![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
177 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Materials that can react or ignite if they are exposed to air and the potential for container failure due to over-pressurization exists
|
Air reactivity
|
|
|
|
Produce disease and are living microorganisms that can mutate and become more deadly
|
Biological agents and toxins
|
|
|
|
Temperature at which the transition from a liquid to a gas state occurs,
|
Boiling Point
|
|
|
|
Used to control the rate of a chemical reaction by speeding up or slowing down
|
Catalyst
|
|
|
|
Caused when two or more chemicals, or the chemical and its container are incompatible
|
Chemical Interactions
|
|
|
|
Caused by both elements and compounds to make new substances with their own physical and chemical properties
|
Chemical Reaction
|
|
|
|
Describes a substances propensity to release energy or undergo change
|
Chemical reactivity
|
|
|
|
Separate elements that bond together to form compound mixture
|
Compound Mixture
|
|
|
|
The amount of acid or base is compared to the amount of water present
|
Concentration
|
|
|
|
indicates the concentration of hydrogen ions in the material being tested
|
Corrosivity
|
|
|
|
Relates to the process of liquefying gases and is the minimum temperature at which a gas can be liquefied no matter how much pressure is applied
|
Critical temperature and pressure
|
|
|
|
The concentration or amount of material to which the body is exposed over a specific time period
|
Dose
|
|
|
|
The radiation dose delivered per unit of time (e.g., mrem / hour)
|
Dose rate
|
|
|
|
Heat Absorbing / Heat producing
|
Endothermic / Exothermic
|
|
|
|
The amount of gas produced by a given volume of liquid at a given temperature
|
Expansion ratio
|
|
|
|
The difference between the upper and lower flammable limits
|
Flammable range (LEL & UEL)
|
|
|
|
The temperature at which enough vapors are given off to support continuous burning
|
Fire point
|
|
|
|
The minimum temperature at which material will ignite but not continue to burn
|
Flash point
|
|
|
|
They are often more toxic than naturally occurring organic chemicals. Decompose into smaller more harmful elements at high temps long periods of time
|
Halogenated hydrocarbon
|
|
|
|
The minimum temperature to which a material must be raised before it will ignite
|
ignition (autoignition) temperature
|
|
|
|
Added to products to control their chemical reaction with other products
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
|
Materials that decompose spontaneously, polymerize, or otherwise self-react and are generally considered unstable
|
Instability
|
|
|
|
Materials made through the sharing or transfer of electrons
|
Ionic and covalent compounds
|
|
|
|
They cause respiratory distress and copious tearing that incapacitate a victim
|
irritants (riot control agents)
|
|
|
|
The maximum temperature that an organic peroxide may be stores safely
|
Maximum safe storage temperature (MSST)
|
|
|
|
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid allowing it to spread more readily / The temperature at which a liquid converts to solid
|
Melting point/Freezing point
|
|
|
|
Miscibility
|
Refers to the tendency or ability of two or more liquids to form a uniform blend or dissolve into each other (koolaid)
|
|
|
|
Substances that interfere with the central nervous system
|
Nerve Agents
|
|
|
|
Derived from materials that are living or were once living
|
organic compounds
|
|
|
|
Lacks carbon chains, but may contain a carbon atom.
|
Inorganic
|
|
|
|
The combining of anything with oxygen or the propensity to yield oxygen which will present a greater hazard
|
oxidation potential
|
|
|
|
The numerical measure of a solutions hydrogen ion concentration as related to acidity or alkalinity
|
pH
|
|
|
|
The characteristic form of a material at ambient temperature
|
Physical state
|
|
|
|
Having a pair of equal and opposite charges
|
Polar
|
|
|
|
Chemical reaction in which small molecules combine to form larger molecules (Shaving Cream, Silly string)
|
Polymerization
|
|
|
|
The ability of a material to emit radioactive energy
|
Radioactivity
|
|
|
|
Materials in which the carbon atoms are linked by only single covalent bonds
|
Saturated Hydrocarbons
|
|
|
|
Materials that have at least one multiple bond between two carbon atoms
|
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
|
|
|
|
Materials that contain the benzene ring, which is formed by 6 carbon atoms and contains double double bonds
|
Aromatic hydrocarbons
|
|
|
|
When this temperature is reached by some portion of the mass of the organic peroxide, irreversible decomposition will begin
|
Self-accelerating decomposition temperature
|
|
|
|
