![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
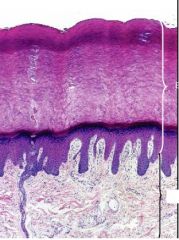
What layers are found here?
|
Dermis and epidermis
|
|
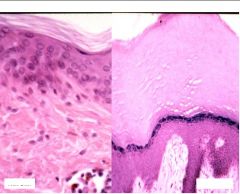
What two types of skin here?
What else is different about them? |
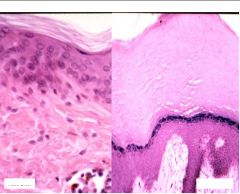
Thick skin and thin skin
Thick: a thick cornified layer and stratum lucidum Thin: thin cornified layer, lacks a stratum lucidum and has hair follicles |
|
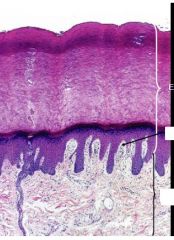
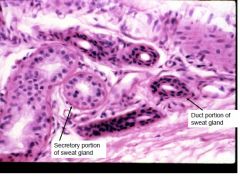
What structure here?
|
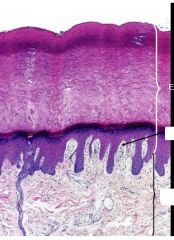
Dermal papillae:
also notice layers of epithelium Stratum Basal Spinosum Granulosum Corneum Papillary layer Reticular layer Simple sweat gland (Eccrine c simple coiled tube) -Duct |
|
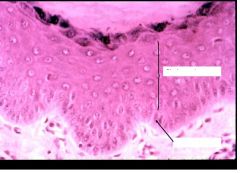
Which layer here?
Unique chars? |
Stratum basal and stratum spinosum
Melanocytes (with colorless cytoplasm) Prickle cells |
|
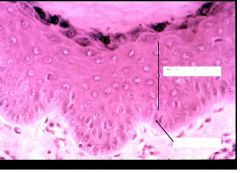
What layers here?
|
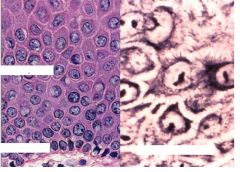
Stratum Basal (melanocytes here too)
Stratum spinosum (prickle cells) (stratum germinativum) |
|
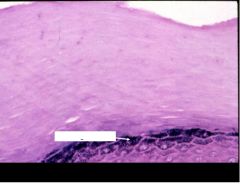
What is this layer?
Other layers or features? |
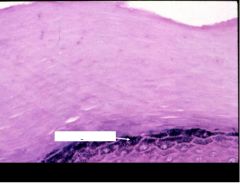
Stratum granulosum (has keratohyalin granules in the cytoplasm)
notices stratum corneum above |
|
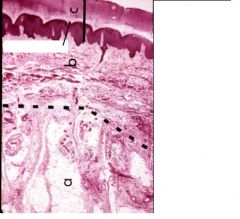
What is here?
|
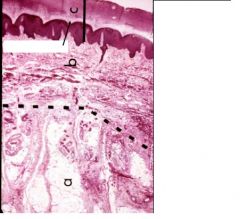
Stratum lucidum
Reticular layer Papillary layer Stratum corneum dermal papillae (dermal ridge) |
|
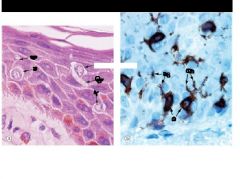
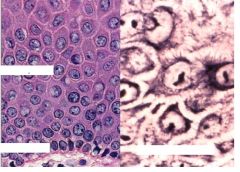
What cell? Others?
|
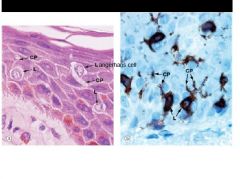
Stratum spinosum
|
|
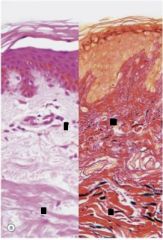
What present?
