![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
133 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
increase in bacterial infections, is seen in which cell
|
neutrophil (50-70%)
|
|
|
|
increase in viral infections, is seen in which cell
|
lymphocyte (20-40%)
|
|
|
|
increase in TB, syphilis, malignancies, is seen in which cell
|
monocyte (3-10%)
|
|
|
|
increase in allergies, parasites & CML, is seen in which cell
|
eosinphils (0-3%)
|
|
|
|
increase in immediate hypersensitivity, CML, is seen in which cell
|
basophil (0-2%)
CML - baso & philly chrom + |
|
|
|
which cell does the following functions: O2 transport to tissue + CO2, removal from tissue & cell nutrition
|
red cell
|
|
|
|
which two cell does the following functions: phagocytic response to bacteria
|
neutrophil & monocyte
|
|
|
|
which cell does the following functions: humoral & cell mediate immunity
|
lymphocyte
|
|
|
|
which cell does the following functions: inflammatory response mediator
|
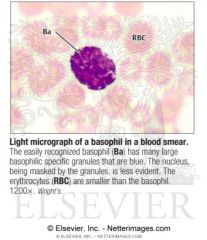
basophil
|
|
|
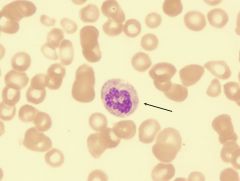
when eva WBC morphology, what morphology is associated with hypersegmented neutrophil
|
pernicious anemia
|
|
|
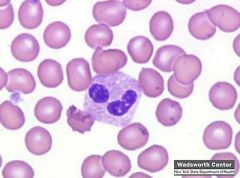
which WBC morphology is associated with hypo segmented neutrophils
|
pelger huet anomlay
pseduo pelger huet (AML, AIDS) |
|
|
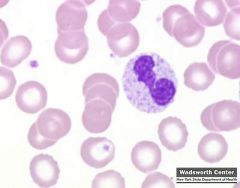
which WBC morphology is associated with toxic granulation & vacuoles
|
bacterial infections
burns chemotherapy |
|
|
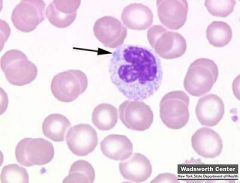
which WBC morphology is associated with dohle bodies (RNA)
|
bacterial infections
burns May-Hegglin |
|
|
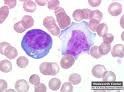
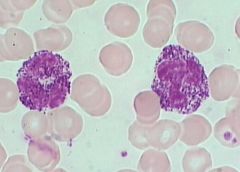
which WBC morph is associated with atypical lymphs (increase size & basophilia - RIGHT photo)
|
IM (epstein bar virus)
other viral infections |
|
|
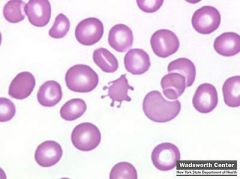
what abnormal RBC shape am I & where am i seen in
|
acanthocyte seen in:
abetalipoproteinemia (aka Bassen Kornzweig synd) severe liver disease |
this formation happens is cause by an alternative of lipids compstx & fluidity of the CM
|
|
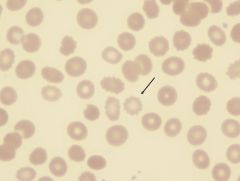
what abnormal RBC shape am I & where am i seen in
|
echinocyte "burr cell" see in:
uremia - back up of urea ass w/ kidney failure artifact (alkaline glass effect) ass w/ malnutritx |
uniform shapre
greek: urchin "created RBC" cause HYPEROSMOTIC solutx |
|
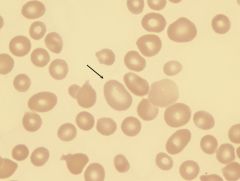
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
macro-ovalocyte seen in:
megaloblasic anemia |
aka Megamacrocyte
inc cabot ring (figure 8) |
|
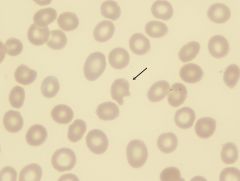
what abnormal RBC shape am I & where am i seen in
|
helmet/horn (keratocyte) seen in hemolytic process
|
|
|
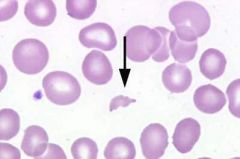
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
schistocyte (RBC fragments) seen in:
DIC and hemolytic process aka bite cells - membrane damages cause by encountered during passage through the vessels |
|
|
