![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Synthesis
|
Reactions that combine smaller molecules to form larger, more complex ones.
|
Na plus Cl.
The bacteria synthesized ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. |
|
|
Biosynthesis
|
Synthesis reactions that take place in living organisms.
|
Photosynthesis makes sugars inside living organisms. This is an example of biosynthesis.
|
|
|
Decomposition
|
Reactions that break down large molecules into smaller ones.
|
ATP ➡️ ADP + Phosphate
Decomposition, carried out by decomposing heterotrophs, broke down the organism, releasing energy. |
|
|
Cell Respiration
|
A decomposition pathway that provides energy for cell function by breaking down larger molecules.
|
Breaking down sugars for energy is an example of cell respiration.
|
|
|
Aerobic Respiration
|
Cell respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen, using oxygen as the oxidizing agent that takes decomposed molecules' electrons.
|
Breathing fuels aerobic cell respiration, providing cells with oxygen for cell respiration.
|
|
|
Anaerobic Respiration
|
Cell respiration that doesn't use oxygen, instead using other molecules and fermenting lactic acid.
|
Holding your breath forces your body to do anaerobic cell respiration, which occurs without oxygen.
|
|

Fermentation
|
"The release of energy during the chemical breakdown of food, especially sugars, in the absence of oxygen."
|
Making alcohol is fermentation done by yeast organisms.
|
|
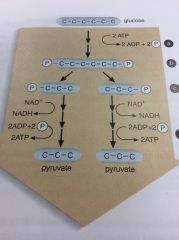
Glycolysis
|
The first stage of respiration, where enzymes start to oxidize glucose and split it into smaller sugars.
|
C6H12O6 - 2C3H6O3.
Glycolysis breaks down glucose, making a tiny amount of ATP. |
|
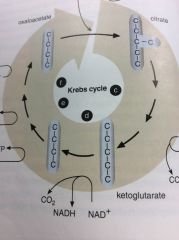
Krebs Cycle
|
The second stage of respiration, which completely oxidizes sugars into CO2.
|
After an enzyme took the third carbon off a 3-carbon molecule, the Krebs Cycle made the remaining 2-carbon molecule into carbon dioxide molecules.
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Organelles where the Krebs Cycle and ETS take place.
|
Mitochondria are cell's powerhouses because they perform respiration, releasing energy.
|
|
|
Cristae
|
Folds in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion that have enzymes for ETS, ATP formation, and the Krebs Cycle.
|
The cristae hold many enzymes necessary for energy release.
|
|
|
Matrix
|
The fluid-filled inside of a mitochondrion.
|
The matrix is the interior of the powerhouse.
|
|
|
Lactate/lactic acid
|
A three carbon acid formed when oxygen is not present.
|
Anaerobic Respiration makes lactic acid when there's no oxygen to use. This is why activity where you can't get enough oxygen burns - there's acid when there isn't oxygen.
|
|
|
Pyruvate/pyruvic acid
|
A three carbon acid made in the partial oxidation of molecules from earlier in glycolysis.
|
The final product of glycolysis.
|
|
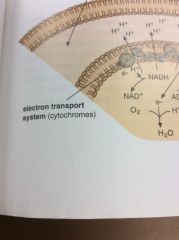
Cytochromes
|
Proteins in the electron transport system, embedded in the inner membranes of mitochondria.
|
They move electrons step by step through the system of cell respiration.
|
|
|
NADH/FADH2
|
Two molecules that easily gain and lose electrons, assisting in reduction and oxidation in cell respiration.
|
NAD+ can be reduced to NADH, and NADH can be oxidized into NAD+.
|
|
|
Alcoholic Fermentation
|
The process by which yeast ferments molecules into alcohol.
|
Moonshiners take advantage of alcoholic fermentation.
|
|
|
Lactic Acid Fermentation
|
One by-product of anaerobic respiration, which happens when pyruvate is made into lactic acid.
|
Happens when there isn't oxygen, it burns.
|
|
|
ETS
|
The last stage of aerobic respiration, where almost all of ATP is formed.
|
This makes 34 ATP molecules.
|
|
|
Facultative Aerobes
|
Bacteria that can survive with either anaerobic or aerobic respiration.
|
They're flexible, switching back and forth.
|
|
|
Obligate anaerobes
|
Bacteria that are poisoned by oxygen, making all of their ATP from fermentation.
|
They are aerophobic!
|
|
|
Obligate Aerobes
|
Organisms that cannot make it long without oxygen.
|
Humans are obligate aerobes.
|
|
|
Hydrolysis
|
A process that decomposes molecules by inserting H and OH into the chemical bonds.
|
Starch to sugars by way of hydrolysis.
|

