![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
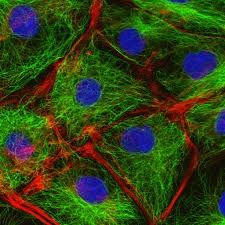
Cytoskeleton |
Changes protein scaffolding also enable some cells to move or change shape |
Includes hollow micro tubules, micro filaments, and intermediate filaments
ex: holds organelles in place and move them around |
|
ER |
Form tubes and channels throughout the cytoplasm, |
Endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes attached in eukaryotes |
|

Golgi |
Consists of series of membranous sacs |
Golgi apparatus
exported from the cells to pass through ER into Golgi |
|
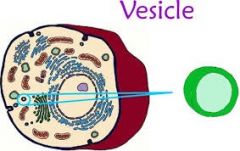
Vesicles |
Packaged in spherical membrane enclosed vesicles that appear to pinch off the Golgi membranes |
Fuse with the plasma membranes
some vesicles deliver their contents to other organelles |
|

Lysosomes |
Special vesicles in animal cells and some other eukaryotes |
Contains enzymes that break down the cells old macromolecules for recycling |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Present in most plant cells |
Vesicles that enlarge after maturing
contain water, organic acids, digestive enzymes, pigments and salts |
|
|
Centrioles |
Tubular structures in cells of animals, and some fungi or algae |
Participate in cell reproduction such as mitosis
consists of cylindrical bundles of micro tubules |
|
|
Cilla |
Short flagella |
Move by whipping in an oar like motion
also help move materials along in cell |
|
|
Flagella |
Long cellular appendages specialized for locomotion |
Ex: found in eukaryotes
Many protists and certain animal cells have flagella |
|
|
Cell/plasma membrane |
Membrane at the boundary of every cell |
Ex: in all cells
selective barrier for ions and molecules |
|
|
Cell wall |
Stiff covering of plasma membrane |
Ex: in plant and algae cells
Constructed partially of cellulose |
|
|
Ribosomes |
Organelle consisting of two subunits |
Ex: RNA
Ribosomes function at the site of protein synthesis |
|
|
Cytoplasm |
The entire contents of the cell, except the nucleus |
80% water and usually colorless |
|
|
Cytosol |
Gelatin like portion of cytoplasm |
Cytosol bathes the organelles of the cell |
|
|
Organelles |
Organized structure within a cell |
Ex: eukaryotic cells
have a specific function |
|
|
Nucleolus |
Structure in the nucleus that synthesizes ribosomal RNA |
Largest structure in the nucleus |
|
|
Cell theory |
Theory that organisms are composed of cells and these cells are all derived from pre-existing cells |
Idea that cells are basic units of life |
|
|
Prokaryotes |
Cell that does not have a membrane enclosed nuclei or organelles |
Simplest living cells |
|
|
Eukaryotes |
Membrane enclose nuclei or organelles |
Larger and more complex than eukaryotes |
|
|
Nucleus |
Central core contains protons and neutrons in eukaryotic cells |
Houses chromosomes |
|
|
Chromosomes |
Thread like structure of nucleic acids and protein |
Ex: found in nucleus
made from double stranded DNA |
|
|
Nucleotide |
Located in the nuclear region |
Chromosomes attached to plasma membrane in an area of the cell |
|
|
Plasmids |
Circular DNA molecules |
Bacteria usually contains one or more smaller DNA molecules called plasmids |
|
|
Tissue |
Group of cells with a common structure and function |
Our bodies are made up of tissue |
|
|
Organ |
Organized group of tissues |
Ex: kidney is an organ
carries specialized functions in a multicellular organism
|
|
|
Organ system |
Anatomical structures that work together to perform a special function or task |
Organ systems work together |
|
|
Organism |
Single living thing |
Ex: dogs, humans, trees |
|
|
Colony |
Distinct group of microorganisms growing together |
Colony of micro organisms |
|
|
Multicellular |
Organism consisting of many cells |
Humans are multicellular |
|
|
Cell differentiation |
Process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell |
Less to more. Becoming more specialized |

