![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
111 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Supine
|
Lying face up
|
|
|
Prone
|
Lying face down
|
|
|
Which cells give rise to the spinal cord?
|
Neuroepithelial cells of the neural tube
|
|
|
Neuroepithelial cells proliferate into which 3 layers?
|
Ventricular, mantle, and marginal layers
|
|
|
Mantle layer cells form what?
|
4 columns: 2 basal plates ventrally and 2 alar plates dorsally...gray matter
|
|
|
Marginal layer forms what?
|
Undergoes myelination and forms white matter
|
|
|
What do the basal and alar plates become eventually?
|
Basal becomes ventral horn matter while alar becomes dorsal horn matter
|
|
|
In general white and gray matter contain what?
|
White contains axons and gray contains neuron cell bodies
|
|
|
Ventricular layer forms what?
|
Ependymal layer (lining of the central canal)
|
|
|
What is the spinal cord enclosed in?
|
In the vertebral canal of the vertebral column
|
|
|
How many vertebrae are there and how are they subdivided?
|
33 vertebrae subdivided as follows: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral (fused), and 4 coccygeal (fused)
|
|
|
Fused sacral and coccygeal vertebrae form what?
|
Fused sacral vertebrae = sacrum
Fused coccygeal = coccyx |
|
|
Intervertebral Discs
|
Separate vertebrae in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions
|
|
|
Intervertebral foramina
|
Holes that permit passage of vessels and nerves into/out of vertebral canal
|
|
|
Does the spinal cord span the entire length of the veretebral canal? Why?
|
No, because of unequal growth rates.
|
|
|
Where does the spinal cord end?
|
At the conus medullaris (~L1-L2)
|
|
|
Where are the spinal cord englargements found? Why are they there?
|
1. Cervical enlargement: found in C5-T1, provide innervation to upper extremities
2. Lumbar enlargement: found in L1-S3, provide innervation to the lower extremities |
|
|
Meninges
|
Comprised of 3 connective tissue layers: dura matter, arachnoid, and pia
|
|
|
Epidural (extradural) Space
|
Area b/w dura mater and vertebral column filled w/fat
|
|
|
Dural Sac
|
Sac formed around the spinal cord, begins at the foramen magnum to S2
|
|
|
External Filum Terminale
|
End of dural sac, anchored to the coccyx. aka coccygeal ligament
|
|
|
Subdural Space
|
"Potential space", expandable if needed
|
|
|
Arachnoid Mater
|
Part of meninges, lines dural sac, not attached to dura
|
|
|
Subarachnoid Space
|
Located b/w the arachnoid and pia mater, has CSF (access via lumbar puncture)
|
|
|
Pia Mater
|
Part of meninges, cannot be separated from spinal cord
|
|
|
Internal Filum Terminale
|
Continuation of pia mater after ther conus medullaris, joins external filum and inferior limit of dural sac
|
|
|
Denticulate Ligaments
|
Sent from pia to fuse dura, anchor spinal cord w/in vertebral canal
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Segment
|
Portion of the spinal cord that develops from 1 somite (segments of mesoderm), has 1 pair of spinal nerves attached
|
|
|
How are spinal roots connected to the spinal cord?
|
By rootlets collectively known as the dorsal and ventral roots
|
|
|
Dorsal Root
|
Posterior, SENSORY
|
|
|
Ventral Root
|
Anterior, MOTOR
|
|
|
The spinal nerve divides into what 2 branches?
|
1. Dorsal primary ramus (DPR)
2. Ventral primary ramus (VPR) |
|
|
1. DR
2. VR 3. DRG 4. DPR 5. VPR 6. WRC + GRC 7. SN |
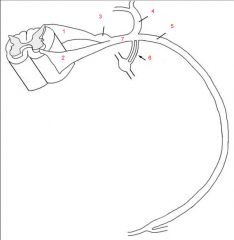
Name the parts.
|
|
|
Dorsal Primary Ramus (DPR)
|
Goes to the back region
|
|
|
Ventral Primary Ramus (VPR)
|
Travels around body wall and distributed primarily to the neck, trunk, and limbs
|
|
|
Dorsal Root Ganglion
|
Associated with the dorsal root
|
|
|
White Ramus Communicans (WRC)
|
Associated with sympathetic system
|
|
|
Gray Ramus Communicans (GRC)
|
Associated with sympathetic system
|
|
|
What are considered "typical" spinal nerves?