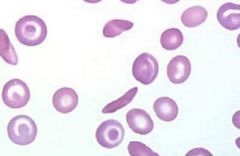
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
sickle cell (drepanocyte)/crescent shape seen in:
HBG SS |
|
|
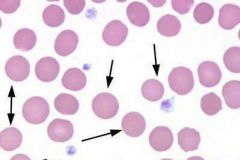
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
hereditary spherocytosis
(increase MCHC) ABO/HDN and other hemolytic process |
|
|
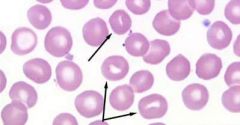
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
stomatocyte (mouth cell) seen in:
hereditary stomatocytosis (>50%) liver disease mouth part is cause by lost of indentation of one side |
|
|
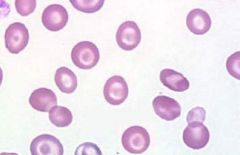
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
target cells (codocyte) seen in:
liver disease HGB C (bar shaped) other hemoglobinopathies |
|
|
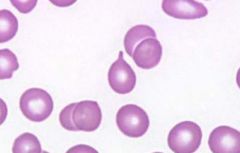
what abnormal RBC shape am I and where am i seen in
|
tear drop cell (dacryocyte) "pear shaped w/ tapered end/tennis racket seen in
extramedullary hematopoiesis (myelofibrosis, myeloproliferative disorders, p. anemia, thalassemia ) |
|
|
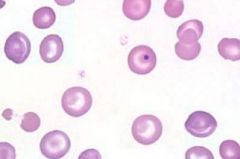
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
howell jolly body indications:
disturbed erythropoiesis hemolytic anemia megaloblastic anemia post splenectomy B12 defncy |
|
|
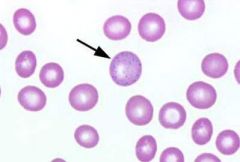
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
basophillic stippling indicates:
thalassemia lead poisoning |
|
|
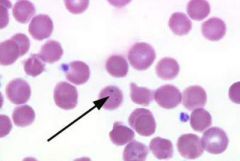
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
pappenheimer bodies/siderotic granules (siderocyte) indicates:
sideroblastic anemia hemoglobinopathies (severe anemia + thalassemia) |
|
|
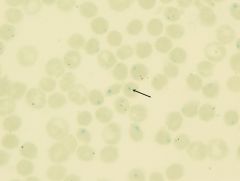
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
heniz bodies indicates:
G6PD defncy thalassemia unstable HGB |
|
|
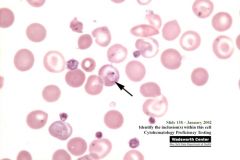
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
cabot ring indicates:
megaloblastic anemia (inc macrocytes) |
|
|
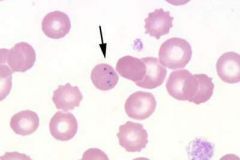
what RBC inclusion am I and what does this indicate
|
parasites indicates:
PA infections (pix shown is babesia) |
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
howell jolly body |
wright and composed of DNA
note: baso stippling has RNA |
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
basophilic stippling |
wright/new methylene blue (super viral stain) and composed of RNA
note: howell jolly body has DNA |
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
pappenheimer bodies/siderocytes |
wright & prussian blue and composed of iron
|
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
heniz body |
super vital stain (ex: brillian cresyl blue/new methylene blue) composed of denature ppt HGB
NOT seen with wright stain |
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
cabot ring |
wright composed of remnants of mitotic spindle
|
|
|
|
if we are looking for this red cell inclusion, which stain would be used & what would the stain show
parasites |
wright and composed of ex: malaria, babesia and trypanosomes
|
|
|
|
