![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where are the vestigial pads in the horse? What are these called? |
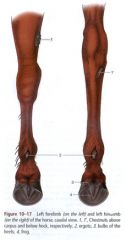
These chestnus are located in the thoracic and pelvic limbs:
In the forelimb chestnuts are located proximal to the carpus In the hind limb chestnuts are located distal to the hock |
|
|
What is the rudimentary metacarpal/metatarsal pad called in the horse? Where are they located?
|
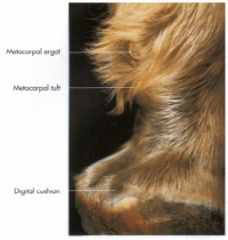
Ergots
Located in all four limbs, caudal to the fetlock Embedded in a tuft of hair |
|
|
What do the flexor and extensor retinaculum hold down in the horse?
|
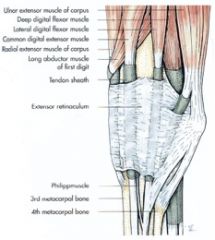
Extensor retinaculum
Binds down the extensor tendons on the dorsal surface of the carpus Flexor retinaculum Binds down the flexor tendons in the carpal canal Connects the accessory carpal bone with the radial carpal and 2nd carpal bones |
|
|
What are the fused digits of the ox? What is the rudimentary metacarpal?
|
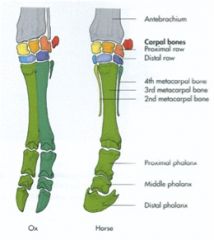
Third and fourth digits are fused. The fifth digit is rudimentary up top. |
|
|
How many metacarpals do the horse have? What are they numbered? What are they called?
|
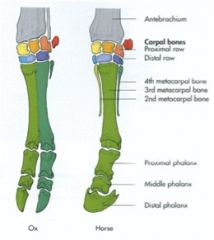
They have three, called 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metacarpals. 2 and 4 are splint bones, 3 is a cannon bone.
|
|
|
How many phalanges does digit 3 have in the horse?
|
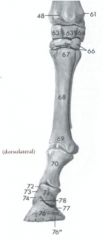
Proximal phalanx – long pastern bone (70)
Middle phalanx – short pastern bone (71) Distal phalanx – coffin bone (76) |
|
|
How many sesamoid bones does the horse have in the thoracic limb?
|
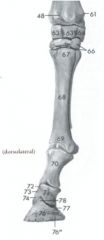
3 - two proximal (medial and lateral) (83) and one distal sesamoid bone (84)
|
|
|
What is the metacarpophalangeal joint called in the horse and ruminant?
|
Fetlock joint
|
|
|
What is the proximal interphalangeal joint called in the horse and ruminant?
|
Pastern joint
|
|
|
What is the distal interphalangeal joint called in the horse and ruminant?
|
Coffin joint
|
|
|
What is the distal sesamoid bone called in the horse?
|
Navicular bone
|
|
|
How many phalanges do digits 3 and 4 have in ruminants?
|
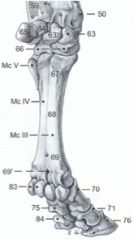
Proximal phalanx (70)
Middle phalanx (71) Distal phalanx (76) |
|
|
How many sesamoid bones do ruminants have?
|
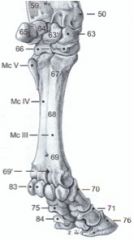
3
Proximal sesamoid bones (2 per digit) - axial and abaxial (83) Distal sesamoid bone (1 per digit) (84) |
|
|
What are the extensors of the large animal forearm?
|
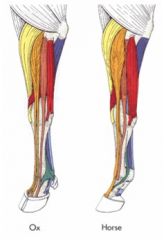
Extensor carpi radialis m.
Common digital extensor m. - (Medial and lateral heads in the ruminant) Lateral digital extensor m. Ulnaris lateralis m. (a flexor!) Extensor carpi obliquus m. |
|
|
What else is extensor carpi obliquus m. known as?
|
Abductor pollicis longus m.
|
|
|
What is the OIAI for externsor carpi radialis m. of the large animal?
|
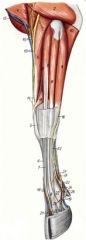
O: Lateral supracondylar crest and radial fossa of the humerus, deep antebrachial fascia, intermuscular septum between ECR and common digital extensor m.
