![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of cells? |
somatic , germline and stem |
|
|
what are somatic cells? |
non sex cells eg. muscle, skin, bone, blood diploid cells divide by mitosis |
|
|
what are diploid cells |
cells with two sets of chromosomes |
|
|
what are germline cells? |
in humans they are called gametes diploid cells they can divide by mitosis to produce more diploid germline cells they can divide by meiosis to produce haploid gametes (sperm and eggs) mutations that occur in them get passed down to offspring |
|
|
what are haploid cells? |
cells with one set of choromosomes |
|
|
what is mitosis |

|
|
|
what is meiosis |
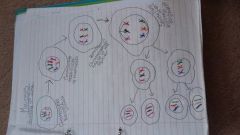
|
|
|
what is differentiation? |
the process which results in cells becoming specialised |
|
|
what are the two types of stem cells |
embryonic stem cells, adult or tissue stem cells |
|
|
what are stem cells |
unspecialised cells that can differentiate into specialised cells of one or more types they are diploid cells and can divide by mitosis |
|
|
what are embryonic stem cells |
in the very early embryo, embryonic stem cells can differentiate into any type of human cell. This is because MOST OF THEIR GENES ARE STILL SWITCHED ON OR EXPRESSED |
|
|
what are adult or tissue stem cells |
their differentiation is restricted to forming types of cells that are found in the tissue or organ in which they are found. (eg stem cells in bone marrow will only produce red blood cells, platelets and various types white blood cells- phagocytes and lymphocytes) They replenish differentiated cells that need to be replaced |
|
|
theraputic uses of stem cells include.. |
bone marrow transplants skin grafts for burns repair of damaged or diseased organs or tissues |
|
|
ethical issues of stem cells... |
are we killing a life? as soon as an egg is fertilized it is technically a new life |
|
|
what are cancer cells? |
they don't respond to the signals that regulate them and tell them to stop dividing. As a result the cells divide excessively (uncontrolled cell division) to produce a mass of abnormal cells, a tumor. If the cancer cells fail to attach to each other or they have lost the molecules that keep them together they can spread throughout the body and form secondary tumours |
|
|
tumors can either be B__________ or M___________ |
Benign or Malignant |
|
|
what is a malignant tumor? |
CANCER It can spread and invade other parts of the body. It is very fast growing. |
|
|
what is a benign tumor? |
NOT cancer it only grows in one place and it grows slowly even though they don't spread they can press on vital organs. |
|
|
what does DNA stand for |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
|
|
what are the different bases in DNA |
Adenine, Thymine Guanine, Cytosine |
|
|
what is the shape of DNA |
double helix |
|
|
what are the names of the components in a nucleotide |
phosphate deoxyribose sugar base |
|
|
stages of DNA replication... |
DNA unwinds and unzips Weak hydrogen bonds break between the bases Primer starts off the replication Free nucleotides from the pool pair up with their complimentary base pair DNA polymerase can only add complementary DNA to the 3' end of the DNA strand So the other side 5' end the complementarty DNA is added in chunks by the enzyme ligase hydrogen bonds form between the bases strong sugar phosphate bonds are made 2 new identical DNA strands are formed |
|
|
for DNA replication you need.... |
original DNA as a template Primers ATP A pool of nucleotides Enzymes- DNA polymerase and ligase |
|
|
why is it important for DNA to replicate properly |
to ensure each new cell receives a full set of chromosomes therefore no genetic information will be lost |
|
|
what is a mutation |
rare random changes to DNA sequences |
|
|
what are the different bases in RNA |
Guanine, Cytosine Adenine, Uricial |
|
|
what types of RNA is there |
mRNA... messenger RNA rRNA... ribosomal RNA tRNA... transfer RNA |
|
|
what is mRNA and what does it do |
Messenger RNA it carries the genetic code from the DNA in the nucleus to a robosome |
|
|
What is rRNA and what does it do |
Ribosomal RNA This along with proteins form the ribosome |
|
|
What is tRNA and what does it do |
Transfer RNA each tRNA carries a specific amino acid to a ribosome |
|
|
what is RNA made up of... |
phosphate ribose sugar base |
|
|
what are introns |
introns don't code for anything and get cut out in RNA splicing |
|
|
what are exons |
exons code for something and they get kept in RNA splicing they get expressed |
|
|
what is transcription |
the copying of DNA sequences to make a primary transcript |
|
|
what is translation |
the production of a polypeptide at a ribosome using information encoded in mRNA |
|
|
what are the steps in transcription and translation |
DNA double helix unzips and unwinds the weak hydrogen bonds break between bases causing DNA strands to seperate free RNA nucleotides (moving freely in the nucleus) find complementary pair on the DNA strand weak hydrogen bonds are formed between the new base pairings strong chemical bonds are formed between the new RNA nucleotides opposite the DNA. This allows a new strand to be formed. weak hydrogen bonds break between the strands allowing mRNA to break away in the DNA and copied RNA there are sections that don't code for anything called introns. And parts that do code for something called exons the introns are removed from the primary transcript through RNA splicing making the mature RNA the mRNA strand is ready to be transported out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm the mature RNA attaches to the ribosome tRNA with a complementary anticodon attaches to the mRNA codons are translated into amino acids one by one the codons are translated into amino acids one by one. All the amino acids join together to form a growing polypeptide chain. Strong peptide bonds form between amino acids |
