![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
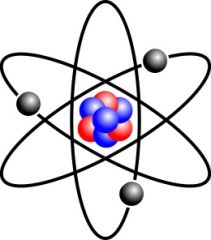
Atom |
Basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by electrons |
1) Hydrogen atom 2) We can't see hydrogen atoms with our eyes. |
|
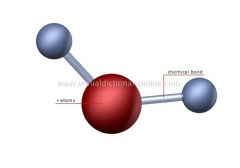
Molecule |
Electrically neutral group bonded by chemical bonds |
1) Water 2) Water is a molecule which is H2O |
|
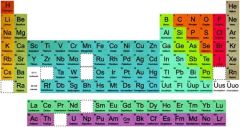
Element |
Substances that cannot be separated into simpler substances |
1) Ion Neon 2) We can see elements in periodic table. |
|
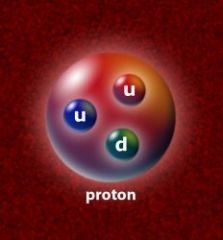
Proton |
Positively charged elementary particle |
1) uud 2) There are 8 protons in oxygen. |
|
Electron |
A stable particle in all atoms |
1) Negative charge 2) Carbon have 8 electrons. |
|
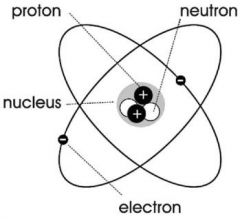
Neutron |
Elementary having no charge |
1) Neutral charge 2) Carbon have 6 neutrons. |
|
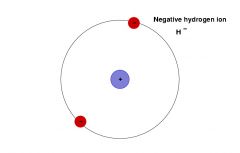
Ion |
Electrically charged atom or group of atoms losing or gaining electrons |
1) H+ OH- 2) Ion can have either have negative and positive charge. |
|
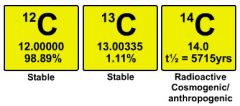
Isotope |
A chemical element the same protons in the nucleus |
1) Carbon 2) Carbon have 3 kinds of isotope. Carbon skeleton. |
|
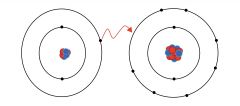
Ionic bond |
Two ions formed by moving one or more electrons |
1) NaCl 2) NaCl is bonded by ionic bond. |
|
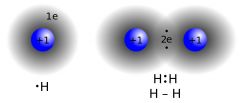
Covalent bond |
The bond formed by sharing electrons |
1) HCl 2) Covalent bond shares their electron shell. |
|
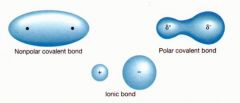
Polar covalent bond |
A type of bond which electrons are shared unequally |
1) CO3 2) There are polar covalent bond and covalent bond. |
|

Law of conversation of matter |
The law of matter cannot be created or destroyed |
1) Chemical formula 2) When we dissolve something , law of conservation of matter involves in chemical formula. |
|
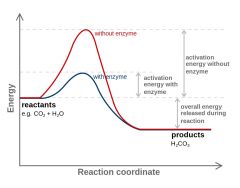
Activation energy |
The least amount of energy required to move atoms or molecules |
1) Chemical formula 2) We can see activation energy from chemical formula and chemical reactions. |
|
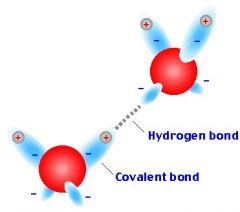
Hydrogen bond |
A type of chemical bond when hydrogen has a covalent bond |
1) Ethanol 2) Ethanol is bonded by hydrogen bond. |
|

PH scale |
A scale that shows substances PH |
1) PH scale paper 2) We can see if something is acid from PH scale. |
|
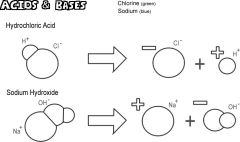
Acid |
A substance with a sour taste |
1) Lemon 2) Lemon is acid and its lower than 7 in PH scale. |
|
Base |
The principal element (base) |
1) Subatomic particles. 2) When we dissolve a substance the base is the result. |
|
Organic compounds |
A compound containing hydrocarbon group |
1) Glucose 2) Organic compounds are made with hydrocarbon. |
|
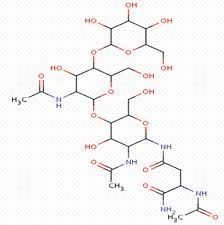
Macromolecules |
A very large molecule |
1) Plastics 2) macromolecule is made if small molecules. |
|