I: Metacarpal tuberosity Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend and fix the carpus and flex the elbow joint |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the common digital extensor m. of the horse?
|
O: Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral border of the radius, lateral collateral ligament of the elbow, lateral surface of the ulna, antebrachial fascia (2-3 heads – radial, humeral and ulnar)
I: Extensor process of distal phalanx and dorsal surface of proximal and middle phalanges Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend the carpus and digit and flex the elbow joint |
|
|
What is the OIAI of the lateral digital extensor m. of the horse?
|
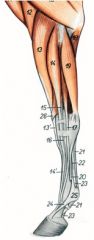
17
O: Lateral tuberosity of the radius, lateral collateral ligament of the elbow, body of the ulna, lateral border of the radius, intermuscular septum I: Dorsal aspect of proximal phalanx Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend the carpus and digit |
|
|
What is the OIAI of the common digital extensor m. of the ruminant?
|
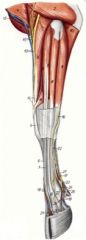
Two bellies:
Medial belly (medial digital extensor, proper extensor of digit III) Lateral belly (common extensor of digits 3 and 4) has superficial and deep heads O: Medial belly (6) – radial fossa and lateral epicondyle of the humerus O: Lateral belly (7) Superficial (humeral) head – radial fossa and lateral epicondyle of the humerus, fascia over elbow joint Deep (ulnar) head – proximal third of caudolateral aspect of radius and corresponding craniolateral aspect of ulna, proximal interosseous space including interosseous ligament I: Medial belly – Middle phalanx of digit 3; distal phalanx of digit 3 in the ox I: Lateral belly – extensor processes of distal phalanges of digits 3 and 4 Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend the carpus and digits and flex the elbow joint |
|
|
How many bellies and heads do the common digital extensor m. of the ruminant have?
|
Two bellies:
Medial belly (medial digital extensor, proper extensor of digit III) Lateral belly (common extensor of digits 3 and 4) has superficial and deep heads |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the lateral digital extensor m. of the ruminant?
|
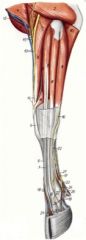
(8)
O: Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral aspect of the radial head, lateral collateral ligament of the elbow, caudolateral surface of the ulna, fascia I: Axial tendon to the dorsal surface of middle phalanx of digit 4, abaxial tendon to the distal phalanx of digit 4 Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend the lateral digit and carpus and flex the elbow joint |
|
|
In the ruminant, what number is the lateral digit?
|
Digit 4
|
|
|
Where do the common digital extensor m. and lateral digital extensor m. insert on the ox?
|
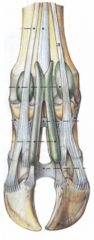
Common digital extensor m.
Medial belly (medial digital extensor) Inserts on middle and distal phalanges of digit 3 Lateral belly (common extensor of digits 3 and 4) Inserts on distal phalanges of digits 3 & 4 Lateral digital extensor m. Inserts on middle and distal phalanges of digit 4 |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the ulnaris lateralis m. of the horse?
|
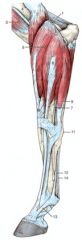
O: Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
I: Short tendon – lateral surface and proximal border of the accessory carpal bone I: Long tendon – metacarpal IV proximally in the horse; fused metacarpal III/IV in the ruminant Innervation: Radial n. Action: Flex the carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What is the OIAI of extensor carpi obliquus m. of horses and ruminants?
|
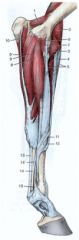
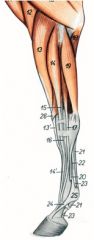
(11 in horse - shown)
O: Horse – Craniolateral middle of radius O: Ruminant – Lateral surface of distal half of radius, craniolateral edge of ulna, interosseous ligament I: Horse – Metacarpal II proximally I: Ruminant – Mediopalmar surface of metacarpal III/lV proximally Innervation: Radial n. Action: Extend the carpus |
|
|
What are the coverings of the extensor tendons called as they pass through the retinaculum? What are their function? Are they in both horse and ox?
|
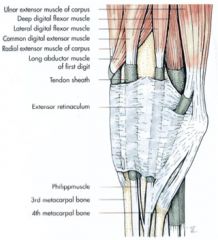
Synovial sheaths
Surrounds the flexor tendons and facilitates their movements against each other and over the palmar surface of the digit Yes - in both horse and ox. |
|
|
In fibrinous necrosis, what are the 3 main causes in order?
|
1 Vasculitis 90% (collagen vascular disease)
2 Uremia 3 TB |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the flexor carpi ulnaris m.?
|
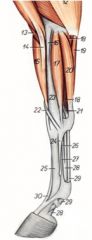
O: Humeral head – Medial epicondyle of the humerus
O: Ulnar head – Medial surface and caudal border of the olecranon I: Proximal edge of the accessory carpal bone Innervation: Ulnar n. Action: Flex the carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the flexor carpi radialis m. of the large animal?
|
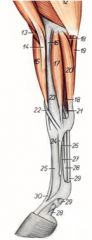
O: Medial epicondyle of the humerus
I: Proximal end of metacarpal II in the horse, metacarpal III/IV in the ruminant Innervation: Median n. Action: Flex the carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What is the OIAI of the pronator teres m. of the ruminant? Which ruminant is it most prominent in?