which PA is infected by a mosquito
|
malaria
|
|
|
|
which PA is infected by a ticks
|
babesiosis
|
|
|
|
which PA is infected by a fleas
|
trypansomes
|
|
|
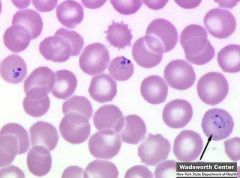
schuffer's granules are seen in which PA
|
Plasmodium vivax
these granules appear as orange to pink colored stippling throughout the red blood cell. They may not be visible when normal staining times are used. To detect these granules, the smears should be allowed to stain for three hours |
|
|
|
what would be the lab results for cold agglutinin disease (CAD) and how would you rerun the sample
|
increase MCV
increase MCHC decrease RBC count warm sample and rerun |
|
|
|
babesia is caused by
|
B. microti
tick: Ixodes dammini = tick fever |
|
|
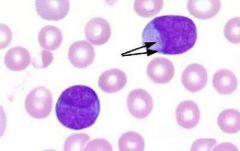
what RBC inclusion am I and where am i see
|
Auer rods are elongated, bluish-red rods composed of fused lysosomal granules seen in:
the cytoplasm of myeloblasts promyelocytes monoblasts and in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia |
|
|
|
what structural mutations is for HGB B
|
Valine for Glutamic Acid (6th postx, beta chain)
|
|
|
|
what structural mutations is for HGB C
|
Lysin for Glutamic Acid (6th postx, beta chain)
|
|
|
|
for HGB D, who does it mostly effect and where does the HGB migrate to
|
east indian people
migrates with HGB S at 8.6 |
|
|
|
for HGB E, who does it mostly effect and where does the HGB migrate to
|
southeast asian people
migrates with HGB C and A2 at 8.6 (hypochromic, microcytic) A2-C-E |
|
|
|
name 3 disease that has problems with heme
|
Fe defncy
Sideroblastic Chronic Dz/Inflamtx |
|
|
|
name 2 problem with globin conditions
|
Thlassemia
HGB E |
|
|
|
name 3 antibody destruction conditions
|
HDN
Transfusion Rtx Autoimmune hemolytic anemia |
|
|
|
name 3 RBC membrane defect conditions
|
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
Hereditary eilliptocytosis (HE) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH): is a rare disease in which red blood cells break down earlier than normal. Persons with this disease have blood cells that are missing a gene called PIG-A. This gene allows a substance called glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) to help certain proteins stick to cells. |
|
|
|
name 2 emz defncy conditions
|
G6PD
Pyruvate kinase (PK) |
|
|
|
name 2 conditions that indicates decrease in blood production and loss
|
Aplastic anemia
Acute blood loss |
|
|
|
name some hemoglobinopathies condtx
|
HGB S, C, etc
|
|
|
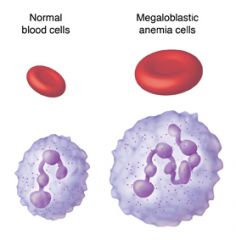
name 2 megaoblastic maturation condtx
|
B12 defncy
Folate defncy |
|
|
|
name 1 non-megaloblastic maturation condtion
|
liver disease
|
|
|
|
name two problems when MCV be microcytic (low) in HGB/HCT
|
problem with heme
problem with globin |
|
|
|
name two problems when MCV be macrocytic (high) in HGB/HCT
|
megaloblastic maturation & nonmegaloblastic maturation
|
|
|
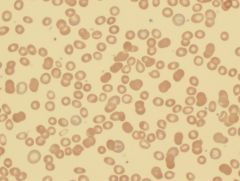
what is the condition that has the following lab results:
decrease Fe decrease Saturation increase TIBC |
iron defncy
|
|
