![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Know the definition of a cerebral contusion.
|
Permanent damage to small blood vessels and the surface of the brain.
|
|
|
Know the pathogenesis of a cerebral contusion.
|
Most often secondary to an acceleration-deceleration injury
|
|
|
Know coup versus contrecoup injuries.
|
Coup injuries occur at the site of impact.
Contrecoup injuries occur opposite the site of impact Common sites are at the tips of the frontal and temporal lobes |
|
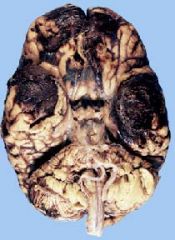
What is this an example of?
|
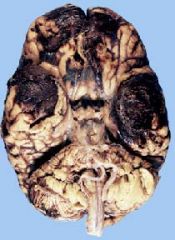
The gross features of a cerebral contusion.
|
|
|
Know the definition of an acute epidural hematoma.
|
Arterial bleed creates a blood-filled space between the bone and dura
|
|
|
Know the pathogenesis of an acute epidural hematoma.
|
-Caused by a fracture of the temporoparietal bone
a. Severance of the middle meningeal artery b. Vessel lies between the dura and inner table of bone -Intracranial pressure increases leading to herniation and death -Can be lucid for several hours after trauma before loss of consciousness |
|
|
Know the clinical features of an acute epidural hematoma.
|
1. Arterial bleed creates a blood-filled space between the bone and dura.
2. Intracranial pressure increases leading to herniation and death 3. Can be lucid for several hours after trauma before loss of consciousness |
|
|
Be able to recognize the gross findings of an acute epidural hematoma.
|
-Caused by a fracture of the temporoparietal bone
-Can be lucid for several hours after trauma before loss of consciousness |
|
|
Know the definition of a subdural hematoma.
|
Venous bleeding between the dura and arachnoid membranes
a. Most often the result of blunt trauma • Examples- car accident, baseball bat b. Due to tearing of bridging veins (superior cerebral veins) between brain and superior sagittal sinus (Slide 15) c. Slowly enlarging blood clot covers the convexity of the brain. • Clot absorbs fluid |
|
|
Know the pathogenesis of a subdural hematoma.
|
Venous bleeding between the dura and arachnoid membranes
a.-Most often the result of blunt trauma -e.g...car accident, baseball bat b.Due to tearing of bridging veins (superior cerebral veins) between brain and superior sagittal sinus (Slide 15) c. Slowly enlarging blood clot covers the convexity of the brain. -Clot absorbs fluid |
|
|
Know the clinical features of a subdural hematoma.
|
-Venous bleeding between the dura and arachnoid membranes
-Fluctuating levels of consciousness -Herniation and death may occur. |
|
|
Be able to recognize the gross findings of a subdural hematoma.
|
-Most often the result of blunt trauma
-Fluctuating levels of consciousness |
|
|
Subdural hematoma:
|
tear of bridging veins producing venous blood clot
|