|
|
what is post-translational modification |
changes made to polypeptides following translation |
|
|
what is a phenotype |
the outward visible appearance of a human |
|
|
differences between mRNA and tRNA |
tRNA is folded, mRNA is not tRNA has base pairing, mRNA hasn't mRNA is single stranded, tRNA is double stranded |
|
|
what is a single gene mutation |
alteration of a nucleotide sequence changes the base order within a gene and so alters the amino acid sequence of the protein coded for |
|
|
types of single gene mutations |
substitution insertation deletion |
|
|
explain substition mutations |
one nucleotide has been switched by another nucleotide. one of the bases are changed in the protein making a different type of amino acid |
|
|
what is missense mutation |
it codes for an amino acid but not the original and right one |
|
|
what is a nonsense mutation |
an amino acid codon is replaced with a premature STOP codon |
|
|
what is an insertion single gene mutation |
an additional nucleotide is added into a DNA sequence. This causes a frameshift as the whole sequence has been shifted making new amino acids |
|
|
what is a deletion single gene mutation |
a nucleotide is removed from a DNA sequence causing a frameshift. |
|
|
what is a frameshift |
when the whole sequence has been shifted affecting all amino acids and making new ones |
|
|
What are chromosome mutations? |
it involves the breakage of one or more chromosomes. The broken end of the chromosome is "sticky" so it can join to another broken end. |
|
|
what are 3 different examples of chromosome mutations |
deletion duplication translocation |
|
|
explain a deletion chromosome mutation |
in the chromosome some of the genes become detached and are lost completely |
|
|
explain a duplication chromosome mutation |
a section of a chromosome replicates itself so that a set of genes is repeated |
|
|
explain translocation |
part of a chromosome becomes attached to another |
|
|
what is a splice site mutation |
if one or more introns have been retained by modified mRNA this results in a protein that doesn't function properly |
|
|
what are some examples of diseases caused by mutations |
Sickle cell disease haemophilia PKU muscular dystrophy |
|
|
what is the human genome |
the total genetic information encoded into the base sequence of DNA |
|
|
what is bioinformatics |
use of computers and statistics in analysis of sequence data |
|
|
what is systematics |
study of the diversification of living organisms past and present compares the human genome to the genomes of other species |
|
|
what is pharmacogenetics |
personalised medicine based on an individuals genome |
|
|
in the future what will bioformatics allow us to predict |
how genes are regulated how the proteins will be synthesised how they will fold and function in the cell how they will interact with other molecules be they natural or synthetic |
|
|
what does PCR stand for |
Polymerase Chain Reaction |
|
|
for PCR you need |
primers free nucleotides the original DNA strand polymerase |
|
|
Steps for PCR |
original DNA strand DENATURE the DNA to separate DNA strands. This involves heating it to 94-96 degrees c next Anneal the DNA meaning primers are added to the 2 separated DNA strands the temperature is cooled to 65 degrees c to help the primers attach to the DNA The primers signal DNA polymerase. At 72 degrees c polymerase molecules attach to the annealed primers and extends them in a 5' to 3' directions. Called Extension. Two identical copies are created |
|
|
what does PCR do |
its a technique for the amplification of DNA in vitro |
|
|
what is phylogenetics |
study of evolutionary techniques relatedness of species |
|
|
what are DNA probes used for |
used to detect the presence of specific DNA base sequences in a sample of DNA- DNA microarr |
|
|
what is a DNA probe |
a short peice of DNA complementary to a target sequence of DNA |
|
|
what is fluorescent labelling |
method of making a fragment of DNA show up under ultraviolet light |
|
|
DNA probes can be used to..... |
to detect single gene mutations determining who a parent is solving crimes |
|
|
what is gel electrophoresis |
method for the separation of DNA fragments using an electric current in gel |
|
|
steps to DNA profiling |
sample containing DNA eg blood DNA isolated from sample and amplified using PCR DNA sample cut into fragments using enzymes array of DNA probes used to identify target DNA sequences; flurecent labels mark identified sequences gel elctrophoresis used to separate the target fragments profile created when UV light shone onto the pattern of separted fragments |
|
|
what are each step in metabolic pathways controlled by? |
a specific enzyme |
|
|
what are anabolic pathways |
build up reactions. lead to the (Bio)synthesis of more complex molecules from simpler ones (building blocks), it requires energy eg. protein synthesis |
