![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four phases of deep wound healing? |
Inflammatory phase Migratory phase Proliferative phase Maturation phase
|
|
|
What is formed in the inflammatory phase of deep wound healing? |
A blood clot to attach the cute edges |
|
|
What cells are present in the inflammatory phase of deep wound healing? How do they get there? |
-Neutrophils and monocytes (macrophages) -Get there by vasodilation and increased permeability |
|
|
What happens to the clot in the migratory phase of deep wound healing? |
It becomes a scab |
|
|
What occurs under a scab in the migratory phase of deep wound healing? |
Epithelial cells bridge the gap underneath it |
|
|
What do fibroblasts do in the migratory phase of deep wound healing? |
Create scar tissue |
|
|
What is scar tissue? |
Collagen and glycoprotein |
|
|
What occurs in the proliferative phase of deep wound healing? |
Growth of epithelial tissue at random Vessels continue to grow |
|
|
What occurs in the maturation phase of deep wound healing? |
Scab sloughs off Epidermis returned to normal thickness |
|
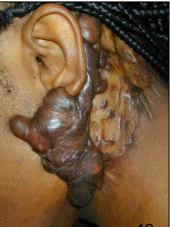
What kind of scar is this? |
Keloid |
|
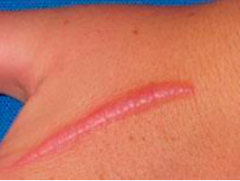
What kind of scar is this? |
Hypertrophic |
|
|
Hyperkeratosis |
Hyperplasia of horny layer |
|
|
Parakeratosis |
Retention of nuclei in stratum corneum |
|
|
Acantholysis |
Loss of cohesion between keratinocytes |
|
|
What lesion results in psoriasis? |
Increased rate of proliferation of mitotic cells |
|
|
Bullous pemphigoid lesion |
Autoimmune cells attack hemidesmosomes (separation of epidermis from dermis) |
|
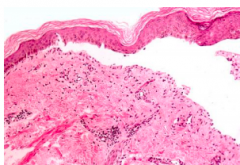
Name the disorder |
Bullous pemphigoid |
|
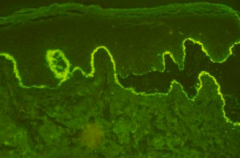
Name the disorder |
Bullous pemphigoid |
|
|
What is attacked in Pempighous vulgaris? |
Desmosomes between stratum spinosum cells |
|
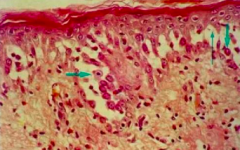
Name the disorder |
Pempighous vulgaris (Notice atrophy of stratum spinosum) |
|
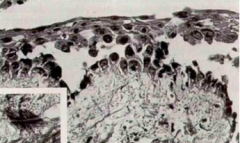
Name the disorder |
Pemphighous vulgaris (Notice atrophy of stratum spinosum) |
|
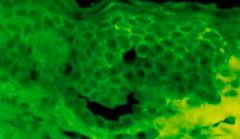
Name the disorder |
Pemphigous vulgaris (Notice "fish net appearance") |
|
|
What kind of genetic disorder is albinism? |
Autosomal recessive |
|
|
Pathogenesis of albinism |
Inactivity of tyrosinase |
|
|
Vitiligo |
Destruction of melanocytes |
|
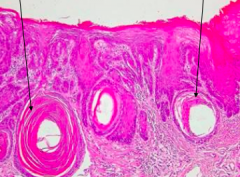
Name the disorder |
Squamous cell carcinoma (Notice swirls) |
|
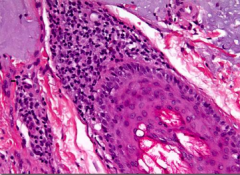
Name the disorder |
Basal cell carcinoma (Notice palisade/fence arrangement) |
|
|
Describe a basal cell carcinoma marking on the skin |
Rolled out margin |
|
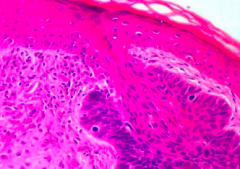
Name the disorder |
Basal cell carcinoma (Notice fence/palisade arrangement) |
|
|
Malignant melanoma |
Malignant transformation of melanocytes |
|
|
ABC's of melanoma diagnosis |
A- Asymmetry B- Border irregularities C- Color variation D- Diameter > 6 mm E- Elevation |
|
|
Neurofibromatosis (Von Recklinghausens disease) |
Schwann cell lesion ****not a skin lesion**** |