|
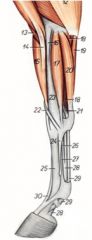
O: Medial epicondyle of the humerus
I: Medial border of the radius Innervation: Median n. Action: Slight flexion of the elbow More prominent in the goat |
|
|
What is the OIAI of the superficial digital flexor m. in the horse?
|
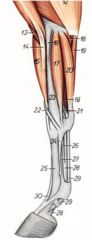
(21, 29)
O: Medial epicondyle of the humerus and caudodistal radius (check ligament) I: Proximal and middle phalanges Innervation: Ulnar n. Action: Flex the digit (except the distal interphalangeal joint) and carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
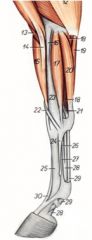
What are the OOOIAI of the deep digital flexor m. of the horse? (hint, hint)
|
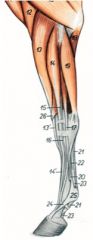
O: Humeral head (22) – Medial epicondyle of the humerus
O: Ulnar head (18) – Medial aspect of the olecranon O: Radial head – Mid caudal surface of the radius I: Flexor surface of the distal phalanx Innervation: Median and ulnar nn. Action: Flex the digit and carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What are the check ligaments of the horse?
|
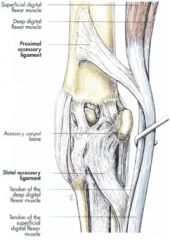
Proximal check ligament:
Accessory ligament of the superficial digital flexor tendon Courses between the radius and the superficial digital flexor tendon Proximal to the carpus Distal check ligament: Accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon Courses between the palmar carpal ligament and the deep digital flexor tendon Distal to the carpus |
|
|
Where is the navicular bursa in the horse?
|
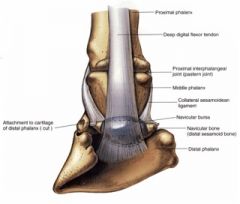
Located between the deep digital flexor tendon and the distal sesamoid (navicular) bone
|
|
|
Do the navicular bursa and coffin joint communicate in the horse?
|
no
|
|
|
What are the OIAI of the superficial digital flexor m. in ruminants?
|
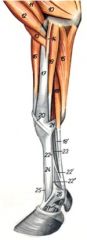
O: Medial epicondyle of the humerus
I: Proximal palmar surface of the middle phalanx of digits 3 and 4 Innervation: Ulnar n. Action: Flex the digits and carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What do the bellies of the superficial digital flexor m. of the ruminant course with?
What do the bellies join to form? |
Divides into two bellies – superficial and deep:
Superficial belly (18) courses within the fascia of the flexor retinaculum, superficial to the carpal canal Deep belly (18’) courses within the carpal canal (fused with deep digital flexor m.) Bellies join distal to carpus |
|
|
What is the OOOIAI (hint) of the deep digital flexor m. of the ruminant?
|
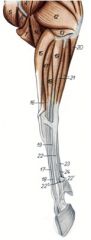
O: Humeral head – Medial epicondyle of the humerus
O: Ulnar head (20) – Olecranon O: Radial head – Caudal surface of the head of the radius I: Flexor process of distal phalanx of digits 3 and 4 Innervation: Median and ulnar nn. Action: Flex the digits and carpus and extend the elbow joint |
|
|
What ligament prevents the fetlock from overextending? What nerve innervates it? Where does it arise from and insert?
|
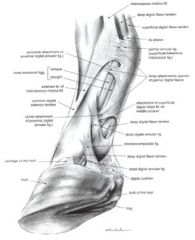
Interosseus
Prevents the fetlock from overextending Innervated by ulnar n. Arises from the distal row of carpal bones and proximal metacarpal III Inserts on the proximal sesamoid bones, and the common digital extensor tendon by way of extensor branches |
|
|
What are the OIAI of the interosseus m. of the ruminant?
|
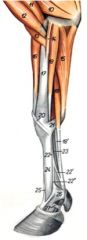
O: Proximal palmar surface of Metacarpal III/IV and palmar carpal ligament
I: Proximal sesamoids; branches to extensor tendons; accessory ligament to superficial digital flexor m. (22’) Innervation: Ulnar n. Action: Support fetlock joints, oppose tension of deep flexor on distal phalanx |
|
|
How is the interosseus ligament different in the horse than in the ruminant?
|
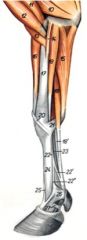
Interosseus composed of both fleshy and tendinous tissue. In young animals it may be almost entirely fleshy
Somewhat more muscular than in the horse although it is predominantly tendinous in older cattle |
|
|
If you cut through the just proximal to the equine carpal joint and then more distally past the carpal joint, what would you cut through?
|
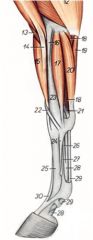
Proximally
Interosseous Distal check ligament Deep digital flexor tendon Superficial digital flexor tendon Distally Interosseous Deep digital flexor tendon Superficial digital flexor tendon |