|
|
what are catabolic reactions |
breakdown reactions lead to the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, usually with the release of energy eg. aerobic respiration |
|
|
how may a metabolic block occur |
a metabolic block may occur due to a gene mutation resulting in the absence of a functional enzyme |
|
|
metabolic pathways are controlled by |
the presence or absence of particular enzymes in the pathway the regulation of the rate of key enzymes within the pathway |
|
|
what are enzymes |
biological catalysts that speed up the rates of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reactions to proceed Enzymes are substrate specific |
|
|
the energy required to initiate a reaction is called its......... |
......... activation energy |
|
|
what is induced fit |
a change of shape to the enzyme's active site brought about because of the presence of a substrate |
|
|
what do enzymes do to activation energy |
lower it |
|
|
products of enzyme reactions have a HIGH/LOW affinity for the active site of the enzyme |
low |
|
|
increasing a substrate concentration will cause the rate of reaction to INCREASE/DECREASE as more active sites will be occupied |
increase |
|
|
a group of enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be called...... |
a multi enzyme complex |
|
|
what is non competitive inhibition |
enzyme inhibition by a substance that permanently alters the active site of the enzyme |
|
|
non competitive inhibitors REDUCES/INCREASES the rate of reaction whatever the substance concentration
|
reduces |
|
|
what is an inhibitor |
a substance that reduces the rate of an enzyme reaction |
|
|
what are competitive inhibitors |
slowing of reaction rate due to the presence of a substance resembling the substance |
|
|
what is feedback inhibition |
a method of metabolic control in which the end product binds to an enzyme that catalyses a reaction early in the pathway |
|
|
what are signal molecules |
molecule that brings about changes in a cell's metabolism |
|
|
what does ATP stand for |
Adenosine Tri Phosphate |
|
|
what is ATP |
a high energy molecule that is generated through respiration |
|
|
what is cellular respiration |
the release of energy from food molecules in cells |
|
|
what is phosphorylation |
when a phosphate group eg.Pi is added to a molecule |
|
|
where does Glycolisis occur |
in the cytoplasm |
|
|
where does the citric acid cycle occur |
in the central matrix of the mitochondria |
|
|
where does the electron transport chain take place |
in the crista of the mitochondria |
|
|
what are NAD and FAD |
coenzymes |
|
|
glucose is broken down to WHAT in the cytoplasm of cells during glycolosis |
pyruvate |
|
|
what is pyruvate |
the end product of glycolosis |
|
|
what are the stages to respiration |
glycolosis citric acid cycle electron transport chain |
|
|
Intermediates of glycolysis are Ph................. by ATP in an energy investment phase |
phosphorylated |
|
|
what is Phosphofructokinase (PFK) |
an enzyme that catalyses the irreversible transfer of a phosphate from ATP to fructose-6-phosphate in glycolosis |
|
|
when ATP and citrate levels are high and the cell doesn't need metabolic energy production to occur what happens to the PFK? |
it gets inhibited |
|
|
what does pyruvate have to be in the presence of for it to be broken down |
oxygen |
|
|
before reaching the citric acid cycle what does the acetyl group combine with and what does it form? |
it combines with coenzyme A to be transferred to the citric acid cycle as acetyl coenzyme A |
|
|
what is coenzyme A |
a substance that carries acetyl groups into the citric acid cycle |
|
|
what is a acetyl group |
it is produced by the breakdown of pyruvate and it joins with oxaloacetate in the citric acid cycle |
|
|
what does acetyl coenzyme A combine with to form citrate |
oxaloacetate |
|
|
what is released from the citric acid cycle |
carbon dioxide |
|
|
what is dehydrogenase |
enzymes that remove hydrogen from their substrates |
|
|
what do NADH and FADH2 release into the electron transport chain |
hydrogen and high energy electrons |
|
|
in the electron transport chain what are high energy electrons used for |
they are used to pump hydrogen ions across a mitochondrial membrane |
|
|
what stage of respiration is the most ATP produced? |
the electron transport chain |
|
|
in respiration what is the final electron acceptor |
oxygen |
|
|
in the absence of oxygen, pyruvate will follow what pathway? |
a fementation pathway |
|
|
if glucose isn't available for respiration the body can use other molecules including...... |
other sugar molecules eg fructose starch glycogen fats proteins |
|
|
why is feedback inhibition important during respiration |
it prevents the build up of an intermediate which is not needed ATP is only produced when required resources are conserved |
|
|
what is creatine phosphate |
a molecule that serves as a source of phosphate and energy in muscle cells |
|
|
what is lactic acid |
its produced by the fermentation of pyruvate in muscle cells |
|
|
what is muscle fatigue |
its a painfull condition caused by the accumulation of lactic acid in muscles |
|
|
what is myoglobin |
a protein in muscle tissue that can bind with oxygen |
|
|
what is a oxygen debt |
it builds up during fementation in muscle cells |