|
|
what is the condition that has the following lab results:
decrease in Fe decrease in TIBC |
chronic disease/inflamtx
note: decrease Fe and decrease Saturation INCREASE TIBC = iron defncy |
|
|
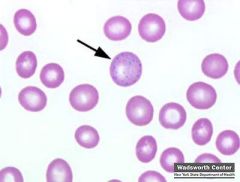
what is the condition that has the following lab results:
baso stippling increase blood lead level increase FEP |
lead poisoning
|
|
|
|
what is the condition that has the following lab results:
Fe normal TIBC normal increase A2 increase F |
thalassemia trait
|
|
|
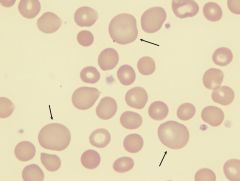
what is the condition that has the following lab results:
decrease B12 decrease Retics pancytopenia oval macrocytes hypersegemented polys howell jolly bodies (HJ) |
B12 defncy
|
|
|
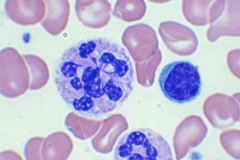
what is the conditions with the following lab results:
Anti-IF + (intrinsic factor) increase MMA (methylmanoic acid) increase homocysteine Normal Schilling Test with IF |
Pernicious anemia
is a chronic illness caused by impaired absorption of vitamin B-12 because of a lack of intrinsic factor (IF) in gastric secretions. |
|
|
|
B12 has a coemz that uses this conversion _______ to _______
|
methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl
|
|
|
|
what is the condition with the following lab results:
decrease serum/erythrocyte folate levels oval macrocytes Anti-IF -- decrease Retics hypersegmented polys increase homocysteine HJ bodies |
folate defncy
|
|
|
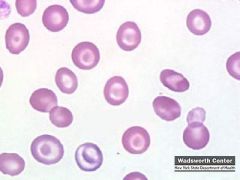
what is the condition with the following lab results
increase liver emz target cells round macrocytes |
liver dz/alki
|
|
|
|
what is the condition with the following lab results:
Donath landsteiner Ab |

PCH
AB mediated: increase in bili decrease haptoglobin DAT + |
|
|
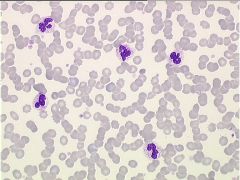
what is the condition with the following lab results:
IgM Ab Cold Agglutinin Titer + |
Cold agglutinin disease, aggregates disappear after the sample is warmed at 37°C
|
|
|
|
what is the condition with the following lab results:
Donath landsteiner Ab |
PCH
AB mediated: increase in bili decrease haptoglobin DAT + |
|
|
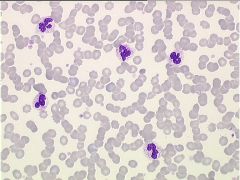
what is the condition with the following lab results:
IgM Ab Cold Agglutinin Titer + |
Cold agglutinin disease, aggregates disappear after the sample is warmed at 37°C
|
|
|
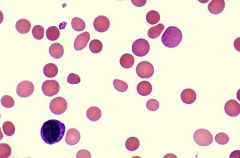
what is the condition ass with the following lab results
|
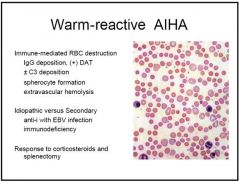
IgG Ab
AB mediated: increase bili decrease haptogloblin DAT + |
|
|
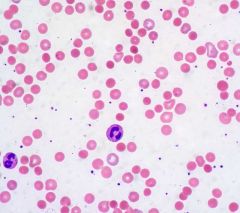
what is the condtx ass with the following lab results:
increase OSMO spherocytes increase MCHC |
hereditary spherocytosis
hallmark: microspherocyte, loss of membrane surface, abn of and intact spleen w/ an intrinsic membrane protein defect = abn RBC morph = cytoskeleton instability |
|
|
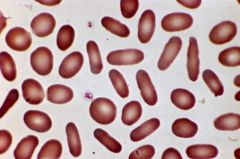
what is the condtx ass with the following lab results:
elliptocytes >15 to 100 % |
hereditary elliptocytosis
|
|
|
|
what is the condition ass with the following lab results:
Ham test + Sucrose hemolysis + CD 55 -- CD 59 -- |
PNH
|
|
|
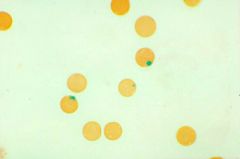
what is the condition ass with the following lab results:
decrease G6PD heniz bodies |
G6PD defncy
|
|
|
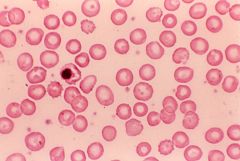
what is the condtx ass w/ the following lab results:
decrease PK NO heniz bodies |
pyruvate kinase (PK) defncy
|
|
|
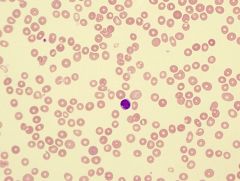
what is the condtx ass w/ the following lab results:
dry tape bone marrow hypocellular BM decrease retics pancytopenia |
aplastic anemia
is a syndrome of bone marrow failure characterized by peripheral pancytopenia and marrow hypoplasia, and mild macrocytosis is observed in association with stress erythropoiesis and an elevated fetal hemoglobin levels. |
|
|
|
what is the condtx ass w/ the following lab results:
normal BM increase retics |
acute blood loss
|
|
|
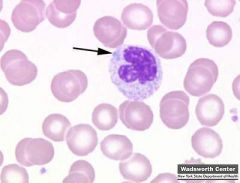
what is this
|
dohle bodies: blue cytoplasmic inclusion that rep remnants of rough endoplasmic reticulum from earlier maturational stages
ass w/ "left shifts" and conjtx w/ toxic granules |
|
|
|
name something that PK defncy (pyruvate kinase) will do that will cause it to become hemolytic anemia
|
PK defncy will rapidly become def in ATP and can undergo hemolysis that then results in hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
|
Osmo frag measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
RBC surface: volume ration
increase in Hereditary Spherocytosis decrease in Thalassemia decrease in Target cells |
|
|
|
Ham's/Acid's hemolysis measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
complement mediated lysis
PNH (definitive) |
|
|
|
Sucrose hemolysis (sugar water) measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
effect on Complement (activated by sucrose) on RBC
PNH (screen only) Ham/Acid is definitive |
|
|
|
Heniz body prep (supervital stain) measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
effect of Oxidizing agent on HGB
G6PD defncy, unstable HGB, HGB H formation triggered by Oxidants (anti-malaria drugs, fava beans and sulphur drugs) |
|
|
|
Sickle cell screen measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
reduce Solubility of deoxygenate
HGB S HGBS w/ Na Dithionate (reducing agent) |
|
|
|
Kleihauer Berke Acid Elution measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
resistance of Fetal HGB to Acid Elution
fetal maternal hemorrhage, hereditary persistence of fetal HGB |
|
|
|
HGB Electrophoresis measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
migration of various HGB
suspect HGB-pathies |
|
|
|
Cold Agglutinin screen measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
presence of Cold AutoAB
cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia IgM Ab, Anti-I specificity |
|
|
|
Donath Landsteiner Test measures what and is a test that indicates this
|
presence of biphasic DL antibody
paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria IgG Ab, Anti-P specificity |
|
|
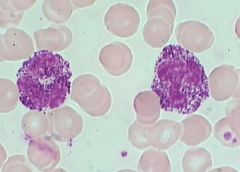
