![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
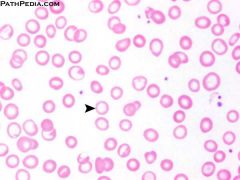
Which type of anemia?
|
Iron deficiency; microcytic, hypochromic anemia
|
|
|
Causes of iron deficiency anemia
|
Chronic bleeds, malnutrition/absorption disorders, increased demand (eg. pregnant)
|
|
|
Iron deficiency findings
|
Low iron, low ferritin, high TIBC
|
|
|
Iron deficiency anemia - which syndrome association?
|
Plummer-Wilson (esophageal webs, atrophic glossitis)
|
|
|
Alpha-thalassemia etiology
|
Alpha-globin gene mutation --> decreased alpha-globin synthesis; 3 and 4 gene deletions are severe
|
|
|
Alpha-thalassemia 3 gene deletion
|
HbH disease (excess beta-globulin forms HbH)
|
|
|
Alpha-thalassemia 4 gene deletion
|
No alpha-globin; excess gamma-globin forms Hb Barts; hydrops fetalis, incompatible with life
|
|
|
Alpha-thalassemia common in which populations?
|
Cis deletion: Asians
Trans deletion: Africans |
|
|
Beta-thalassemia etiology
|
Splice site point mutations, promotor region mutations --> decreased beta-globins
|
|
|
Beta-thalassemia common in which population?
|
Mediterranean
|
|
|
B-thalassemia minor features
|
Heterozygote, B-globin deficient; asymptomatic; Increased HbA2 for diagnosis
|
|
|
B-thalassemia major featurse
|
Homozygote; B-globin absent; marrow expansion - "crew cut" on skull XR, chipmunk facies; increased HbF
|
|
|
Lead poisoning pathophys
|
1) Ferrochelatase, ALA dehydratase inhibition --> decrease heme synthesis
2) rRNA degradation inhibition --> basophilic stippling |
|
|
Lead poisoning clinical features ("LEAD")
|
Lead lines (Burton's lines) on gingivae
Encephalopathy & Erythrocyte stippling Abdo colic & sideroblastic Anemia Drops (wrist and foot); Dimercaprol treatment |
|
|
Treatment for lead poisoning
|
Dimercaprol and EDTA; succimer for kids
|
|
|
Sideroblastic anemia etiology
|
ALA synthase deficiency, X-linked; reversible - alcohol, lead, isoniazid
|
|
|
Thalassemia - type of anemia
|
Microcytic, hypochromic
|
|
|
Sideroblastic anemia - type of anemia
|
Microcytic, hypochromic with ringed sideroblasts
|
|
|
Sideroblastic anemia lab findings
|
Increased iron, normal TIBC, increased ferritin
|
|
|
Sideroblastic anemia treatment
|
Pyridoxine (cofactor for ALA synthase)
|
|
|
Folate deficiency etiology
|
Malnutrition (alcohol), malabsorption, antifolates (MTX, TMP, phenytoin), increased requirements (pregnancy)
|
|
|
Folate deficiency clinical features
|
Hypersegmented PMNs, glossitis, increased homocysteine, NORMAL methylmalonic acid
|
|
|
B12 deficiency etiology
|
Poor nutrition, malabsorption (Crohn's), pernicious anemia, Diphyllobothrium lactum (fish tapeworm), proton pump inhibitors
|
|
|
B12 deficiency clinical findings
|
Hypersegmented PMNs, glossitis, increased homocysteine, INCREASED methylmalonic acid, neuro findings
|
|
|
B12 deficiency neurological signs
|
Bilateral; peripheral neuropathy, posterior column degeneration, lateral corticospinal degeneration, dementia
|
|
|
Orotic aciduria - associated anemia
|
Megaloblastic, not responsive to folate or B12 in children (UMP synthase deficiency)
|
|
|
Nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia - causes
|
Liver disease, alcoholism, reticulocytosis (Increased MCV), drugs (5-FU, AZT, hydroxyurea)
|
|
|
Intravascular hemolysis clinical findings
|
(RBC breakdown in vessels) Decreased haptoglobin, increased LDH, hemoglobin in urine
|
|
|
Extravascular hemolysis clinical findings
|
(RBC breakdown by spleen) Increased LDH, increased UCB, normal haptoglobin
|
|
|
Anemia of chronic disease
|
Increased hepcidin (inflammation) --> decreased Fe release and transport
|
|
|
Anemia of chronic disease lab findings
|
Decreased Fe, increased ferritin, decreased TIBC
|
|
|
Aplastic anemia
|
Failure/destruction of myeloid stem cells; pancytopenia (hypocellular bone marrow with fatty infiltration)