|
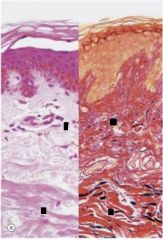
Papillary and reticular layers
|
|
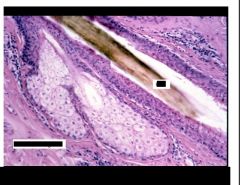
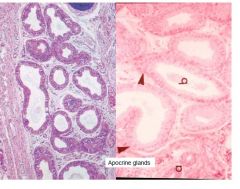
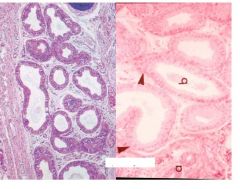
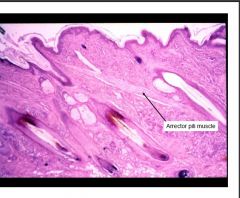
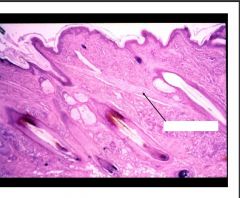
What is present?
|
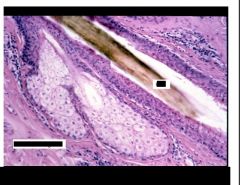
Sebaceous gland (holocrine excretion)
and hair follicle (arrector pili muscle) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
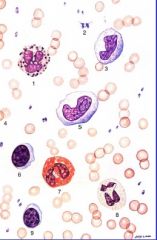
What cells present?
|
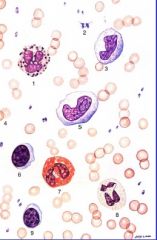
Leukocytes-
neutrophils eosinophils basophils monocytes lymphocytes |
|
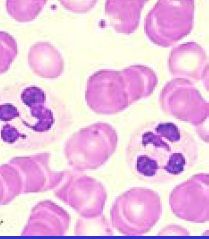
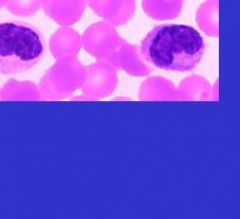
What cell is here?
|
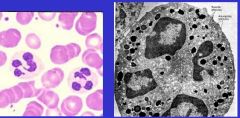
It is a Granulocyte, a Neutrophil with polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) or polys
|
|
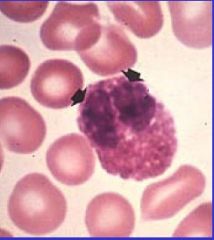
What cell is here?
|
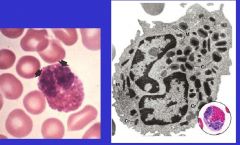
Eosinophil-bilobed nucleus, elongated crystalloid in large, specific granules
|
|
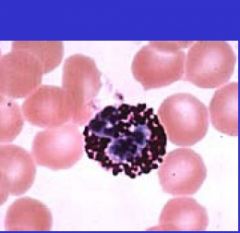
What cell is here?
|
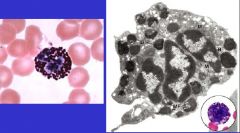
Basophil
multilobed nucleus with 2-3 lobes prominent granules that stain deep violet or purple in electron appear as two separate nuclei, granules are filled with electron-dence material |
|
What cell here?
|
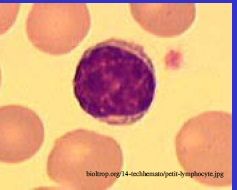
Lymphocyte
-usually small -nucleus is slightly indented and dark staining -basophilic but scanty, with cytoplasm forming a thin ring IN EM nucleus is round but can be indented slightly, small golgi, few mitrochondria and a large number of free ribosomes |
|
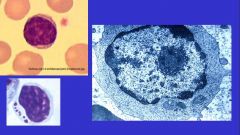
What cell?
