Skeletal Muscle |
|
|
|
Cardiac Tissue |
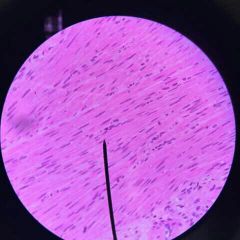
Function: pumps blood to all part of body Location: Heart |
|
|
|
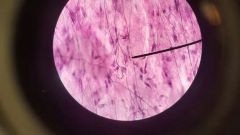
Smooth muscle tissue |
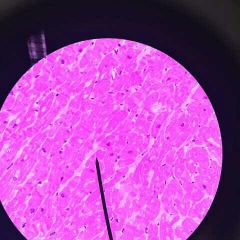
Function: Motion Location: Artery |
|
|
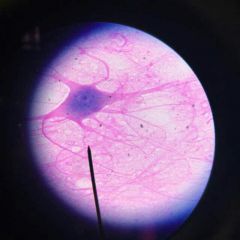
Giant motor Nueron |
Location: Nervous system Function: Converts stimuli into nerve impulses |
|
|
|
Sarcolemma |

Membrane of muscle tissue cells |
|
|
|
Sarcoplasm |
Cytoplasm of muscle tissue cells |
|
|
|
Epithelial |
Covers body surfaces, internal and external |
|
|
|
Connective tissue |
Protection and support of body structures |
|
|
|
Muscle Tissue |
Provides the force necessary for movement |
|
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Coordination of body activities |
|
|
|
Lumen |
The space that lies nect to the apical surface of certain epithelial tissue |
|
|
|
Apical surface |
The outer edge, surface of skin |
|
|
|
Basal surface |
Attaches to the connective tissue |
|
|
|
Basement membrane |
A thin structure which usually consists of two layers that are located between the connective tissue and epithelial cells |
|
|
|
Avasucular |
Lacking a blood supply, epithelial tissue lacks blood vessels |
|
|
|
Squamous |
Flattened |
|
|
|
Cuboidal |
As tall as they are wide |
|
|
|
Columnar |
Calls that are taller than their width, cylindrical and rectangular |
|
|
|
Transitional |
These cells change shape as they are are stretched |
|
|
|
Simple |
Single layer of cells |
|
|
|
Stratified |
Tissue is two or more layers of cells in thickness |
|
|
|
Psuedo Stratified |
A single layer of cells that appeared to be stratified, not all of the cells extend to the apical surface |
|
|
|
Cilia |
Hair like structures that move substance along the surface of cells. Found in psuedo Stratified columner epithilium |
|
|
|
Microvilli |
Finger like cytoplasmic projections that increase surface area. Found in nonciliated simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
|
Goblet cells |
Modified Columnar cells that secrete mucous |
|
|
|
Connective Tissue |
Characterized by fewer cells and a lot of intercellular matrix |
|
|
|
Fibroblast |
Cells that secrete fibers and ground substance. Found in connective tissues |
|
|
|
Macrophages |
Macrophages produced from monocytes |
|
|
|
Plasma cells |
Produce antibodies |
|
|
|
Mast cells |
Release histamine to cause vasodilation |
|
|
|
Adipocytes |
Fats cells store triglycerides |
|
|
|
Chondrocytes |
Cartilage cells produce and maintain cartilage |
|
|
|
Osteocyte |
Bone cells maintain osseous tissue |
|
|
|
Matrix |
Material that fills the area between cells |
|
|
|
Ground substance |
Non cellular material secreted between connective tissues. Calcium hydroxyapatite - bone. Chondroitin sulfate - cartilage. |
|
|
|
Fibers |
Help strengthen and support connective tissue |
|
|
|
Collagen Fibers |
Long chains of protein collagen, are flexible that resists stretching |
|
|
|
Elastic Fibers |
Composed of the protein elastin, better than collagen fibers, can be stretched as 1 and1/2 times their length without being damaged and are able to return to their original length |
|
|
|
Mesenchyme |
Embryonic tissue from which other connective tissues eventually arise |
|
|
|
Areolar C.T |
Most prevalent type of connective tissue, fibers are randomly arranged to provide elasticity and strength in several planes of motion |
|
|
|
Adipose tissue |
Made up of adipocytes, storage triglycerides |
|
|
|
Reticular Connective Tissue |
Composed of a network of reticular fibers and reticular cells |
|
|
|
Dense regular C.T |
Collagen fibers are parallel that provides great strength and one plane of motion example tendon |
|
|
|
Dense Irregular C.T |
Irregularly arranged collagen fibers, often found in sheets |
|
|
|
Elastic Connective Tissue |
Contains many loosely arranged elastic fibers, example lungs and elastic arteries |
|
|
|
Cartilage |
Contains Collagen elastic fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate |
|
|
|
Lacunae |
Space where chondrocytes and osteocytes are located |
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage |
Most abundant cartilage in the body it is flexible and provides support. Example covers joint surfaces |
|
|
|
Fibro cartilage |
Intervertebral disks. Usually stained blue |
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage |
Outer ear |
|
|
|
Ossues Tissue |
Bone |
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle |
Striated, voluntary, fibers are parallel, nuclei located peripherally |
|
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
Striated, involuntarily, nucleus is located centrally, connected via intercalated discs |
|
|
|
Smooth muscle tissue |
Non-striated, involuntary, nucleus is centrally located, spindle-shaped |
|
|
|
Nuerons |
Nerve cells |
|
|
|
Neuroglia |
Cells that support the function of neurons |
|

