![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Circulation |
continuous one way circuit of blood through blood vessels propelled by the heart |
|
|
Location of the heart |
|
|
|
Three tissue layers of heart |
|
|
|
Endocardium |
|
|
|
Myocardium |
|
|
|
Epicardium |
|
|
|
pericardium |
|
|
|
myocardium special features |
|
|
|
Right side of heart |
receives blood low in oxygen that has passed through body already and pumps it to lungs through pulmonary circuit |
|
|
Pulmonary circuit |
portion of the cardiovascular system which carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated (oxygen-rich) blood back to the heart. |
|
|
Left side of heart |
receives highly oxygenated blood from lungs and pumps it throughout body via systemic circuit |
|
|
Systemic circuit |
carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart |
|
|
Left/right heart chambers separated by: |
partitions called septum - interatrial septum separates atria - interventricular septum separated two ventricles |
|
|
interatrial septum |
partition separating two atria |
|
|
interventricular septum |
partition separating two ventricles |
|
|
Atria |
-upper chambers - mainly blood receiving |
|
|
Ventricles |
- lower chambers - forceful pumps |
|
|
vena cava |
large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart |
|
|
inferior vena cava |
carries blood from the lower body |
|
|
superior vena cava |
carries blood from the head, arms, and upper body |
|
|
Right atrium |
- receives blood from body tissues - returning blood carried in veins |
|
|
Right ventricle |
- receives blood from right atrium - pumps it to lungs |
|
|
Left atrium |
- receives oxygen rich blood from lungs via pulmonary veins |
|
|
Left ventricle |
- pumps highly oxygenated blood to all of body - blood goes into aorta first then into branching systemic arteries that take blood to tissue |
|
|
Valves |
- direct blood flow through heart - located at entrance/exit of each ventricle |
|
|
Atrioventricular valves |
ENTRNACE valves |
|
|
Semilunar valves |
EXIT valves |
|
|
Right atrioventricular (entrance) valve |
- tricuspid - 3 flaps that open/close |
|
|
Left atrioventricular (entrance) valve |
- bicuspid/mitral - permits blood to flow from left atrium to left ventricle - ensures forward blood flow into aorta |
|
|
chordae tendinae |
- thin fibrous threads to papillary muscles arising from walls of ventricles - function is to stabilise valve flaps when ventricles contract to prevent backflow of blood when heart beats |
|
|
Pulmonary valve (exit) |
- located between right ventricle & pulmonary trunk - prevents blood from returning to ventricle |
|
|
Aortic valve (exit) |
- located between left ventricle and aorta - prevents backflow of blood from aorta into ventricle |
|
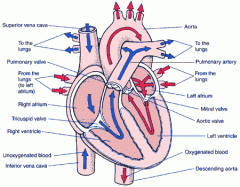
|
- |
|
|
coronary circulation |
is the blood supply to myocardium composed of: - left coronary artery |
|
|
left coronary artery |
branches into circumflex artery and left-anterior descending artery |
|
|
right coronary artery |
snakes around heart inferior to right atrium |
|
|
coronary sinus |
dilated vein that opens into right atrium near inferior vena cava |
|
|
cardiac cycle (heartbeat) |
Heart muscle contraction begins in thin-walled upperchambers, atria, followed by contraction of thick muscle in lower chambers,ventricles. |
|
|
systole |
active phase, contraction |
|
|
diastole |
resting phase |
|
|
cardiac output |
volume of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute is termed cardiac output (CO) |
|
|
stroke volume |
volume of blood ejected from ventricle with each beat |
|
|
heart rate |
number of times heart beats per minute |
|
|
Heart conduction system |
heart muscle is stimulated to contract by electric energy passing along cells |
|
|
Nodes (2 types) |
sinoatrial node |
|
|
sinoatrial node |
- initiates heartbeats by generating action potential at regular intervals |
|
|
atrioventricular node |
located in interatrial septum at bottom right atrium |
|
|
Specialised fibers (3 types) |
|
|
|
Atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) |
- fibers travel down both sides of interventricular septum in groups called right and left bundle branches |
|
|
Conduction pathway (sinus rhythm) |
|
|
|
Sinus rhythm |
normal heart rhythm originating at sinoatrial node |
|
|
Control of heart rate (3 systems) |
|
|
|
autonomic nervous system influence on heart |
modifies heart rate according to changing body conditions |
|
|
sympathetic nervous system influence on heart |
|
|
|
parasympathetic nervous system influence on heart |
|
|
|
Bradycardia |
slow heart rate |
|
|
Tachycardia |
heart rate more than 100bpm |
|
|
sinus arhythmia |
regular variation in heart rate |
|
|
premature ventricular contraction (PVC) |
ventricular contraction initated by Purkinje fibers instead of SA node |
|
|
Lub |
|
|
|
Dub |
|
|
|
Murmur |
any abnormal sound heard |
|
|
Murmur types (2) |
|
|
|
Organic murmur |
any abnormal sound caused by structural change in heart or vessels connected with heart |
|
|
functional murmurs |
normal sounds such as rapid filling of ventricles |
|
|
heart studies (4) |
|
|
|
Electrocardiograph |
|
|
|
catheterization |
thin tube passed through veins of arm or groin then into right side of heart |
|
|
echocardiography |
high frequency sound waves sent to heart from small instrument on chest surface recorded as they return from bouncing off heart |
|
|
Heart inflammation (3 types) |
|
|
|
Endocarditis |
|
|
|
Myocarditis |
|
|
|
Pericarditis |
|
|
|
arrhythmia |
abnormal rhythm of heartbeat |
|
|
flutter |
heartbeat up to 300bpm |
|
|
fibrillation |
300-600bpm |
|
|
heart block |
interruption of electrical impulses in heart's conduction system |
|
|
correction of arrhythmias |
- artificial pacemakers |
|
|
Congenital heart disease |
problems with heart's structure that are present at birth
|
|
|
Rheumatic heart disease |
|
|
|
Coronary artery disease |
involves walls of blood vessels that supply heart muscle |
|
|
types of coronary artery disease (3) |
- myocardial infarction |
|
|
Myocardial infarction |
|
|
|
Angina pectoris |
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
|
|
|
Heart failure |
|