|
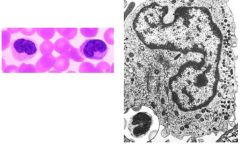
Monocyte-
large cells nucleus is oval or horseshoe or kidney shaped -nucleus is pale staining (vesicular) -cytoplasm is abundant and has blue-grey fine granules like "ground glass" IN EM nucleus indented, the GOlgi is well developed and the cytoplasmic granules are electron dense and homogeneous |
|
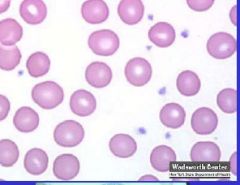
What cell?
|
Platelets (thrombocytes)
-non-nucleated disc like cell fragments come off the megakaryocyte |
|
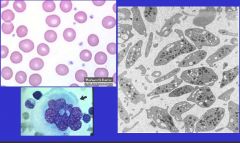
What cell is this?
|
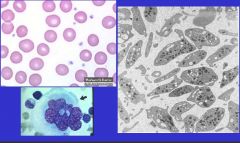
Megakaryocyte
cell giant EM membrane-bound platelets may contain many cytoplasmic organelles like mitoch or fragments of Golgi apparatus. The most prominent organelles are the electron-dense granules |
|
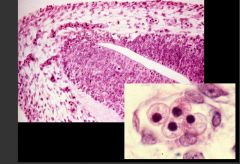
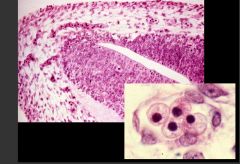
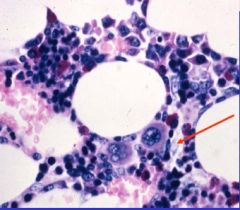
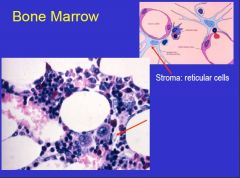
What structure is this?
|
Red marrow section
-many nucleated cells of developing blood cell lines. |
|
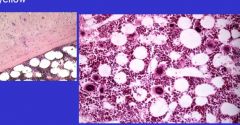
|
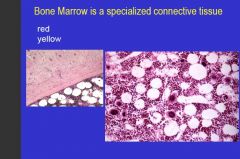
abundant fat cells between developing blood cells.
Large, thin-walled blood vessels called sinusoids present |
|
|
|
|
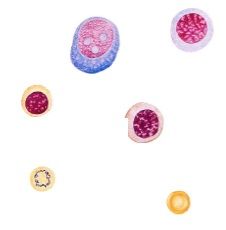
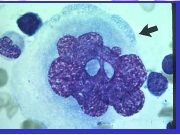
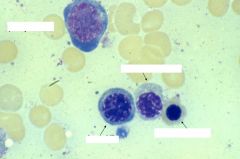
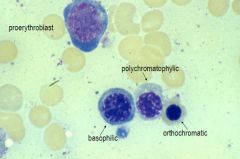
What cells here?
|

Basophilic Erythroblast
-cytoplasm strongly basophilic nucleus begins to condense and no nuclei -basophilia due to large number of ribosomes making hemoglobin Polychromatophilic erythroblast -Nucleus is smaller with more compact heterochromatic -cytoplasm is blue-grey or mottled cytoplasmic staining reflects a decrease in number of polyribosomes and an increase in the amount of hemoglobin Orthochromatic erythroblast (normoblast) -has small, pyknotic nucleus, the cytoplasm is acidophilic and nucleus will be extruded at this stage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
During devel
1.) Nu lobated 2.) cell volume decreases and is filled with granules (specific to cell type neutrophilic, eosinophilic or basophilic metamyelocytes) Metamyelocyte -nu indented (horseshoe or kidney shaped) -specific granules dominate -band cells can form, which are immediate precursors of mature forms of 3 metamyelocytes |