|
|
what is skeletal muscle |
muscle attached to the skeleton that brings about locomotion |
|
|
two types of skeletal muscle tissue fibres |
fast twitch and slow twitch |
|
|
what are slow twitch fibres good for |
endurance activities like long distance running, cycling, cross country skiing. |
|
|
what are fast twitch fibres good for |
activities like sprinting or weightlifting |
|
|
do slow twitch muscle fibres have many mitochondria or not many |
many mitochondria |
|
|
do slow twitch muscle fibres have a small or large blood supply |
a large blood supply |
|
|
how do slow twitch muscle fibres generate ATP |
aerobic respiration |
|
|
do fast twitch muscle fibres have a lot or a few mitochondria |
only a few |
|
|
do fast twitch muscle fibres have a larger or lower blood supply than slow twitch |
lower blood supply |
|
|
howdo fast twitch muscle fibres generate ATP |
through glycolysis |
|
|
what are the two systems in the nervous system |
the CNS and the PNS |
|
|
what does CNS stand for |
Central Nervous System |
|
|
what does PNS stand for |
Peripheral Nervous System |
|
|
what does the CNS include |
the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
what does the PNS system include |
the somatic system and autonomic system |
|
|
what is the somatic nervous system |
we have to think about doing it consious thoughts physical action leg muscles moving to run for a bus hand moving to scratch nose choosing a film on netflix knee jerk reaction from hammer hit |
|
|
what is the autonomic system |
happening without you thinking about it your not really aware of it heart rate speed up due to activity peristalsis in stomach to digest food enzymes realeased in stomach hands sweating due to stress |
|
|
is the somatic system mainly voluntary or involuntary |
mainly voluntary |
|
|
is the autonomic system mainly voluntary or involuntary |
involuntary |
|
|
examples of external receptors |
skin eye retina ear cochlea |
|
|
examples of internal receptors |
CO2 receptors thermoreceptors |
|
|
what does antagonist mean |
they do the opposite of each other |
|
|
what systems in the nervous system are antagonist |
the sympathetic system and parasympatheic system |
|
|
what systems are part of the autonomic system |
the sympathetic system and parasympatheic system |
|
|
what is the phrase used to describe the sypathetic system |
fight or flight |
|
|
what is the phrase used to describe the parasympathetic system |
rest and digest |
|
|
what is the action on heart like when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
heart rate increases |
|
|
what is the action on heart like when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
heart rate decreases |
|
|
what is the action on breathing rate like when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
breathing rate increaes |
|
|
what is the action on breathing rate like when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
breathing rate decreases |
|
|
what is the bronchiole wall like when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
they are relaxed and larger |
|
|
what is the bronchiole walllike when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
they are constricted and smaller |
|
|
what is peristalsislike when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
peristalsis decreases |
|
|
what is peristalsislike when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
peristalsis increases |
|
|
what is enzyme secretion ratelike when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
decreased rate |
|
|
what is enzyme secretion ratelike when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
increased rate |
|
|
what is the affect on the adrenal glandlike when the sympathetic nerves kick in |
increased affect |
|
|
what is the affect on the adrenal glandlike when the parasympathetic nerves kick in |
there is no effect |
|
|
when the sympathetic system kicks in where is blood diverted to |
from the gut and skin to the heart |
|
|
when the parasympathetic system kicks in where is blood diverted to |
from the heart to the gut and skin again |
|
|
what are the three sections of the brain |
central core limbic system cerebral cortex |
|
|
what does the central core contain |
medulla and cerebellum |
|
|
what does the medulla controll |
breathing heart rate sleep and arousal |
|
|
what does the cerebellum controll |
balance muscular coordination |
|
|
what is the limbic system responsible for |
Long Term Memory emotion behaviour motivation |
|
|
what gland does the limbic system contain |
the pituitary gland |
|
|
what is the cerebral cortex |
the center of conscious thought and memories |
|
|
what are the 3 key functions of the cerebral cortex |
receives sensory information coordinates voluntary movement making decisions based on experience |
|
|
what are the two halves of the cerebral cortex joined by |
the corpus callosum |
|
|
what does the corpus callosum allow the brain to do |
allows the brain to function together, as both systems are in communication together |
|
|
what is the syndrome called when you either have your corpus callosum cut or you are born without one |
split brain syndrome |
|
|
what serious condidtion can result in having your corpus callosum cut |
epilepsy |
|
|
what are the localised regions that the cerebral cortex is divided into |
sensory motor association |