Pourable mixture of a solid and a liquid
|
Slurry
|
|
|
|
Mixture in which all the ingredients are completely dissolved
|
Solution
|
|
|
|
The weight of a solid or liquid compared to an equal volume of water
|
Specific gravity
|
|
|
|
The ability of a substance to change from a solid to the vapor phase without passing through the liquid phase
|
Sublimation
|
|
|
|
Influences the hazards present and the measures taken to control an incident that involves that product
|
Temperature of product
|
|
|
|
Some materials generate more highly toxic gases than others do;
|
Toxic products of combustion
|
|
|
|
Weight of a vapor compared to air
|
Vapor density
|
|
|
|
The force exerted on the inside of a closed container by the vapor in the space above the liquid in the container
|
Vapor pressure
|
|
|
|
These agents are extremely toxic, with the symptoms of exposure on appearing for minutes, hours, to days
|
Vesicants (blister agents)
|
|
|
|
Measure of the thickness of a liquid
|
Viscosity
|
|
|
|
Ease with which a liquid or solid can pass into a vapor state
|
Volatility
|
|
|
|
Describes the sensitivity of a material to water without the addition of heat or confinement
|
Water reactivity
|
|
|
|
The ability of a substance to form a solution with water that can be important in determining control methods
|
Water solubility
|
|
|
|
Instrument readings used to determine the degree of hazard and values used to establish exposure limits
|
Parts per million/billion (ppm/ppb)
|
|
|
|
causes the death of 50 percent of a group of test animals exposed to it by any route other than inhalation
|
Lethal dose (LD50)
|
|
|
|
The amount of a material in the air that, that caused the death of 50 percent of test animals by inhalation
|
Lethal concentrations (LC50)
|
|
|
|
An OSHA term for the maximum concentration averaged over 8 hours per day of 95 percent healthy adults for 40 hours per week
|
Permissible exposure limit (PEL)
|
|
|
|
An American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) term for maximum concentration, averaged of 8 hours/day 40 hours/week
|
Threshold limit value time-wighted average (TLV-TWA)
|
|
|
|
This is the maximum average concentration, averaged over a 15-minute period to which a healthy adult can safely be exposed (15 minutes 1 hour/in between)
|
Threshold limit value short-term exposure limit (TLV-STEL)
|
|
|
|
This is the maximum concentration to which a healthy adult can be exposed without risk of injury, and the exposure to higher concentrations should not occur
|
Threshold limit ceiling (TLV-C)
|
|
|
|
This is the maximum level to which a healthy worker can be exposed for 30 minutes and escape without suffering irreversible health effects
|
Immediately dangerous to life and health value (IDLH)
|
|
|
|
The radiation absorbed dose equals the energy absorption of 100 ergs per gram of irradiated material (an erg is a unit of work energy)
|
RAD
|
|
|
|
Roentgen equivalent man
|
Rem
|
|
|
|
international unit of intensity of X rays or gamma rays. Used to measure the amount of radiation produced
|
Roentgen (one roentgen equals 1000 Milliroentgens)
|
|
|
|
Positively charged radiation particle emitted by some radioactive materials and is not considered dangerous unless ingested
|
Alpha particles
|
|
|
|
Type of radiation that can damage skin tissue, and they can damage internal organs if they enter the body
|
Beta Particles
|
|
|
|
Type of radiation particle that may cause skin burns and can severely injure internal organs, Can penetrate nearly any material
|
Gamma particles
|
|
|
|
Disintegrations of radiation per second (measure of radiation)
|
Activity
|
|
|
|
represents the amount of energy deposited per unit mass of absorbing material
|
Absorbed dose
|
|
|
|
Measure of the rate of decay of radioactive material
|
Half-life
|
|
|
|
the effect from a localized source spreads uniformly throughout the surrounding space. such as the light from a match, radiation from a piece of uranium, and the sound of a cricket
|
Inverse square law
|
|
|
|
Methods of protecting oneself from harmful exposure to radiation
|
Time, Distance, Shielding
|
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cryogenic Liquid Tank Car. 2.2
|
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Nonpressure Tank Car. 3,4,5,6,8, and 9
|
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pneumatically Unloaded Covered Hopper Car. 4,8,6,8, and 9
|
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pressure Tank Car. 2.1,2.2,2.3, and 3
|
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Non Pressure Intermodal
3,6,and 8 |
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pressure Intermodal
2.1, 2.2, 2.3, and 3 |
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Intermodal Tube Containers
2 |
|
|

