![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what line divides the pelvis into two regions?
|
the linea terminalis
|
|
|
what surface of the pelvic bone does the linea terminalis appear on?
|
the medial surface
|
|
|
which part of the pelvis is above the linea terminalis?
|
the false pelvis
|
|
|
which part of the pelvis is below the linea terminalis?
|
the true pelvis
|
|
|
what is the other name for the true pelvis?
|
the pelvic cavity
|
|
|
are abdominal or pelvic viscera found in the pelvic cavity?
|
both
|
|
|
what two anatomical landmarks lie in the same vertical plane in proper anatomical position?
|
the ASIS and anterior aspect of the superior edge of the pubic symphysis
|
|
|
where is the true pelvis with respect to the false pelvis?
|
true is inferior and posterior to false
|
|
|
does the false pelvis or true pelvis enclose the pelvic cavity?
|
true
|
|
|
what structures form the circumference of the pelvic inlet?
|
the linea terminalis (pectineal line of the pubis and arcuate line of the ileum) and sacral promontory
|
|
|
what are the bones of the pelvic wall?
|
sacrum, coccyx, pelvic bones inferior to the linea terminalis
|
|
|
the fusion of what three bones forms each pelvic bone?
|
the ilium, pubis, and ischium
|
|
|
what are the ligamentous components of the lateral pelvic wall?
|
the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligament
|
|
|
where does the sacrospinous ligament extend?
|
between the sacrum and coccyx and iscial spine
|
|
|
where does the sacrotuberous ligament extend?
|
posterior superior iliac spine to the medial aspect of the iscial tuberosity
|
|
|
which is more superficial, the sacrotuberous or sacrospinous ligaments?
|
sacrotuberous
|
|
|
what is the function of the sacrotuberous and sacrospinus ligaments?
|
they prevent the sacrum from tilting upward, and they convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina
|
|
|
what are the three major apetures of passage in the pelvis?
|
the obturator, the greater sciatic foramen, and the lesser sciatic foramen
|
|
|
what closes most of the obturator foramen?
|
the obturator membrane
|
|
|
what passage remains in the obturator foramne?
|
the obturator canal
|
|
|
what structures form the greater sciatic foramen?
|
the greater sciatic notch, the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments, and the spine of the ischium
|
|
|
what structures form the lesser sciatic foramen?
|
the lesser sciatic notch, ischial spine, sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments
|
|
|
what does the greater sciatic foramen provide communication between?
|
the pelvic cavity and lower limb
|
|
|
what does the lesser sciatic foramen provide communication between?
|
the perineum and gluteal region
|
|
|
what are the boundaries of the pelvic outlet?
|
the pubic symphysis (anterior), inferior border of the pubis, ramus of the ischium + iscial tuberosity (lateral), and sacrotuberous ligament and coccyx (posterior)
|
|
|
what passes through the pelvic outlet?
|
the terminal parts of the urinary and gi tracts
|
|
|
what does the pelvic diaphragm do?
|
closes the puelvic outlet inferiorly and forms both the muscular floor of the pelvic cavity and roof of the perineum
|
|
|
what parts of the gi system normally reside in the pelvis?
|
the rectum
|
|
|
which direction does the levantor ani muscle pull the rectum?
|
anteriorly
|
|
|
what is it called where the anorectal junction is pulled anteriorly?
|
the anorectal angle
|
|
|
how many lateral flexures does the rectum have when viewed anteriorly and why do they exist?
|
three, and they exist because of internal transverse folds
|
|
|
what is the rectal ampulla?
|
the lower part of the rectum that's expanded to hold fecal mass until defacation
|
|
|
what are the pelvic parts of the urinary system?
|
the ureters, urinary bladder, and terminal part of the urethra
|
|
|
what prevents urine reflux up the ureters?
|
the oblique manner in which they enter the bladder
|
|
|
where do the ureters enter the pelvic cavity in relation to the common iliac?
|
anterior to the common iliac
|
|
|
what crosses the ureters in the pelvis in males?
|
the ductus deferens
|
|
|
what crosses the ureters in the pelvis in females?
|
the uterine artery
|
|
|
what muscle forms the majority of the bladder and what type of muscle is it?
|
the detrusor, smooth muscle
|
|
|
what does the apex of the bladder point towards?
|
the superior edge of the pubic symphysis
|
|
|
where does the median umbilical ligament extend?
|
from the apex of the bladder to the umbilicus
|
|
|
what shape is the bottom of the bladder and where on it do the ureters enter and is its drain?
|
a triangle. the ureters enter on the upper corners and it drains from the lower corner
|
|
|
what is the trigone?
|
the smooth area between the ureter openings and the urethra
|
|
|
what is the uvula?
|
on the trigone's inferior angle, a small eminance produced by the middle lobe of the prostate
|
|
|
what forms the neck of the bladder?
|
where the inferolateral surfaces and base meet
|
|
|
what's under the neck of the bladder?
|
prostate in males, pelvic diaphragm in females
|
|
|
what are the parts of the urethra in males?
|
preprostatic, prostatic, membranous, and spongy
|
|
|
what are the male reproductive accessory glands?
|
the prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral glands
|
|
|
does the ductus deferns travel in the inguinal canal?
|
yes
|
|
|
what does the ductus deferens do?
|
carries spermatozoa from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
|
|
|
what artery does the ductus deferens bend around?
|
the inferior epigastric artery
|
|
|
does the ductus deferens cross the ureter anteriorly or posteriorly to it?
|
anterior to the ureter
|
|
|
what is the enlargement of the ductus deferens right before it joins the seminal vesicle?
