![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oxidising power |

Back (Definition)
|
|
|
Explain trend in bond enthalpy down Group 7 |
Cl2 to I2 - decreases down the group as atomic radius increases -> greater shielding -> weaker attraction between the bonding electrons and the nucleus.
F2 does not fit the trend - atoms are so close together that the lone bonding pair of electrons for each atom causes repulsion |
|
|
State and explain trend in boiling points down Group 7 |
Boiling points increases down the group Size of diatomic molecule increases -> bigger Van der Waals forces -> more energy needed to overcome VdW forces |
|
|
State and explain trend in electronegativity down Group 7 |
Decreases down the group. Bonding electrons closer to the nucleus -> less shielding -> nucleus attracts bonding pair of electrons more strongly
So element has greater electronegativity |
|
|
State the trend in appearance in Group 7 |
Colour of the elements gets darker down the group |
|
|
Trying out the tests |
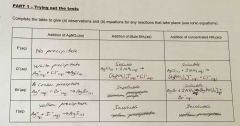
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Trying out the tests |
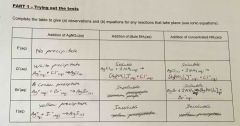
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Oxidising power |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Reducing power |
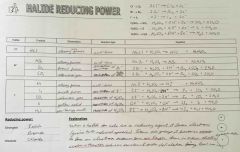
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Uses of Chlorine |
Safe - low concentrations used
Purify drinking water &assuming pools
HClO chloric (I) acid - kills microorganisms |
|
|
Disproportionation reaction |
Type of redox reaction where an element in the reaction undergoes oxidation and reduction simultaneously, forming 2 products. |
|
|
Disproportionation reaction |
Type of redox reaction where an element in the reaction undergoes oxidation and reduction simultaneously, forming 2 products. |
|
|
Redox reaction |
Reaction where both reduction and oxidation occur |
|
|
Disproportionation reaction |
Type of redox reaction where an element in the reaction undergoes oxidation and reduction simultaneously, forming 2 products. |
|
|
Redox reaction |
Reaction where both reduction and oxidation occur |
|
|
Reducing agent |
An electron donor |
|
|
Disproportionation reaction |
Type of redox reaction where an element in the reaction undergoes oxidation and reduction simultaneously, forming 2 products. |
|
|
Redox reaction |
Reaction where both reduction and oxidation occur |
|
|
Reducing agent |
An electron donor |
|
|
Oxidising agent |
An electron acceptor |

