![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a hernia?
|
Any structure passing through another so as to end up in the wrong place.
Protrusion of a viscus through an abnormal opening, so as to end up in the wrong place. Protrusion of tissue or viscus through the muscle tissue or membrane in which it is normally maintained |
|
|
Complications hernias?
|
Incarceration - formation of adhesions results in the contents of the hernia being fixed in place
Obstructed - bowel contents cannot pass through them Strangulated - ischaemia occurs because the blood supply has been compromised |
|
|
What is an inguinal hernia?
|
2 types: direct and indirect
Direct - hernia pushes through posterior wall of inguinal canal Indirect - hernia psses hrough the internal inguinal ring and possibly out the ext ring |
|
|
Cause of indirect hernia?
|
Failure of the embryological connection between peritoneum + tunica vaginalis to close = patent processus vaginalis
This passage is needed for the decent of the testis in men. Therefore very uncommon in females - consider testicular feminisation. If the processus vaginalis contains peritoneal fluid only = communicating hydrocele |
|
|
Rx indirect hernia?
|
Surgical closure processus vaginalis with high ligation
|
|
|
Causes direct inguinal hernia?
|
Chronic increase abdo pressure, e.g:
Chronic cough Constipation Urinary obstruction Weight lifting Ascites Abdo surgery |
|
|
Inguinal anatomy
|
Inguinal ligament - runs pubic tubercle to ant sup iliac spine
Internal inguinal ring - mid point inguinal ligament or 1.5cm above femoral pulse External ring - just above and medial to the pubic tubercle |
|
|
Where does the ing lid run?
|
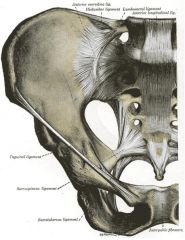
|
|
|
What makes up the inguinal canal?
|
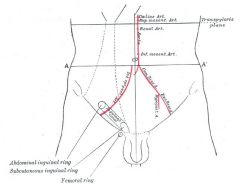
Floor = inguinal ligament
Roof = fibres transversalis, int oblique + conjoint tendon Front = Ext oblique aponeurosis + int oblique Back = lateral;transversalis fascia medial;conjoint tendon |
|
|
Examination inguinal hernia?
|
Ask patient to reduce lump themselves.
Ask patient cough - inguinal hernias appear infero-medial to the ext ring Differentiate direct from indirect - occlude internal ring after reduction then get patient to cough - if it reappears = direct hernia |
|
|
Where is a femoral hernia?
|
Inferior and laterial to pubic tubercle
Remember - inguinal are superior and medial |
|
|
Boundaries femoral canal?
|
Ant + medial = inguinal ligament
Lateral = femoral vein Posteriorly pectineal ligament and pectineus muscle |

