![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Leukemia
|
mutation of stem cells that causes impaired production of normal RBCs, WBCs, and or platelets
must ID as acute or chronic spleen becomes site of extramedullary hematopoesis categorized based on cell lineage and maturity |
|
|
lsadkfj
|
|
|
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) causes
|
usually by chromosomal translocation, causes inc oncogene expression or dec supressor gene expression
-may be caused by genetics or toxic (environ) exposure -inversions, deletions, pt mutations, translocations |
|
|
AML diagnosis
|
cytochemical stains
election microscopy immunophentyping/flow cytogenetics |
|
|
Clinical features of AML
|
-cells dysfunc and may lead to : fever, infection
-anemia occurs and leads to: fatigue, weakness -thrombocytopenia causes: easy bruising, petechiae (red spots from capillaries breaking), mucosal bleeding -headache, blindness, joint pain, heart palpitations, gum infiltration |
|
|
Lab features of AML
|
peripheral blood
-blood counts variable -blasts are present -auer rods: monoblast, myeloblasts, promyelocyte inclusions ==> if no auer rod, just say blast -may see anemia and giant platelets -nRBCs -pseudo-hypo seg -hyperseg of segs |
|
|
F cell
|
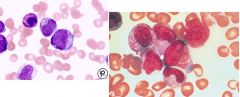
many auer rods
|
|
|
Diagnosis AML
|
-200 WBC (peripheral blood) classified
-hypercellular BM -20% or greater myeloblasts found in marrow or blood -500 cell differential on BM smear |
|
|
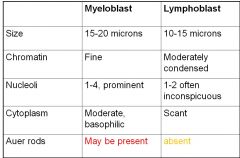
myeloblasts distinguished by:
|
auer rods
cytochemical stains surface markers |
|
|
myeloblast vs lymphoblasts morph comparison
|
|
|
|
cytochemical stains
|
-used to classify acute leukemias
-performed on BM smears -(+) rxns occur wil be assoc w/particular lineage -ID's lipids or enzymes w/in blast pop |
|
|
Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
|
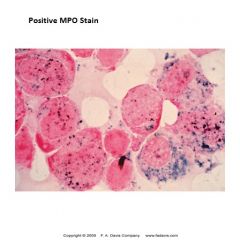
-stains prim grans that contain peroxidase
-myelo line will stain strongly pos -(-) rxn differentiates ALL from AML |
|
|
Sudan Black B
|
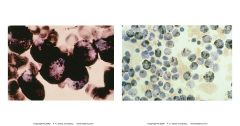
Stains phospholipids and other intracellular lips found in prim and sec grans of myeloid cells
neg in lymphs differenctiates ALL from AML sensitive for granulocyte precursors |
|
|
Specific esterase
|
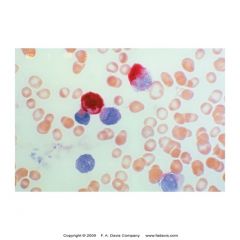
-prim grans of myeloid cells
-myeloblasts (strong +), segs, baso, masts -eos, mono, lymphs ==neg -specific for few of myeloid series |
|
|
Nonspecific esterase
|
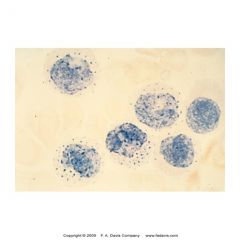
==monocytes
-monoblasts stain strong positive -mono, histo, macro, megakary stain positive while granulocytes stain negative -used to ID monoblasts and monocytes in Acute monoblastic and myelomonocytic leukemia |
|
|
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
|
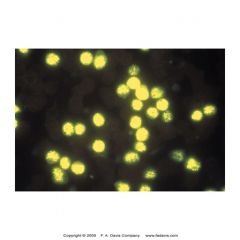
=lymphoblasts
-intranuclear enzyme found in stem cells and immature lymphoid cells w/in BM -90% lymphoblastic leukemias (B or T) -5-10% myeloblastic leukemia -30% of blast crisis phase of CML |
|
|
Acid phosphatase
|

stains T lymphoblasts
|
|
|
Tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)
|
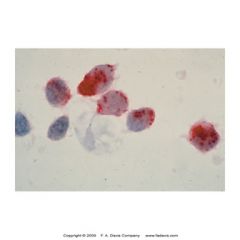
stains B lymphocytes in hairy cell leukemia
|
|
|
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
|

-stains glycoproteins and glycogen in many cell types
-ALL exhibits "Block staining" in lymphoblasts (left) -erythroblasts in erythroleukemia usually exhibits intense granular pattern (right) |
|
|
immunophenotype
|
-used instead of staining
