![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Orem's definition of self health care |
The practice of activities that individuals personally initiate and perform on their own behalf in maintaining life, health and well-being. |
|
|
Social Determinants of Health (SDOH) |
Ecological approach to public health
The conditions in which people are born, grow up, live, work, and age, including their health.
Factors out in the community that will assist people to become healthier.
Example: community is safe to exercise outside |
|
|
Domains of Learning |
Cognitive: how you store information Affective: how you feel about information Psychomotor: learn by doing
|
|
|
Adult learners motivated to learn when... |
*They think they need to know something *New information is compatible with life experiences *Value the person delivering the information *Believe they can make necessary changes implied by new information |
|
|
Formative learning |
learning along the way or along the line of the course |
|
|
Summative learning |
Summary of learning at the end |
|
|
Educational Process |
1. Identify educational need 2. Establish goals and objectives 3. Select appropriate educational methods 4. Evaluate learning and teaching |
|
|
What factors will make people change behavior |
1. Knowledge 2. Attitude 3. Behavior |
|
|
Things to consider in education preparation |
Locus of control Age of learners (adult or young) Hierarchy of needs Developmental stages Phases of crisis What strategies to educate How to involve the learners |
|
|
Don Ardell's Wellness Model |
Disease oriented perspective Health is absence of disease
Death Optimal health _________________________________________ |
|
|
Holisitc model |
Health is complex and interconnected *Social *Environmental *Physical *Emotional *Spiritual *Intellectual |
|
|
LaLonde's model from 1974 |
4 determinants of health
1. human biology 2. environment 3. Lifestyle 4. Health care
|
|
|
US Surgeon General "Health People" |
Report on health promotion and disease prevention
3 determinants
1. Inherited biology 2. Environmental 3. Behavioral |
|
|
Assessment of health |
Health Risk Appraisals Wellness Inventories Clinical Practice Guidelines |
|
|
Health Risk Appraisals |
Goal is the primary prevention and reduction or early detection of disease Appraisals includes: *Questionnaire *Basic lab tests *Physical exam *Provides appraisal age and achievable age |
|
|
Diabetes II linked to risk factors |
Risk factors *Diet high in CHO and saturated fats *Obesity *HTN *Smoking *ETOH *Stress *Family hx Screening *Blood glucose Recommendation Healthy diets, exercise, quit smoking, monitor BG regularly |
|
|
Coronary Artery Disease linked to risk factors |
Risk factors *Diet high in sat. fats and cholesterol *Obesity *Sedentary lifestyle *Stress *Family history *ETOH *Smoking Screenings *Cholesterol with lipid profile *BP *Stress EKG Recommendation *Healthy diet, exercise, monitor BP, quit smoking, reduce stress, regular screenings |
|
|
HTN and CVA linked to risk factors |
Risk factors *Diet high in Na+ and low in calcium *Obesity *Stress *Sedentary lifestyle *ETOH *Family history Screening *BP check Recommendations health diet, exercise, reduce stress, monitor BP |
|
|
Breast Cancer linked to risk factors |
Risk factors *female *obesity especially postmenopausal *diet high in fat *early menarche, late menopause *ETOH (3 or more drinks per day) *HRT (estrogen and progesterone) Screenings BSE monthly Mammogram Recommendations screenings, teaching about BSE, when to get mammogram |
|
|
Colorectal Cancer linked to risk factors |
Risk factors *diet low in fiber and high in fat *stress *smoking *family hx Screenings rectal exams after 40yrs Colonoscopy after 50 yrs Recommendations Screenings |
|
|
Mammorgram screening ages |
Women with non high risk (age 20-40) clinical exam every 3 yrs
40 yrs and up mammogram every year |
|
|
Healthy Eating |
Drink 6 glasses of water/day 22-26g/day of fiber
|
|
|
Fat Free |
less than .5gm/serving
|
|
|
Low fat |
3 gm or less of fat/serving
|
|
|
Lean |
less than 10 gm of fat and 4 gm saturated fat/serving |
|
|
Calorie Free |
less than 5 cal/serving |
|
|
Low calorie |
40 cal or less/serving |
|
|
Light |
means nothing in particular |
|
|
When looking at food labels |
note the serving size check what % of calories come from fat check dietary fiber look at ingredient list |
|
|
Peak ages for laying down bone mass--Calcium |
20yrs for males 18yrs for females |
|
|
Amount of calcium |
2000 to 2500 mg daily is upper limit 10-18 yrs 1200mg/day Pre-menopausal and HRT female 1000mg/day Postmenopausal female w/o HRT 1500 mg/day Pregnant or lactating 19yrs and older 1400 mg Pregnant of lactating 18yrs and younger 2000mg |
|
|
Calcium Supplements |
should be taken in split doses 500-600 mg throughout the day