Identify car by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cryogenic Intermodal
2.2 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Dry Bulk Cargo Trailer
5.1, and 9 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Non-Pressure liquid Cargo Tank
3.1, and 3.2 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Low Pressure Liquid Cargo Tank
3.1, 3.2 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Corrosive liquid Cargo Tank
Class 8 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cryogenic Liquid Cargo Tank
2.2 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Compressed Gas Tube Trailer
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify Trailer by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pressurized Cargo Tank
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify Tank by type and at least one hazard class
|
Non Pressure Facility Tank
Class 3, and 8 |
|
|
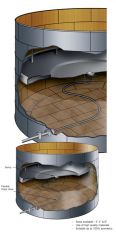
Identify Tank by type and at least one hazard class
|
Floating Roof facility tank
Class 3, and 8 |
|
|

Identify Tank by type and at least one hazard class
|
Spheroid Facility Tank
class 2 |
|
|
|
What percentage of a facility tank has to be underground for it to be considered an underground tank?
|
10 % of the tank
|
|
|

Identify Tank by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pressure vessel Facility tank
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify Tank by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cryogenic Facility Tank
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify container by type and at least one hazard class
|
Ton Container
class 2 |
|
|

Identify by type and at least one hazard class
|
Pipeline
2,3,6,8, and 9 |
|
|

Identify non bulk container by type and at least one hazard class
|
Bag
1,4,6,8, and 9 |
|
|

Identify non bulk container by type and at least one hazard class
|
Carboy
6, 8 |
|
|

Identify non bulk container by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cylinder
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify non bulk container by type and at least one hazard class
|
Cryogenic Cylinder
Class 2 |
|
|

Identify non bulk container by type
|
Drums
|
|
|
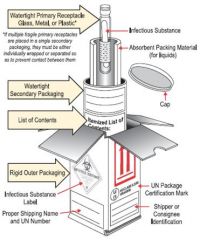
What type of radio active packaging would this fall under?
|
Type A, Cardboard boxes wooden crates, cylinders often with inner containment vessel
|
|
|
|
What type of Radiological Packaging is this
|
Type B radiological Packaging. Steel, concrete, and lead pipes. Size ranges from small and can weigh up to 100 tons
|
|
|

What type of Radiological Packaging is this
|
Type B radiological Packaging. Steel, concrete, and lead pipes. Size ranges from small and can weigh up to 100 tons
|
|
|

Colormetric tubes, M18A2 Chemical Detection Kit, ICAM, M8/M9 Paper, Enzyme Tickets (256 Kit) Infrared Specrometry (ACADA, ICAM), PID's can all be used to detect what
|
Nerve, and Blister Agents
|
|
|
Hand Held Assays, and Infrared Spectrometry (only in presence) can be used to detect what type of agent
|
Biological agents and toxins
|
|
|

Riot Control Agents can be detected using what?
|
Colormetric tubes, Ion-Mobility Spectrometry, Can not be detected with air monitoring devices
|
|
|

For determining UNKNOWNS what is the order in which you should monitor materials
|
Radioactivity, Combustibility, Oxygen availability, pH, if liquid, Hydrogen sulfide,
Carbon Monoxide, Organic vapors |
RCOPHCO (Rachel Came Over & Pulled Her Coat Off / Really Cool Officers Probably Hate Chemical Officers)
|
|

What are some pros/cons Carbon Monoxide Meters
|
PRO: Measures the concentration of Carbon Monoxide.
CON: Only Measures Carbon Monoxide |
|
|

Pros/Cons of Colormetric tubes
|
Pro: Detects specific gases and vapors
Con: You have to know what material you are looking for, does not give specific quantities |
|
|

Pros/Cons of Combustible gas indicators
|
Pro: Measures the concentration of a combustible gas or vapor in the atmosphere
Con: Does not work in Oxygen Deficient environments |
|
|

Pros/Cons of Oxygen Meters
|
Pro: allows user to know if Oxygen in atmosphere is Enriched or Deficient, Measures percentage of oxygen
Con: Must be calibrated prior to use. |
|
|

The electrical circuit in a combustible gas meter is known as what?
|
a Wheatstone Bridge
|
Important for test purposes
|
|

What are Passive dosimeters used for
|
Used to monitor for the threshold level value/time weighted average, (TLV/TWA)and the threshold level value/short term exposure limit (TLV/STEL)
|
|
|

What is the Multirae and what is it used to detect?
|
Multirae is used to detect certain toxic chemicals, oxygen levels, Lower explosive Limit. STEL, and the Volatility of a material
|
|
|

Pros/Cons of the MultiRAE
|
Detects Organic, and some Inorganic vapors, Determines the presence of flammable vapors in the air,
Con: Requires warm-up period, may be affected by power lines |
|
|
|
What do pH indicators, or meters identify.
|
pH stands for Potential for Hydrogen. pH meters and paper, measure level of Acid or Base substances
|
|
|