|
T2-T12 in which DPR travel to back and VPR travel to neck, trunk, limbs
|
|
|
What are considered "atypical" spinal nerves?
|
Spinal nerves in the cervical, lumbar, sacral, and T1 b/c VPR don't just travel around body wall--form nerve plxuses and travel out into limbs/extremities
|
|
|
Nerve Plexus
|
Network of mixing nerves, only formed by VPR
|
|
|
In general, how do spinal nerves exit the vertebral column?
|
Through the intervertebral foramina
|
|
|
How do cervical spinal nerves exit the vertebral column?
|
Exit SUPERIOR to their same numbered vertebra (i.e. C5 nerve passes through intervertebral foramen b/w C4 and C5 vertebrae)
|
|
|
How does the C8 nerve exit the vertebral column?
|
Since there's not C8 vertebra, it exits superior to T1
|
|
|
How do the spinal nerves after C8 exit the vertebral column?
|
They exit inferior to their corresponding vertebra
|
|
|
Cauda Equina
|
Collection of nerve roots in the lumbar and sacral regions
|
|
|
Dendrite
|
Carries impulse TOWARDS cell body
|
|
|
Axon
|
Carries impulse AWAY from cell body
|
|
|
Neuron terminology: Nucleus
|
Collection of cell bodies in CNS
|
|
|
Neuron terminology: Tract
|
Collection of axons in CNS
|
|
|
Neuron terminology: Ganglion
|
Collection of cell bodies in PNS enclosed by CT covering
|
|
|
Neuron terminology: Nerve
|
Collection of axons/dendrties in the PNS enclosed by CT sheath
|
|
|
Pseudounipolar
|
Type of neuron structure in which have 1 process that splits into 2 (very common in PNS)
|
|
|
Afferent Neuron (provide definition and neuron structure)
|
Conduct impulses TOWARDS CNS, pseudounipolar, sensory
|
|
|
Efferent Neuron (provide definition and neuron structure)
|
Conduct impulses AWAY from CNS, multipolar, motor
|
|
|
Somatic Structures
|
Derived from somites; include skeletal muscle, skin, bones, and joints, generally involved in moving
|
|
|
Visceral structures
|
Include organs, glands, blood vessels (inside body stuff), general involved in involuntary actions
|
|
|
What are the four general functional types of neurons?
|
GSA, GSE, GVA, and GVE
|
|
|
Mixed Nerves
|
Nerves that contain both sensory and motor neurons
|
|
|
GSA
|
Afferent impulse from skin, skeletal muscles, bones, ligaments and tendons
|
|
|
GVA
|
Afferent impulse from organs, glands, mucous membranes and blood vessels
|
|
|
GSE
|
Efferent impulse to skeletal muscle
|
|
|
GVE
|
Efferent impulse to smooth and cardiac muscle, secretory impulses to glands
|
|
|
Dermatome
|
Segment of skin associated with each spinal cord segment and enrve pair
|
|
|
Cutaneous Nerves
|
Nerves that innervate the skin
|
|
|
1. GSA
2. GVA 3. GSE 4. GVE |
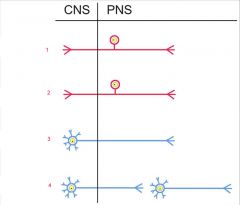
Name the type of general functional neuron.
|
|
|
Which ribs do not articulate with their own vertebral bodies?
|
1, 11, 12
|
|
|
How is it possible that we can do lumbar puncture?
|
Spinous processes separate in flexion
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the mamillary processes on lumbar vertebrae?
|
Attachment of muscles
|
|
|
Orientation of zygaphophyseal joints favor what type of mov't in the thoracic region?
|
Rotation
|
|
|
Orientation of zygaphophyseal joints favor what type of mov't in the lumbar region?
|
Flexion, extension, and lateral bending
|
|
|
Kyphosis
|
Abnormal increase in the thoracic curvature
|
|
|
Lordosis
|
Abnormal increase in lumbar curvature
|
|
|
Scoliosis
|
Abnormal lateral curvature accompanied by rotation of vertebrae
|
|
|
Spina Bifida
|
Verteral arches fail to close so meningnes/spinal cord may/may not protrude
|
|
|
Spina bifida occulta
|
Laminae of L5 and/or S1 fail to develop normally and fuse
|
|
|
Spina bifida cystica
|
Severe, herniation of meninges
|
|
|
Spondylolysis
|
Defect in vertebral arch (pars interarticularis), common site L4 and L5
|
|
|
Spondylololisthesis
|
Bilateral defect of pars interarticularis separating vertebrae into 2 pieces, anterior displacement of L5 body on sacrum
|
|
|
What are the extrinsic muscles of the back and what innervates them?