calcium carbonate or citrate best absorbed
Calcium citrate should be taken w/o food |
|
|
Foods that interfere with calcium absorption |
spinach, legumes, rhubarb, caffeine, and wheat bran |
|
|
Foods high in calcium |
salmon with bones, kale, soy beans, turn-ups |
|
|
Energy Drinks contains.... |
Taurine: amino acid produced in the body, Regulates heart rate and muscle contractions Guarana: stimulant with high levels of caffeine Ginseng: stimulant Caffeine |
|
|
Vitamin D |
Children 1-18yrs 400 IU Adults 19-40 yrs 400-800 IU Adults 50 yrs and older 800-1000 IU Pregnant and Breastfeeding all ages 400-800 IU |
|
|
Osteoporosis Risk Factors |
Female Family history Ancestry from Northern Europe and Asia Small bone structure Lifestyle_ sedentary, caffeine, ETOH Postmenopausal Stress |
|
|
Osteoporosis prevention |
diet high in calcium and magnesium limit caffeine weight bearing exercises HRT in menopausal women maintain an alkaline pH in blood stream |
|
|
Cholesterol Production |
Saturated fat in diet will stimulate live to increase cholesterol production
Dietary sources are from animal products |
|
|
High density lipoproteins |
Good cholesterol helps remove deposited cholesterol in arteries |
|
|
Low density lipoproteins |
Bad cholesterol lays down cholesterol in arteries |
|
|
Cholesterol Guidelines: Adults |
>240mg/dl high risk with greater than or equal to 160 mg/dL LDL
200-239mg/dl borderline with 130-159mg/dL LDL
<200 mg/dl low risk with goal that is less than or equal to 100 mg/dl LDL |
|
|
Cholesterol Guidelines: Pediatric |
>200 mg/dl high risk
171-199 mg/dl borderline
<170mg/dl low risk |
|
|
recommendations to increase the ratio of HDL |
Exercise Stress management Real garlic 1-2 oz red wine or real grape juice |
|
|
Recommendations to reduce cholesterol |
Low fat diet esp. animal fat Increase fiber Exercise Omega 3 fish oil Red rice yeast |
|
|
C reactive protein |
Produced in the liver when arteries are inflamed Used as an indicator of inflammation *may be reliable predictor for CVD *Increasing fiber intake to 20 gm or more reduced CRP |
|
|
C reactive protein levels |
<1 mg/L = low level of prediction of CV event 1-3mg/L = moderate level >3 mg/L = high risk for futrue CV event |
|
|
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) |
*Measures inflammation in arteries *High levels of MPO directly linked to a high risk of cardiac event within next 6 mos. *Low levels MPO showed low risk *Can help ED providers determine whether a pt's c/o chest pain is cardiac related or other cause *MPO may be better predictor of short-term risk than CRP |
|
|
Skin Cancer |
90% of skin cancer is caused by UV (A, B,C) radiation
1 sunburn before age 18 yrs increases changes of skin cancer by 78%
Basal cell is most common (1 in 5 in US)
Melanoma risk is 1 in 60 but increasing *can occur on non-exposed areas |
|
|
Sun Protection Factor |
SPF of 15 or 30 for UVB
Should have PABA or Parasol
Against UVA, products should contain 97% titanium dioxide or zinc oxide |
|
|
Skin Cancer ABC's |
A: Asymmetry- one half unlike the other half B: Border irregular- scalloped or poorly circumscribed border. C: Color varied-from one area to another shades of tan and brown, black, sometimes white, red, or blue D: Diameter- larger than 6mm as a rule E: Evolving- Nevis is changing over time |
|
|
Exercise |
Regular exercise at least 3xs per week for 1 hr Determine target heart rate Vary exercise to use different muscle groups Wear appropriate shoes |
|
|
Calculating target heart rates |
220-age x 65(can go up to 75) |
|
|
Definition of stres |
any stimulus that disturbs or interferes with the normal physiological equilibrium of an organism
*Stress is neither good nor bad by itself"
Stressors are: environmental, emotional, chemical, social, physical, spiritual |
|
|
3 components to stress-illness relationship |
Activators Reactions Consequences |
|
|
Han Selye's 3 phases of bodily stress response |
Alarm reaction State of resistance Stage of exhaustion |
|
|
Alarm reaction |
Physiological indicators of alertness Fight or flight Defense Mechanism mobilized -increased BP, HR, Resp, perspiration -decreased WBCs and interferon -Pupils dilate, adrenaline and cortisol released -Stored energy floods bloodstream |
|
|
State of resistance |
Signs of alarm reaction diminished Resist noxious stimuli
|
|
|
Stage of exhaustion |
-If stimuli or responses not diminished, exhaustion occurs -Adaptive energy is depleted -Resistance is decreased -Illness may follow |
|
|
Kobasa and Maddi's Hardiness Theory
3 Cs |
Control: have a sense of control in life Challenge: not always a victim, but just another challenge in life to overcome Commitment: they can say no, but fully commit when they say yes |
|
|
rosenstocks health belief model |
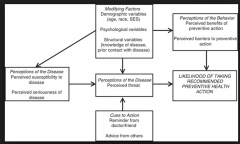
|