What do pH indicators, or meters identify.
|
pH stands for Potential for Hydrogen. pH meters and paper, measure level of Acid or Base substances
|
|
|

Pros/Cons of Radiological Detectors
|
Pros: Used to monitor Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Neutron Particles
Con: No response does not mean area is safe. |
|
|
|
What are Reagents
|
A substance or solution combined with a material causing a chemical reaction
|
Used in detection devices such as Colormetric Tubes to bring out a chemical change
|
|

What are the three levels of Radioactive material found on DOT placards
|
Radioactive I - Low
Radioactive II - Medium Radioactive III - High |
|
|

What does "Activity" Mean on a Radioactive Placard?
|
1. Rate of disintegration or decay
2. Listed in Bq, Ci, or in SI units 3. Not amount of contents but amount of radioactivity |
|
|

The box at the bottom of a radiological placard is where you find the Transportation Index. What is it?
|
Transport Index ranges from 1-10 based on maximum radiation in mrem/hhour at 1 meter from package measures degree of safety and hazard
|
|
|

How many personnel must be on a sampling team?
|
two personnel preferably 3
|
|
|
|
What must a HazMat Team do prior to leaving to take a sample?
|
Make sure that all items are prepared, Have a back up sample team ready in the same level of PPE as sampling team.
|
|
|
|
True of False Sample must be Decontaminated when finished with mission.
|
True, Very important to Decontaminate sample bags
|
|
|
|
What is an SOP/LERP
|
SOP stands for Standard Operating Procedure/ LERP stands for Local Emergency Response Plan
|
|
|
|
What are sample numbers?
|
Sample numbers are identification numbers used for taking sample. Sample numbers should be placed on primary sample container, exterior sample container, bag, and on the Change of custody form.
|
|
|
|
Is a chain of custody form necessary during the sample process.
|
a chain of custody form must be kept during the sample process, This is a legal document.
|
|
|
|
What is the minimum information on the Chain of Custody Form
|
1.Date, Time, Location of Sample
2. Identification of Sampler 3. Physical Description of sample 4. Sample number |
Sample Numbers are consecutive
|
|
|
What are some examples of Chain of Custody forms
|
Department of Defense (DD) form 1911
Department of the Army (DA) 4137 Centers for Disease Control Chain of custody form |
|
|
|
What happens if a sample is transfered to another person or entity
|
It must be documented on the Chain of custody form, and supervised by others
|
|
|
|
What is Computer Aided Management of Emergency Operations (CAMEO)
|
System of software applications used to plan and respond to chemical emergencies
|
Developed by EPA's Emergency Preparedness and Prevention Office (CEPPO)
|
|
|
What is the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry's (ATSDR)
|
Scientific and administrative database, provides access of info on hazardous substances from Superfund sites
|
Created by Area Location of Hazardous Atmospheres (ALOHA)
|
|
|
What is the Chemical Hazard Response Information System (CHRIS)
|
Program developed by the Coast Guard deals with Aquatic incidents reactivity on approximately 1200 chemicals
|
Useful for initial response, evacuation procedures, and PPE
|
|
|
What is MEDITEXT Medical Management
|
Contains information to assist in evaluating and treating acute exposures to INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS
|
Treatment for chemical release exposure's, updated regularly by Experts, hygienists, physicians, and safety professionals
|
|
|
What is HAZARDTEXT Hazard Management
|
Provides info needed for response to Spills, Leaks, Fires, or explosions of Hazardous Materials
|
|
|
|
What is the Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
|
Provided by the National Library of Medicine. Addresses the impact of more than 4000 substances on health and environment
|
ANIMAL STUDIES
|
|
|
What is the Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS)
|
Provides EPA health risk assessment info. Used to determine safe levels of human and environment exposure to chemicals
|
more than 450 Chemicals
|
|
|
What is the Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances (RTECS)
|
Offers toxicity of more than 135000 substances a world wide database offers specifics on health effects
|
|
|
|
Why are Maps Diagrams helpful at an incident
|
It helps those not familiar with incident location to prepare for incident.
|
Disadvantage may be that Maps may be out of date
|
|
|
What is a rapid vaporization
|
A release of Cryogenic Liquid above -130 Degrees
|
|
|
|
What is the temperature that a Cryogenic Liquid is happy
|
Below -150 Degrees
|
|
|
|
What is the expansion ratio for cryogenic liquids
|
1 to 560 - 1445 The higher the expansion ration the more gass produced and the larger the danger area becomes
|
|
|
|
What are Hepatoxins?
|
Chemicals that produce liver damage
|
|
|
|
What are Nephrotoxins?
|
Chemicals that produce kidney damage
|
|
|
|
What are Neurotoxins?
|
Chemicals that produce there primary toxic effects on the nervous system
|
|
|
|
Carbon Monoxide, and Benzene do what to the body
|
Decrease hemoglobin in th eblood of function; deprive hematological body tissues of oxygen
|
|
|
|
What happens when a chemical may cause pulmonary problems
|
the agent attacks the lungs
|
|
|
|
What do reproductive toxins target
|
The reproductive organs
|
|
|
|
What do Cutaneous Hazards affect
|
The skin
|
|
|
|
What are some methods for determining the pressure in bulk packaging of facility containers?
|
Gauging lines, fittings, Temperature of contents.
|
May be inaccurate could take up to 6 hours to change temp readings
|
|
|
Determine the amount of product in a damaged bulk package
|
Shipping Documents, Gauging devices, frostline. Look whats on the ground compared to number on shipping documents
|
|
|

