![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Structure: Triglycerides |
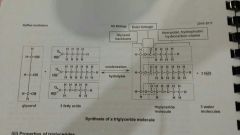
1. Macromolecule 2. Condense glycerol + 3 fatty acids 3. Ester linkage btw OH and COOH
|
|
|
Structure & properties : Glycerol |
Alcohol w/ 3 carbon ea w/ OH grp
- polar molecule - form h-bond w/ water - soluble in water |
|
|
Structure & Properties: Fatty Acids |
Long non-polar, hydrophobic hydrocarbon chains w/ carboxyl grp - saturated: only c-c and c-h single bonds - unsaturated: has c=c double bond ♢Trans: no kink ♢Cis: kink Properties - non-polar: many c-h bonds - ✖h-bond w/ H2O: insoluble : hydrophobic - weak acids: carboxyl dissociate |
|
|
Properties: Triglyceride |
1. Non-polar: ✖H-Bond w/ H2O: insoluble |
|
|
F (x): Triglyceride |
1. Major fx: energy storage (38kJg-1) - 2x as much energy per gram ♢ higher proportion of C-H atoms + lower proportion of O2 for =vilant mass of c.hydrates. ○higher prop. C-h bonds for oxidation: more atp: compact energy store ♢Insoluble: does not affect water potential: efficient storage molecule 2. Production of Metabolic H2O during oxidation 3. Protect internal organs, thermal insulation, improve buoyancy, reservoir for fat soluble vitamins |
|
|
Structure: Phospholipids |
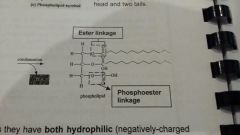
Component: 2 non-polar hydrophobic CH tails + glycerol + phosphate head Bond: glycerol - phosphate = phosphoester linkage Glycerol - tail = ester bond
|
|
|
Properties: Phospholipids |
- Amphipathic: Both h.phobic and h.phillic ♢ h.phillic charged phosphate head interact w/ h2o ♢ in h2o, aggregate and form hydrophobic core |
|
|
Fx: phospholipids |
1. Major comp of cell membranes ♢phospholipid bilayer ○acts as boundary- compartmentalisation ○hydrophobic core: low permeablilty for polar and charged molecules - barrier ♢move laterally -> membrane fluidity ♢liposome: vesical surrounded by phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
Properties: Cholesterol |
1. Insoluble in h2o, soluble in organic solvants 2. Slightly amphipathic, hydrophilic oh grp and hydrophobic ring structure 3. Fused ring structure is rigid => mechanical stability to fluid lipid layer |
|
|
Fx: cholesterol |
1. Regulates membrane fluidity - @high temp, cholesterol restricts phospholipid movement, preventing overly fluid membrane 2. Prevents close packing at low temperature |

