![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
where do you find collagen type 1?
|
most abundant in ct, also in bone, dentin
|
|
|
where is collagen type 2
|
primarily hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
where is collagen type 3?
|
reticular fibers
|
|
|
where is collagen type 4?
|
basal lamina
|
|
|
components of ct? (1, 2.a.b.c., 3)
|
1. ground substance 2. fibers: a. collagen b. reticular c. elastic 3. cells
|
|
|
macrophage derived from?
|
monocytes.
|
|
|
mast cells filled with?
|
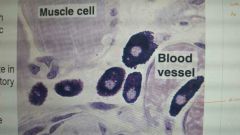
basophilic secretory granules. participate in inflammatory response. release histamine.
|
|
|
what is emphysema?
|
oxidation of the inhibitor of elastase by cigarette smoke. loss of lung elasticity
|
|
|
Ehlers-danlos syndrome
|
faulty collagen. skin hyperextensibility. joint hypermobility
|
|
|
marfan syndrome
|
defect in fibrillin (comp of elastin). abnormally elastic ct. defective aorta. unusually long limbs.
|
|
|
what is an enterocyte?
|
an intestinal cell
|
|
|
red fibers (muscle) powered by?
|
oxidative phosphorylation. fatigue resistant. postural control. more myoglobin
|
|
|
white fibers (muscle) powered by?
|
anaerobic glycolysis. rapid contraction.
|
|
|
maculae adherens aka?
|
desmosomes
|
|
|
cardiac muscle cell junctions:
|
intercalated disks, fasciae adherens, maculae adherens, gap junctions
|
|
|
radial glia
|
form struts for migrating neurons during development
|
|
|
microglia
|
phagocytic. remove debris of dead and dying cells. arise in bone marrow, migrate to cns
|
|
|
choroid plexus
|
continuous with ependymal cell layer. secretes csf.
|
|
|
satellite cells
|
surround cell bodies, particularly prominent in sensory neurons
|