|
|
|
Aplastic anemia clinical symptoms
|
Fatigue, malaise, pallor, purpura, mucosal bleeds, petechiae, infection
|
|
|
Aplastic anemia causes
|
Radiation, drugs, viruses (parvovirus B19, EBV, HIV, HCV), Fanconi's anemia (DNA repair defect), idiopathic
|
|
|
Drugs causing aplastic anemia
|
Benzene, chloramphenicol, alkylating agents, antimetabolites
|
|
|
Aplastic anemia treatment
|
Withdrawal of cause, immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, antithymocyte globulin), BM transplant, RBC/platelet transfusion, C-CSF, GM-CSF
|
|
|
Conditions with non-hemolytic, normocytic anemia
|
Anemia of chronic disease
Aplastic anemia Chronic kidney disease (decreased EPO) |
|
|
Conditions with intrinsic hemolytic normocytic anemia
|
Hereditary spherocytosis
G6PD deficiency (E/I) Pyruvate kinase deficiency HbC defect Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (I) Sickle cell anemia |
|
|
Hereditary spherocytosis
|
Defect in RBC membrane skeletal protein; small and round RBCs with no central pallor; premature RBC removal by spleen
|
|
|
Hereditary spherocytosis clinical findings
|
Labs: increased MCHC, RCDW, decreased MCV
Splenomegaly, aplastic crisis (parvovirus B19) |
|
|
G6PD deficiency
|
X-linked; decreased glutathione, RBC damage from oxidative stress; extravascular RBC destruction
|
|
|
G6PD deficiency clinical findings
|
Back pain, hemoglobinuria few days following stress (infection, fava beans, sulfa drugs)
|
|
|
G6PD deficiency blood smear
|
Heinz bodies and bite cells
|
|
|
Heterozygous G6PD deficiency protective against
|
P. falciparum
|
|
|
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
|
AR; decrease in ATP production --> rigid RBCs; hemolytic anemia in newborn
|
|
|
HbC defect
|
Beta-globin mutation: glutamic acid --> lysine mutation at residue 6; milder version of sickle cell
|
|
|
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
|
Complement mediated RBC lysis; triad: hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia, venous thrombosis
|
|
|
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria treatment
|
Eculizumab (complement activation inhibitor)
|
|
|
Sickle cell anemia
|
Glutamic acid --> Valine at position 6, beta-globin; low O2, dehydration leads to cell sickling - anemia and vaso-occlusion
|
|
|
"Crew cut" skull XR typical for
|
Sickle cell anemia, thalassemias
|
|
|
Sickle cell disease - complications in homozygotes
|
Aplastic crisis (parvo B19)
Autosplenectomy (Howell-Jolly); risk of encapsulated bacterial infection Splenic sequestration crisis Salmonella osteomyelitis Painful vaso-occlusive crisis Renal papillary necrosis |
|
|
Sickle cell treatment
|
Hydroxyurea (increase fetal Hb), BM transplant
|
|
|
Conditions with extrinsic hemolytic normocytic anemia
|
Autoimmune
Microangiopathic Macroangiopathic Infections |
|
|
Cold agglutinin disease
|
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, serum IgM antibodies bind to RBCs in cold weather, causing clumping
|
|
|
Warm agglutinin disease
|
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, serum IgG bind to RBCs, then damaged by splenic macrophages (spherocytes), degraded in spleen
|
|
|
Direct Coomb's test
|
anti-Ig antibodies added to patient's serum; RBCs agglutinate if RBCs are coated with Ig
|
|
|
Indirect Coomb's test
|
normal RBCs added to patient's serum; serum agglutinates if serum has anti-RBC surface Ig
|
|
|
Microangiopathic anemia
|
RBCs damanged when passing through obstructed vessel lumen
|
|
|
Micro/macro-angiopathic anemia - blood smear
|
Schistocytes
|
|
|
Conditions with microangiopathic anemia
|
DIC, TTP, HUS, SLE, malignant hyperthermia
|
|
|
Macroangiopathic anemia
|
Hemolytic anemia caused by prosthetic heart valves, aortic stenosis --> mechanical destruction
|