which WBC disease has the following characteristics:
large azurophillic granules |
Alder Reilly
increase in Mucopolysaccharides (Hunger, Hurler) |
|
|
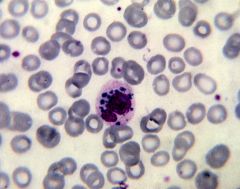
which WBC disease has the following characteristics:
large lysosomes (fusion of primary granules) |
Chediak Higashi
albinism (lack of pigment) increase susceptibility to infection abn gene fail to release granules for bacterial infection - inherit auto recess |
|
|
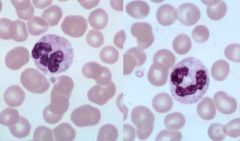
which WBC disease has the following characteristics:
Large platelets decrease # Dohle bodies in segs Mono and Lymphs |
May Hegglin
does not affect leukocyte functions |
|
|
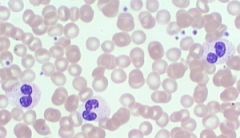
which WBC disease has the following characteristics:
Hyposegmented polys |
Pelger Huet
normal function |
|
|
|
which condtx characterizes the following lab results:
LAP increase Toxic granulation increase Dohle bodies - present Philadelphia chromosome - not present |
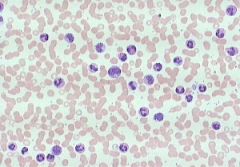
Leukemoid
Leukemoid reactions are characterized by blasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes, and metamyelocytes in the peripheral blood. Leukemoid reactions may be secondary to benign or malignant conditions. The WBC count is often in a range of 50.0-100.0 x10 9/L. |
|
|
|
which condtx characterizes the following lab results:
LAP decrease Toxic granulation decrease Dohle bodies - not present Philadelphia chromosome - present |
CML
p. chrom is due to abn chrom creating a new gene. bld cell swapping = creates extra short chrom 22: PA chrom/extra long chrom 9 |
|
|
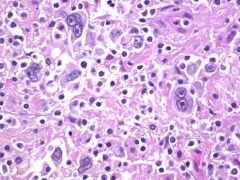
which of the following Lymphoma is characterized with the following lab results:
Reed Sternberg cell: present Incidence: bi-modal Spread: stepwise (predictable) |
Hodgkin lymphoma
|
|
|
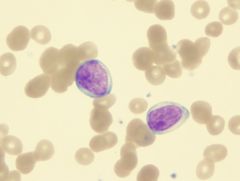
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M0), which PO cell are seen
|
M0: myeloblast w/out differentiation
|
|
|
|
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M0), which PO cell are seen
|
M0: myeloblast w/out differentiation
|
|
|
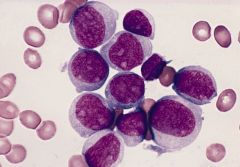
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M1), which PO cell are seen
|
M1: myeloblast w/ minimal maturatx
|
|
|
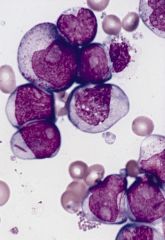
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M2), which PO cell are seen
|
M2: myeloblast w/ maturatx
Bone marrow smear from a patient with acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation showing several blasts with prominent nucleoli, a promyelocyte, and a myelocyte. Two of the blasts contain prominent Auer rods. (Wright-Giemsa stain) |
|
|
|
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias, which PO cell are seen
|
M2: myeloblast w/ maturatx
Bone marrow smear from a patient with acute myeloblastic leukemia with maturation showing several blasts with prominent nucleoli, a promyelocyte, and a myelocyte. Two of the blasts contain prominent Auer rods. (Wright-Giemsa stain) |
|
|
|
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M1), which PO cell are seen
