![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Clinical HHT
|
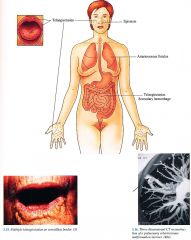
|
|
|
Synonym
|
Osler-Weber-Rendu
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
Autosomal dominant HHT1: endoglin gene on 9q33 34 Autosomal dominant HHT2: ALK1 gene on chromosome 12
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
DNA linkage analysis or mutation detection
|
|
|
Incidence
|
1 2:100,000; M=F; all races, most common in whites
|
|
|
Age at Presentation
|
Early childhood to young adulthood with epistaxis in 50% of patients Cutaneous, gastrointestinal telangiectasias usually begins in the third to fourth decade
|
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
HHTI: Mutation in endoglin gene on chromosome 9q33 34, a transforming growth factor (TGF) p binding protein on endothelial cells essential for angiogenesis HHT2: Mutation on chromosome 12 encoding for activin receptor like kinase I (ALKI) expressed on endothelial cells
|
|
|
Clinical
|
Skin
Telangiectasias on face, palms, soles, subungual region Mucous Membranes Telangiectasias on vermillion, oral and nasopharyngeal mucosa, conjunctiva Ear Nose Throat Epistaxis recurrent in more than 80% of patients Gastrointestinal Telangiectasias with secondary hemorrhage; hepatic AVMs Pulmonary Arteriovenous fistulas complicated by hemorrhage, cerebral abscesses |
|
|
D/Dx
|
CREST syndrome Generalized essential telangiectasia Ataxia telangiectasia (p. Il 2) Fabry disease (p. 306)
|
|
|
Lab
|
Chest x ray screen, follow up MRI if positive
Complete blood count (CBC) Guaiac stool screen Endoscopy if symptomatic |
|
|
Management
|
Referral to otolaryngologist cautery, packing, estrogen, septal dermoplasty for recurrent epistaxis; transfusions, iron supplementation
Referral to gastroenterologist if symptomatic Referral to thoracic surgeon excision, embolization of A V fistula Referral to dermatologist pulsed dye laser for telangiectasias |
|
|
Prognosis
|
HHT1 families have increased incidence of pulmonary A V fistulaes
HHT2 families with increase in hepatic AVMs |

