![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Reference range of Absolute Values: cells/μL |
2300-8100 |
|
|
Reference range of Absolute Values: cells/μL Lymphocytes |
800-4800 |
|
|
Reference range of Absolute Values: cells/μL Eosinophils |
0-400 |
|
|
Reference range of Absolute Values: cells/μL Basophils |
0-100 |
|
|
Reference range of Absolute Values: cells/μL Monocytes |
450-1300 |
|
|
leukocytosis |
>50x10^9/L |
|
|
leukopenia |
<4.5 x 10^9/L |
|
|
chronic myelogenous leukemia |
increases in all granulocytes including eosinophils and basophils. involvement of platelets including giant hypogranular forms. Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase markedly decreased |
|
|
Leukemoid reaction |
Increases in neutrophils and their immature forms, possible increased monocytes-but absence of basophils and eosinophils. No dyspoietic morphology. No abnormal platelet morphology, Markedly increased leukocyte alkaline phosphatase. |
|
|
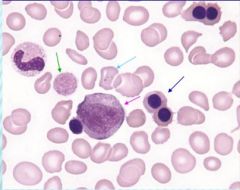
leukoerythroblastosis |
|
|
left shift |
Immature forms in circulation accompanied with the morphologic changes affecting the cytoplasm and nucleus |
|
|
increase in band forms and an occasional metamelocyte |
mild left shift |
|
|
metamyelocytes, myelocytes and an occasional promyelocyte in circulation |
moderate left shift |
|
|
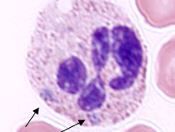
Doehle bodies |
|
|
cause of Doehle bodies |
asynchronous maturation |
|
|
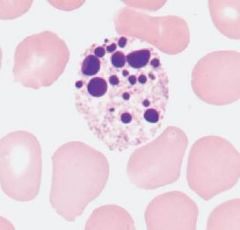
Toxic granulation, Vacuolization |
|
|
necrobiotic cell |
|
|
monocytosis |
> 1.1 X10^9/L |
|
|
pediatric lymphocytosis |
>10.0 X 10^9/L |
|
|
adult lymphocytosis |
> 4.8 X10^9/L |
|
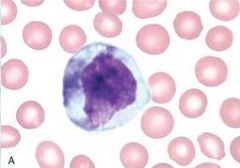
|
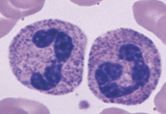
reactive lymphocyte |
|
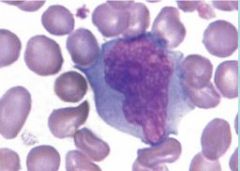
|
reactive lymphocyte |
|
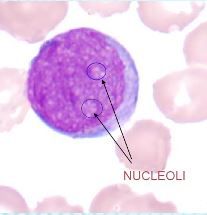
|
myeloblast |
|
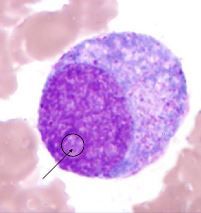
|
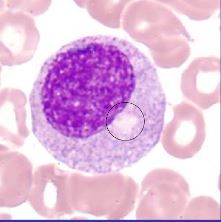
promyelocyte |
|
|
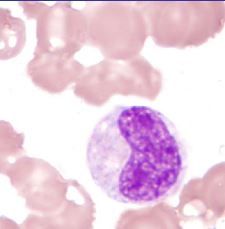
myelocyte |
|
|
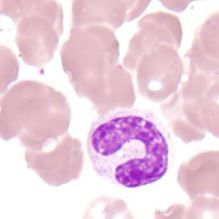
metamyelocyte |
|
|
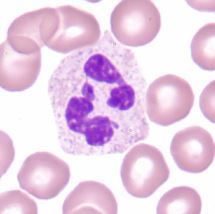
band |
|
|
segmented neutrophil |
|
|
leukemias are in the |
bone marrow |
|
|
lymphomas are in the |
lymphatic system |
|
|
causes of leukocytes neoplasms |
radiation, organic solvents, Epsten Barr associated with Burkitt non- Hodgkin lymphoma, Human T cell lymphotrophic virus type 1, therapy- cancer treatments |
|
|
Leukocyte neoplasms. Chromosomal abnormalities, Genetic lesions |
Burkitt's lymphoma. Chronic myelogenous leukemia |
|
|
oncogene |
cause dominant acting cancer mutations |
|
|
protooncogenes |
codes for proteins involved in normal cell cycle regulation |
|
|
tumor suppressor genes |
codes for proteins that resist malignant transformation |
|
|
molecular pathway alteration |
blocked differentiation. transcriptional repression, programmed cell death |
|
|
kills cells by reproducing unstable ions that damage DNA |
radiation therapy |
|
|
monoclonal antibodies and Imatinib mesylate |