|
M1: myeloblast w/ minimal maturatx
|
|
|
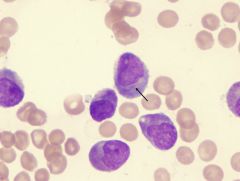
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M3), which PO cell are seen
|
M3: Promyelocyte (APL)
|
|
|
|
which Acute myeloid leukemia has the following PO cell seen
|
M4: myeloblast and monoblast (AMMOL)
|
|
|
|
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M3), which PO cell are seen
|
M3: Promyelocyte (APL)
|
|
|
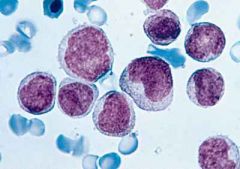
in Acute Myeloid Leukemias (M4), which PO cell are seen
|
M4: myeloblast and monoblast
|
|
|
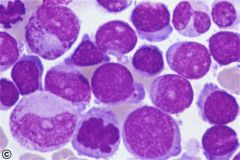
which Acute myeloid leukemia (M6) has the following PO cell seen
|
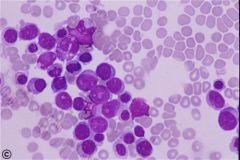
M6: Erythrocyte series
|
|
|
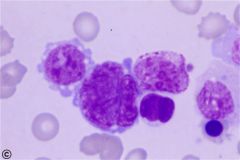
which Acute myeloid leukemia (M7) has the following PO cell seen
|
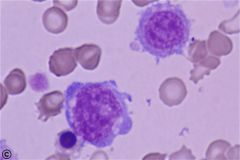
M7: Megakarocyte
|
|
|
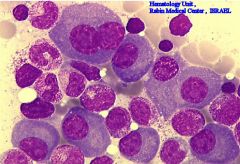
which of the condition has the following characteristics
Bone involvement: yes Serum viscosity +/- Immunoglobin: IgG (Bence-Jones) |
Multiple myeloma
|
|
|
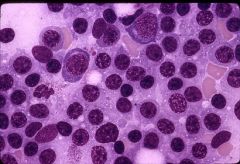
which of the condition has the following characteristics
Bone involvement: no (organ) Serum viscosity: increase Immunoglobin: IgM (heavy chain) |
Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia demonstrating excess mature lymphocytes, lymphoplasmacytic cells and plasma cells
|
|
|
|
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
glycogen
Erythroleukemia ALL ("chunky" +) |
|
|
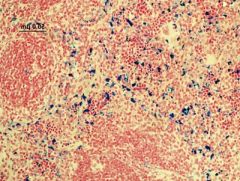
Prussian blue a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Iron
Sideroblastic anemia Prussian blue stain for iron Nuclei, hemofuschin—bright red Hemosiderin(iron)—blue Background—pink |
|
|
|
LAP a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests (3)
|
Alkaline phosphatase
increase Leukemoid Reaction P. vera decrease CML |
|
|
|
Peroxidase/Sudan Black a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Myeloperoxidase/lipid
AML M1 - M4 + AML M5 -- ALL -- |
|
|
|
Specific Esterase a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Esterase in Granulocyte precursors
AML M1 - M4 + AML M5 -- |
|
|
|
Non Specific Esterase a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Non Specific Esterase in Monocyte Precursors
|
|
|
|
TRAP a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
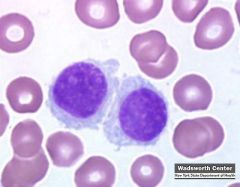
Tartrate Resistant Acid Phosphatase
Hairy cell leukemia Hairy cells are characterized by their fine, irregular pseudopods and immature nuclear features. Bone marrow aspiration is often unsuccessful because of complete infiltration by hairy cells, resulting in a dispersed spongy web of cells in an increased meshwork of reticulin fiber. |
|
|
|
Abnormal NBT a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Abnormal granulocyte function
Chronic Granulomatous Disease |
|
|
|
Auer Rods a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Coalition of 1 degree granules
AML + ALL -- |
|
|
|