Carbohydrates |
Organic compounds including hydrogen and oxygen |
1) Bread Milk 2) We need to eat carbohydrates to have energy.
|
|
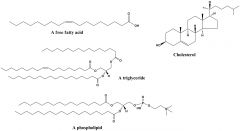
Lipids |
A organic compounds insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol |
1) Cells of animal 2) Lipids are soluble in water and it protect animal genes. |
|

Proteins |
The plant or animal tissue with a lot of molecules |
1) Beans Grains Nuts 2) Beans contain a lot of proteins. |
|
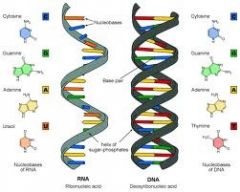
Nucleic Acids |
Complex compounds with high molecular weight |
1) DNA, RNA 2) Nucleic Acids contain genetic informations. |
|
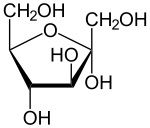
Monosaccharides |
A simple sugar |
1) Disaccharide, polysaccharide 2) monosaccharide contains C H O. |
|
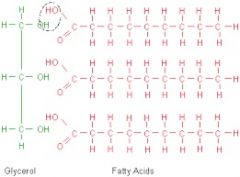
Fatty acids, glycerol |
Consist of a long hydrocarbon chain |
1) Perfumes, Cosmetics 2) Fatty acids and glycerol consist a long hydrocarbon chain. |
|
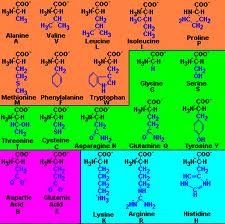
Amino acids |
An organic compounds that contains at least one amino group |
1) Valine, Lysine 2) There's 22 kinds of amino acids. |
|
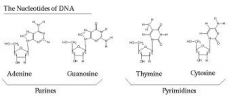
Nucleotides |
Any group of molecules that build block of DNA or RNA |
1) DNA, RNA 2) There is DNA and RNA in nucleotides. |
|
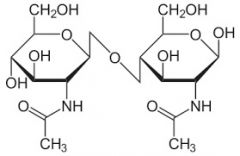
Disaccharide |
Group of carbohydrates |
1) Milk sugar 2). Disaccharide is a group of carbohydrates. |
|
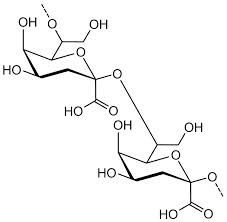
Polysaccharide |
A carbohydrate containing more than three monosaccharide |
1) Starch, Glycogen 2) Polysaccharide have more than three monosaccharide. |
|
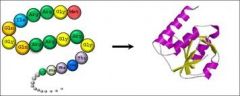
Polypeptide |
Chain of amino acids linked together |
1) Hemoglobin 2) Hemoglobin have 1 polypeptide. |
|
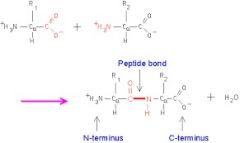
Peptide Bond |
A covalent bond formed by joining the carboxyl group |
1) Dipeptide 2) Peptide bond is formed by carboxyl group. |
|
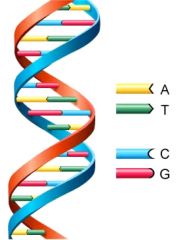
DNA |
Genetic information |
1) A T G C 2) DNA contains genetic information that decide our appearance. |
|
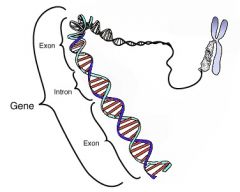
Gene |
The basic physical unit of heredity |
1) Heredity 2) Gene decide our heredity. |