|
the ampulla
|
|
|
what do the seminal vesicle and ductus deferns join to form?
|
the ejaculatory duct
|
|
|
what does teh ejaculatory duct connect with in the prostate?
|
the prostatic urethra
|
|
|
are the seminal vesicles lateral or medial to the ductus deferens on the base of the bladder?
|
lateral
|
|
|
what does the prostate surround?
|
the urethra
|
|
|
what is the urethral crest?
|
the raised portion of the posterior part of the prostatic urethra
|
|
|
what is the seminal colliculus
|
the raised portion of the prostatic urethra below the urethral crest
|
|
|
what is on either side of the urethral crest?
|
a urethral sinus
|
|
|
what empties into the urethral sinuses?
|
the ducts of the prostate
|
|
|
what are the accessory glands for the female reproductive system?
|
the greater vestibular glands
|
|
|
what are the three parts of the uterus?
|
the fundus, body, and the cervix
|
|
|
what position is the uterus usually in relative to the vagina?
|
anteverted (tipped anteriorly relative to the axis of the vagina)
|
|
|
what position is the uterine body usually in?
|
anteflexed (bent anterioly relative to the axis of the cervix
|
|
|
what does the uterine body usually rest on?
|
the bladder
|
|
|
where are mature eggs ovulated into?
|
the peritoneal cavity
|
|
|
is the vagina usually collapsed?
|
yes, except at its superior end where the cervix holds them apart
|
|
|
where is the vagina in relation to the urethra, urinary bladder, and rectum?
|
posterior to the urethra and urinary bladder, and anterior to the rectum
|
|
|
what is the median umbilical fold?
|
a fold over the urachus
|
|
|
what are the medial umbilical folds?
|
peritoneal folds over the umbilical artery remants
|
|
|
which part of the rectum is only covered by peritoneum on its anterior surface?
|
the middle third
|
|
|
which part of the rectum is covered by peritoneum on its anterior and lateral aspects?
|
the upper third
|
|
|
which part of the rectum is not covered by peritoneum?
|
the lowest third
|
|
|
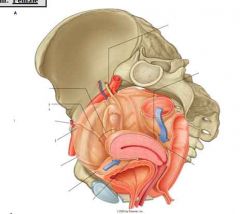
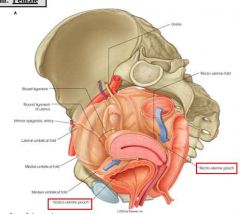
what is the retrovesical pouch?
|
only in males, the pouch between the bladder and rectum
|
|
|
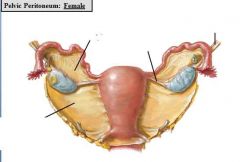
what is the broad ligament?
|
a double layer of peritoneum extending over the uterus to the lateral walls and floor of the pelvis. it keeps the uterus in position
|
|
|
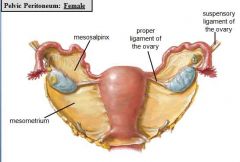
what are the three subcompartments of the broad ligament?
|
the mesometrium, mesosalpinx, and mesovarium
|
|
|
what is the mesometrium?
|
the portion of the broad ligament that attaches the body of the uterus to the pelvic walls
|
|
|
what is the mesosalpinx
|
the portion of the broad ligament between the uterine tube and ovary
|
|
|
what is the mesovarium
|
the portion of the broad ligament that supports the ovary
|
|
|
where is the mesovarium in relation to the mesosalpinx and mesometrium
|
perpendicular to the plane containing the mesovarium and mesosalpinx
|
|
|
what is the suspensory ligament of the ovary?
|
a ligament containging vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to and from the ovary. a continuation of the broad ligament
|
|
|
what attaches the inferior pole of the ovary to the uterus?
|
the (proper) ligament of the ovary
|
|
|
what travels between the broad ligament and deep inguinal ring?
|
the round ligament
|
|
|
what are the round ligament and ligament of the ovary to analagous to in males
|
the gubernaculum
|
|
|
what is the vesiculouterine pouch?
|
only in females, a peritoneal lined pounch between the bladder and the uterus
|
|
|
what is the recto-uterine pouch?
|
only in females, a peritoneal-lined pouch between the uterus and rectum
|
|
|
what is the lowest portion of a female's pelvic cavity when she's supine?
|
the recto-uterine pouch
|
|
|
in the female, is the urethra opening anterior or posterior to the vagina?
|
anterior
|
|
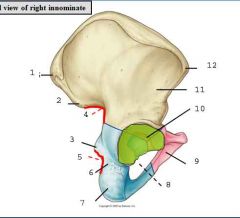
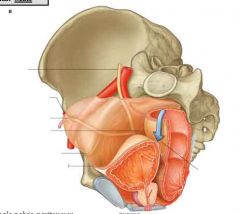
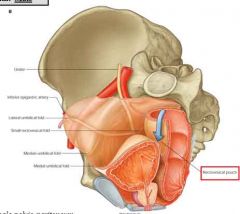
name them
|
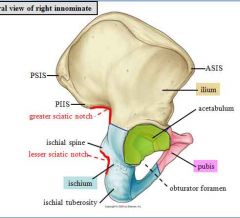
answers
|
|
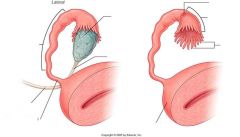
...
|
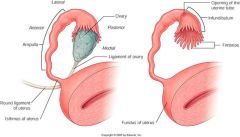
..
|
|
..
|
..
|
|
.
|
.
|
|
.
|
.
|