A plug like device, used to separate contents of pipeline, clean pipelines and inspect pipelines is called what
|
A PIG
|
|
|
|
Types of damages to containers and tank cares are classified as
|
Damaged no release
Undamaged no release Damaged release Undamaged release |
|
|
|
a narrow split or break in the container metal, that can penetrate through metal is classified as what?
|
A crack.
Should not be moved until offloaded Considered Criticl |
|
|
|
a reduction in the thickness of the container shell MADE BY A BLUNT OBJECT
|
A Score
Should not be moved until offloaded considered critical |
|
|
|
A reduction in the thickness of the container shell made by a SHARP, CHISEL-LIKE OBJECT
|
A Gouge
Should not be moved until offloaded Considered Critical |
|
|
|
A deformation of the container metal caused by impact with a BLUNT OBJECT
|
A Dent
Should not be moved until offloaded Considered Critical |
|
|
|
What is the Guide to Hazardous Chemical Reactions
|
Contains information mixing of chemicals on 160 different chemicals
|
|
|
|
What organization is responsible for the Guide to Hazardous Chemical Reactions
|
NFPA 491M
|
|
|
|
What is the Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards
|
Provides reactive hazardson every reactive hazard that has been documented has over 5000 elements
|
|
|
|
What organization is responsible for Handbook of Reactive Chemical Hazards
|
Bretherick
|
|
|
|
What is the Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference
|
has 5000 chemicals deemed important and potentially hazardous. for chemical reactions Based on OSHA standard and Cancer research center
|
|
|
|
What Organization is responsible for the Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference
|
Lewis
|
|
|
|
What is the proper Tank Spacing for a Floating Roof, Fixed , or horizontal tank
|
Not over 150 feet in diameter, shall be 1/6th the sum of the adjacent tanks diameter but no less than 3 feet apart
|
|
|
|
what do tank venting and flaring systems do
|
Minimize the threat of a rupture
|
|
|
|
What are some local recourses for dispersion pattern predictions
|
Weather service, Computer Models, Industrial facilities, call colleges and universities, county, state, or federal agencies, HD, EPA, Coast Guard
|
|
|
|
Steps for determining the extent of the physical safety and health hazards within the endangered area
|
First, Determine concentration
Second, determine acceptable exposure limits |
|
|
|
How do you determine the potential outcomes within the endangered area and to improve the situation
|
Know the product, the container, the environment and know if it is a spill, leak or fire
|
|
|
|
What are the LEL evacuation limits determined by EPA
|
Less than 10%LEL - Continue working 10% - 25% LEL - Continue working with continuous monitoring greater than 25% withdraw
|
|
|
|
What are the three response objectives
|
Offensive, Defensive, and non-intervention.
|
Based on estimated outcomes, stage of the incident, Consider how to stop the even from occurring an to stop future events
|
|
|
How do you Change Applied Stress?
|
1. Move Stressor
2. Move Stressed System 3. Shield Stressed System |
|
|
|
How do you change the Breach size?
|
1. Chill Contents
2. Limit Stress Levels 3. Activate Venting System 4. Mechanical Repair |
|
|
|
How do you change quantity of of hazard released
|
1. Change container position
2. Minimize pressure differential 3. Cap off breach 4. Remove contents |
|
|
|
How do you change the size of the danger zone?
|
Barriers, Adsobents (Add to), Absorbents (Soak up), Dilution (add water), Reactants (Foam), Overpack
|
|
|
|
How to change exposures contacted
|
1. Provide Shielding
2. Begin evacuation 3. Personal Protective Equipment |
|
|
|
How to change the severity of harm
|
1. Rinse off contamination
2. Increase distance from source 3. Provide shielding 4. Provide Prompt medical |
|