targeted therapy- acts specifically on genetic lesions that cause cancers |
|
|
Chronic GVHD |
transplantation complication after 100 days |
|
|
Syngeneic transplant |
between identical twins |
|
|
Allogeneic transplant |
between different donors |
|
|
Autologous transplant |
from a person's own marrow |
|
|
cytochemistry |
study of chemical constituents of cells which with the help of the staining properties help determine the lineage |
|
|
who does not have myeloperoxidase? |
lymphocytes |
|
|
chemical used for MPO? |
3,3’ diaminobenzidine or p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride and catechol |
|
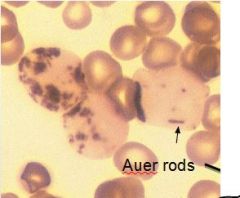
|
Myeloperoxidase enzyme found in the primary granules of neutrophils, eosinophils and some in monocytes |
|
|
What does Sudan Black do and what is it's purpose? |
It stains fats, sterols and phospholipids- differentiates between ALL and AML. |
|
|
Lymphoids are _______ to Sudan Black. |
negative
|
|
|
Granulocytes are ______ to SBB. |
positive |
|
|
Monocytes are ________ to Sudan Black. |
negative |
|
|
What do esterases do? |
Differentiate neutrophillic granulocytes from monocytic cell |
|
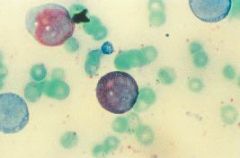
|
positive reaction to esterase stain |
|
|
who is positive and who is negative to α-naphthyl acetate esterase stain? |
Monocytes are positive however, granulocytes and lymphoid cells are generally negative |
|
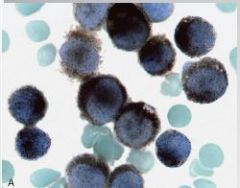
|
positive reaction to esterase by monocyte |
|
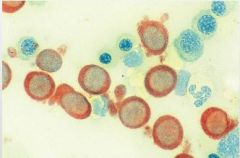
|
monocyte positive for Alpha-Naphthyl Butyrate Esterase
|
|
|
Diagnosing ALL and erythroid AML or abnormal erythroid presursors in MDS |
Periodic Acid Schiff |
|
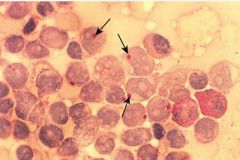
|
periodic acid schiff stain |
|
|
Factor VIII antibodies |
positive in megakaryoblastic Leukemia |
|
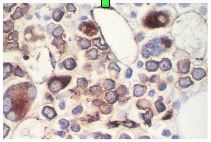
|
positive reaction to Factor VIII in a person with acute megakaryocytic leukemia |
|
|
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity |
differentiates Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia from leukemoid reaction |
|

|
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity |
|
|
CML has reduced score |
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity |
|
|
acid phosphatase |
identifies hairy cells |
|
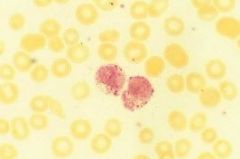
|
Acid Phosphatase |
|
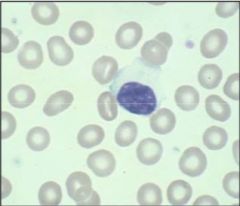
|
lymphocytosis |
|
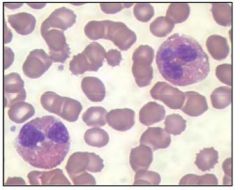
|
eosinophilia |
|
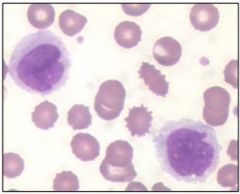
|
monocytosis |
|
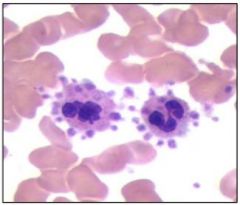
|
platelet satellitosis |
|
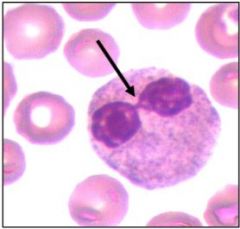
|
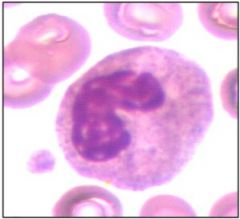
Pelger Huet |
|
|
Pelger Huet |
|
|
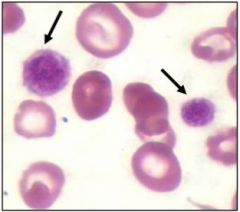
May Hegglin |
|
|
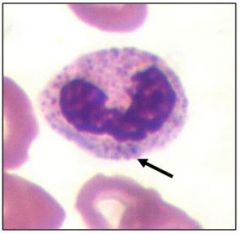
May Heggelin with doehle bodies |
|
|
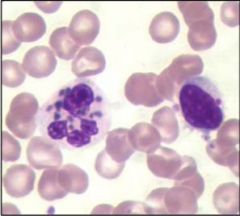
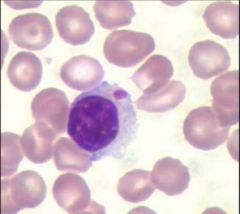
Chediak Higashi |
|
|
Chediak Higashi |
|
|
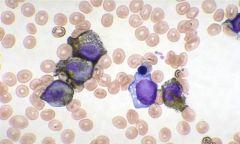
Perioxidase stain |
|
|
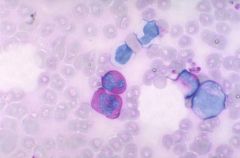
PAS stain |

