![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
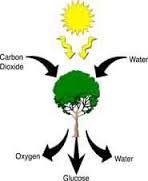
Photoautotroph
|
Autotrophs that gets energy from the sun
|
|
|

Photosynthesis
|
The process of a organisms getting their energy from sunlight.
|
Plants do this. Photosynthesis involves the sun.
|
|
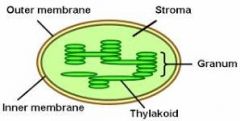
Thylakoids
|
Membranes that form closed sacs located in plants and algae in the chloroplast. Float inside the cell.
|
Thylakoids are in plant and algae cells.
|
|
|
Grana
|
Stack of thylakoid sacs.
|
Found in plant and algae cells.
|
|
|
Stroma
|
Space surrounding the thylakoids. Enzymes in Stroma catalyze the formation of sugar from carbon dioxide and water using light energy captured in the thylakoids.
|
Found in plant and algae cells.
|
|
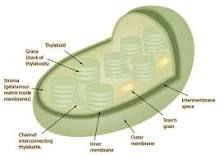
Chloroplast
|
Organized outer structure that separates the thylakoid from the cytoplasm and regulates flow of materials into and out of the chloroplast.
|
Chloroplasts have thylakoid sacs in them.
|
|
|
Chlorophyll
|
Green pigment found in the thylakoids. Contained in two forms, absorb light in violet/blue and orange/red ranges, not green.
|
The green light that is not absorbed is what gives leaves the green color.
|
|
|
Light reactions
|
Convert visible light into chemical energy, it's products are used in the Calvin cycle, powers sugar production in Calvin cycle. Pigment molecules in the thylakoids absorb light then it's converted.
|
Light reactions involve photosynthesis.
|
|
|
Calvin cycle
|
The energy of the molecules from the the light reactions is used to make 3 carbon sugars from carbon dioxide in a series of reactions.
|
Product of light reaction is used in the Calvin cycle.
|
|
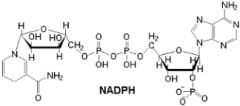
NADPH
|
Reduced form of NADP+, the end of electron flow lights reactions, provides protons and electrons needed to reduce carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle.
|
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
|
|
|
PGAL
|
Split 3 carbon phosphate molecule. Requires one molecule of ATP and NADPH from the light reaction.
|
Pant Cells use PGAL to coninue on the Calvin circle.
|
|
|
Photoinhibition
|
A decline in photosynthesis, some substances damage chloroplasts by reacting with pigments and proteins.
|
Damaged chloroplasts in plant or bacteria cells.
|
|
|
Saturation point
|
When photosynthesis increases to its maximum point and rate levels off.
|
Carbon dioxide concentration increases the rate of photosynthesis.
|
|
|
Limiting factors
|
Effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
|
Light, water, temp, and nutrients are limiting factors in a forest.
|
|
|
Rubisco
|
Enzyme that incorporates carbon dioxide into sugars in the Calvin cycle. Able to bind with oxygen or carbon dioxide
|
Oxygen Interferes with carbon fixation
|
|
|
Photorespiration
|
Result is that the organism loses fixed carbon atoms instead of gaining them. May help to reduce photo inhibition.
|
Plants and bacteria can do photorespiration
|
|
|
C4 plants
|
Two systems of carbon dioxide fixation that occurs In different parts of the leaves, twice as efficient, grow more rapidly than C3 plants. Evolve in warm climates
|
Plants, 4 carbon acid
|
|
|
Stomates
|
Many plants reduce their water loss by partly closing their stomates. When they are closed carbon dioxide levels get very high.
|
Plants use stomates.
|
|
|
Aerobic cell respiration
|
Cell respiration occurring with the presence of oxygen. During this energy released as glucose gradually oxidizes and breaks down to carbon dioxide.
|
|
|
|
Chemoautotroph
|
Bacteria that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic substances such as iron, sulfur, and other minerals. Form sugars from carbon dioxide
|
Bacteria. Found where there is no sunlight are chemo autotrophs.
|
|
|
Photoautotroph
|
Plants that depend on photosynthesis for both energy and carbon compounds.
|
Flowers. Plants are photoautotrophs
|