-classify the clone of leukemic blasts using Abs agains cell surface markers -particular nomenclature for type of leukemia based on: morphologic info immunophenotypic info cytochemical info unique presentation |
|
|
FAB classification of AML (acute myelocytic leukemia)
|
M0 - acute myeloblastic leukemia minimallly differentiated
M1- acute myeloblastic leukemia w/o maturation M2 - acute myeloblastic leukemia w/maturation M3 - acute promyelocytic leukemia, hypergranular M4 - acute myelomonocytic leukemia M6 - erythroleukemia M7 - acute megakaryoblastic leukemia |
|
|
M0
|
acute myeloblastic leukemia minimally differentiated
lots of blasts MPO and SBB neg NO auer rods |
|
|
M1
|
acute myeloblastic leukemia w/o maturation
at least 5% blasts are MPO and SBB pos auer rods may be present |
|
|
M2
|
acute myeloblastic leukemia w/ maturation
20% of nucleated BM cells are blasts >10% of neutrophils beyond the pro stage monocytic component is <20% of nonerthroid cells 50% of blasts are MPO and SBB pos auer rods in blasts freq |
|
|
M3
|
acute promyelocytic leukemia, hypergranular
have lots of promyelocytes == prim granules -auer rods and F cells in blasts and pros -progoagulant/fibrinolytic activity of granules results in DIC -MPO strong pos -hypergranular (prim grans) and hypogranular varients |
|
|
M4
|
Acute myelomonocytic leukemia
myeloblasts and monoblasts -mix of malignant cells w/both myelocytic and monocytic features -large cells -abundant basophilic cytoplasm -azurophilic granules -may show pseudopod cytoplasmic extensions -lacy chromatin -1-4 nucleoli -NSE strong pos -Specific esterase pos -monoblasts are MPO or SBB neg -promonoblasts |
|
|
M6
|
erythroleukemia
red cell balst in marrow and perphiral blood |
|
|
M7
|
acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
young megakaryroblast -some small with scant basophilic cytoplasm -some large w/abudndant cytoplasm and blebbing pseudopod formation -megakaryoblastic fragments or micromegakaryocytes w/giant, hypogranular platelets -cytochem stains not helpful -diagnosis based on immunophenotype ***CD 41, 61 -symptoms: pallor, weakness, excessive bleeding, abdom masses -rarest -both children and adults |
|
|
AML w/myelodyplasia
|
-primarily in adults
-dysplasia in at least 2 cell lines -pseudo pelgeroid neuts, hypogran, nucleated adn multinucleated reds, megoloblastic features, ringed sideroblasts, micromagakary with 1 lobe -can follow myelodysplastic syn |
|
|
acute basophilic leukemia
|
-rare
-commonly occurs as blast transformation form CML -predom circulating cell appears blast like w/1-3 neucleoli and prominent coarse basophilic granules -special stains and immunophenotyping distinguish acute basophilic leukemia from acute promyelocytic leukemia -CD 9, 13, 33, 34 |
|
|
Acute myelofibrosis
|
-rare
-pancytopenia -marrow hyperplasia of erythroid, granulocytic, and megakaryocytic components combined w/fibrosis -splenomegaly absent |
|
|
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
|
-malignant dz caused by mutation of lymphoid precursor cells
-results in : anemia thrombocytopenia neutropenia overpop of lymphoblasts in tissues (liver, spleen, meninges, gonads -predom dz in children -clinical features: bone/jt pain, hepatoslenomegaly, lymphadenopathy |
|
|
ALL 3 subtypes
|
L1 (more likely in children)
-lymphoblasts small w/scant cytoplasm -uniform in size -indistinct nucleoli L2 (more likely in adults) -blast larger -more pleomorphic -prominent nucleoli -contain abundant cytoplasm L3 (leukemic phase of burkitt's lymphoma) -intensely basophilic cytoplasm -has many vacuoles -more mature lymphoid cells are TdT negative = b cells |