CD 13, CD 33 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Myleoblasts
AML + ALL -- |
|
|
|
CD 2, 3, 5, 7 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests (3)
|
T-lineage
T-ALL + B-ALL -- AML -- |
|
|
|
CD 10, 19, 22 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
B-lineage
B-ALL + T-ALL -- AML -- |
|
|
|
t (15, 17) a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Chromosome Translocation inv Retinoic Acid Receptor Gene
Acute Progranulocytic Leukemia (AML M3) Treat w/ ATRA (ALL Trans Retinoic Acid) |
|
|
|
CD 34 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Stem cells
Stem cells for transplant |
|
|
|
CD 42, 61 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Megakaryocytes
AML M7 |
|
|
|
CD 116, 14 a stain/cell marker indicates this ______ and is important for the following tests
|
Monoblasts
AML M4 and AML M5 |
|
|
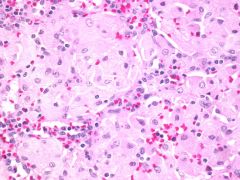
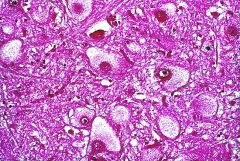
which of the lysosome/lipid storage disease is shown
|
Gaucher
is a genetic disease in which a fatty substance (lipid) accumulates in cells and certain organs. Gaucher's disease is the most common of the lysosomal storage diseases. It is caused by a hereditary deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase (also known as acid β-glucosidase). The enzyme acts on a fatty substance glucocerebroside (also known as glucosylceramide). When the enzyme is defective, the substance accumulates, particularly in cells of the mononuclear cell lineage. Fatty material can collect in the spleen, liver, kidneys, lungs, brain and bone marrow. |
|
|
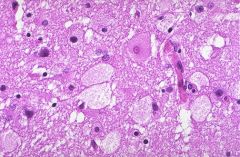
which of the following lysosome/lipid storage disease is shown
|
Tay Sach
|
|
|
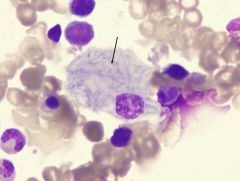
Gaucher disease has which accumulated lipid _____ with what lab results are usually seen
|
Glucocerebroside
Lab ID: macrophage macrophage cytoplasm looks like an unfolded crumpled piece of paper |
|
|
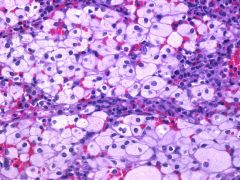
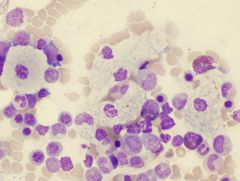
Niemann-Pick disease has which accumulated lipid _____ with what lab results are usually seen
|
Sphingomylein
Lab ID: macrophage macrophage has globular cytoplasm - sea blue histiocytes Neimann-Pick is a disease in which excess material is stored inside cells (metabolic storage disease). These cells are referred to as "foam cells" because of their foamy or soap-suds appearance. |
|
|
|
Tay-Sach disease has which accumulated lipid _____ with what lab results are usually seen
|
Spingo-lipids (GM2 ganglioside: nerves cells in brain leading to premature death cells)
Lab ID: vacuolated lymphocytes, foam cells (BM) diagnosed by increase Startle Reflex, Cherry Red Spot in Macuala of Eye & CNS studies |
|
|
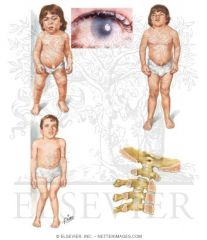
Huerler, Hunter disease has which accumulated lipid _____ with what lab results are usually seen
|
Mucopolysaccharides (bd of by products: dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate
Lab ID: large granules in lymphocytes (Alder Reilly Bodies) Histiocytes and Lymphocytes (BM) |
|