|
By CN XI/accessory nerve:
1. Trapezius By ventral/anterior primary rami: 2. Latissimus dorsi 3. Rhomboid Major 4. Rhomboid Minor 5. Levator Scapulae 6. Serratus posterior superior and inferior |
|
|
What are the intrinsic muscles of the back and what innervates them?
|
By dorsal/posterior primary rami:
(Superficial to deep) Splenius capitis Erector spinae Semispinalis capitis |
|
|
What do the muscles in the R suboccipital triangle do?
|
Total of 4 small muscles, assist w/extension and lateral bending at atlanto-axial joints, rotation of head at C1 and C2
|
|
|
What innervates the trapezius?
|
Accessory Nerve/CN XI
|
|
|
What innervates the latissimus dorsi?
|
Thoracodorsal nerve
|
|
|
What innervates the rhomboid major and minor muscles?
|
Dorsal scapular nerve
|
|
|
What innervates the levator scapulae?
|
Dorsal scapular nerve (also VPR C3-C4)
|
|
|
What innervates the splenius, semispinalis capitis, and erector spinae?
|
Dorsal primary rami
|
|
|
What is the action of the trapezius?
|
Elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula
|
|
|
What is the action of the latissimus dorsi?
|
Extends, adducts, medially rotate humerus
|
|
|
What is the action of the rhomboid major and minor muscles?
|
Retract scapula
|
|
|
What is the action of the levator scapulae?
|
Elevate scapula
|
|
|
What is the action of the splenius?
|
Extends, rotates head and neck
|
|
|
What is the action of the semispinalis capitis?
|
Extends and rotates head
|
|
|
What is the action of the erector spinae?
|
Extend head; extend and laterally flex vertebral column; regulate flexion of vertebral column
|
|
|
Epidural vs. Spinal block
|
Epidural: Anesthesia injected into epidural space
Spinal: Anesthesia injected into subarachnoid space (usually L3-L4) |
|
|
Why might a patient experience a headache after a spinal block?
|
B/c of reduced CSF volume
|
|
|
Superficial extrinsic back muscles move what?
|
NOT THE BACK! Move pectoral girdle and upper limb
|
|
|
Where does the trapezius originate? Insert?
|
Originate at occipital bone, ligamentum nucahe, and the spinous processes
Insert at spine of the scapula and acromonium; lateral 1/3 of clavicle |
|
|
Where does the latissimus dorsi originate? Insert?
|
Originates at thorocolumbar aponeurosis (T6-L5 vertebrae, iliac crest)
Inserts on medial side of the humerus |
|
|
Where do rhomboid major and minor originate? Insert?
|
Originate at vertebral spines
Insert at medial border of the scapula |
|
|
Where does levator scapulae originate? Insert?
|
Originate: Cervical transverse processes
Insert: Superior angle of the scapula |
|
|
What do the intrinsic back muscles move?
|
Move the head and vertebral column
|
|
|
Where do the splenius muscles originate? Insert?
|
Originate: Spinous processes
Insert: Skull and cervical transverse processes |
|
|
Where does the erector spinae originate? Insert?
|
Originate at sacrum and iliac crest
Insert on ribs and transverse processes |
|
|
What are the 2 main classifications of joints? What specific types of joints fall under them?
|
1. Synarthroses (fixed): Fibrous and Cartilaginous
2. Diarthroses (movable): Synovial |
|
|
What are the types of fibrous (solid) joints?
|
1. Sutures
2. Gomphosis 3. Syndesmoses |
|
|
What are the types of cartilagenous (solid) joints?
|
1. Synchondroses
2. Symphyses |
|
|
Which types of synovial joints are monoaxial?
|
1. Pivot (trochoid)
2. Plane (Gliding) 3. Hinge |
|
|
Which types of synovial joints are biaxial?
|
1. Saddle
2. Condylar |
|
|
Which types of synovial joints are multiaxial?
|
1. Ball and socket
|
|
|
What borders the triangle of auscultation?
|
1. Trapezius
2. Latissimus dorsi 3. Medial border of scapula |

