![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which are the 8 UN Millenium Development Goals?
|
1) Eradicate extreme poverty/hunger
2) Achieve universal primary education 3) Promote gender equality 4) Reduce child mortality 5) Improve maternal mortality 6) Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and others 7) Ensure environmental sustainability 8) Global partnership for development |
|
|
Which role does Information Systems Research play?
|
Environment (People, Organizations, Technologies) contribute business needs to IS Research by requirements and field testing.
IS Research builds design artifacts & processes which are constantly evaluated (design cycle) and applicated in the appropriate environment. IS Research contributes to the knowledge base and the KB, consisting of foundations (frameworks, models, methods etc.), contributes applicable knowledge to the IS Research. |
|
|
IPAT
|
Impact = People * Affluence * Technology
|
|
|
Threshold hypothesis
|
In every society, some period of economic growth brings improvements in quality of life, but only until a certain threshold. From that point on, more economic growth may cause quality of life to deteriorate.
|
|
|
Main problems of economic system
|
* Irreversible damages to natural system
* Depletion of human resources * Social and human costs |
|
|
Def. "Economy"
|
From oikonomia (gr. "household management"). Composed of oikos, "house" and nemein, "to manage".
|
|
|
Chrematistike vs. oikonomia
|
"Chrematistike" is the non-natural way to earn money and turn a profit whereas "oikonomia" is the covering of basic needs.
|
|
|
How can achievement of happiness be categorized?
|
Hedonic: Short-lived, induced by senses and pleasures, can often by acquired by wealth.
Eudaimonic: Produced by virtuous behavior, aims at the excellence in all its dimensions. Less immediate but longer-lived – cannot be produced by wealth. |
|
|
Happy Planet Index
|
HPI = happy life years (life satisfaction * life expectancy) / ecological footprint
|
|
|
Def. "Sustainable Development"
|
Development should be sustainable so that it meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Sustainable dev. implies limits imposed by present technology and social organization on environmental resources and by the ability of the biosphere to absorb effects of human activities. The former can be managed and improved.
|
|
|
Sustainability strategies
|
Sufficiency <----- Efficiency -----> Consistence
|
|
|
Sufficiency strategy
|
"How much is enough or too much, respectively?"
Change in social dimensions: Consuming the right quantity of material goods and services, a quantity that is just necessary and sufficient for optimal health, well-being and happiness, escaping both the Charybdis of underconsumption (poverty) and the Scylla of overconsumption. |
|
|
Efficiency strategy
|
"How can we increase scope of economic activity?"
Optimize products and proceccess and recycle rather than innovation. Mixture between offensive and defensive behavior. Reduce material quantity. |
|
|
Consistency strategy
|
"How can we align economy and environment?" Non-interfering vs. Synergetic and symbiotic.
Materials and processes are innovated to make material flows more consistent with natural behavior. |
|
|
How will the global footprint (GtCO2e) change concerning ICT?
|
IC Footprint will increase from 0.54 (2002) to an estimated 1.43 by 2020 (+164%). The embodied carbon will increase from 0.11 to 0.35 (+218%), whereas the footprint from use will increase from 0.43 to 1.08 (+151%).
|
|
|
By how much can the overall global footprint be reduced by 2020?
|
Global footprint can be reduced to 30 GtCO2e instead of 51,9 (compared to business-as-usual).
Using various SMART-Systems the ICT-caused footprint can be reduced by 6.2 GtCO2e saving 1014 billion US-$. |
|
|
How do energy costs affect server costs?
|
In 1996, power and cooling costs were about 16% of the actual hardware costs. In 2010, power/cooling costs take about 72% of the total costs.
|
|
|
What is power compared to energy?
|
Power is measured in kW and rather a spot-measurement. Energy is cumulated power, described in kWh and typically measured over the entire year.
|
|
|
What measurement points exist to measure energy turnover at a data center?
|
1) Total facility power (all energy consumption of data center)
2) IT Equipment Power (energy cons. by IT hardware including fans and power supplies) 3) Server power (only energy cons. by IT hardware) |
|
|
What is PUE and DCiE and what is it good for?
|
Power Usage Effectiveness
PUE = Total facility energy / IT equipment energy Data Center Infrastructure Efficiency DCiE = 1 / PUE * 100% Usage: - Improve operational efficiency - Benchmark with competitors - Measure progress - Repurpose power |
|
|
What is DH-UR and DH-UE and what is it good for?
|
Deployed HW Utilization Ratio
DH-UR = No. servers running live apps / Total no. deployed servers Deployed HW Utilization Efficiency DH-UE = Min. no servers necessary to handle peak load / Total no. of deployed servers Usage: Same as PUE/DCiE |
|
|
What can be done to improve energy efficiency?
|
- Improve internal design of supporting equipment (SE)(less power, same job)
- Match sizing of SE to actual IT load - Use free cooling or similar to reduce power consumption of SE - Use energy and power efficient IT equipment - Reduce required IT equipment maintaining level of provided computational work (e.g. by virtualization) |
|
|
What is a virtual machine / hypervisor?
|
Virtual machine: Computing environment abstracting hardware resources of physical computer
Hypervisor: Virtualization platform that enables to run multiple OS on a single "host" computer. |
|
|
What benefits does server virtualization have?
|
- Lower cooling and power costs
- Reduced space requirements - High availability and disaster recovery - Increased provisioning - Increased resource utilization - On-demand computing |
|
|
What is a private and a public cloud?
|
Private cloud sits behind the corporate firewall, the public cloud does not. A hybrid cloud has some parts of both a private and a public cloud.
|
|
|
Comparison of private vs. public cloud
|
Infrastructure owner: Third party / Enterprise
Scalability: Unlimited, on-demand / Ltd. to local infrastructure Control and management: manipulate only VM / high level of control -> more expertise needed Cost: lower / high Performance: Hard to achieve guaranteed perf. / guaranteed perf. Security: Concernings reg. private data / Highly secure |
|
|
What kinds of cloud levels exist?
|
IaaS --> SaaS (PaaS) -> HuaaS
based on Hardware, completed by administration and business support |
|
|
What kinds of IaaS exist?
|
Higher Infrastructure Services, e.g. Google BigTable or Basic Infrastructure Services e.g. Computational, Storage or Network.
Or simply a resource set can be provided, such as Amazon EC2. |
|
|
What kinds of SaaS/PaaS exist?
|
Applications like Google Docs or application services like opensocial or OpenID.
Part of SaaS are PaaS that provide a programming or execution environment, like Django or Windows Azure, resp. |
|
|
What are the benefits of Cloud Computing?
|
- Lower financial investment / nearly unlimited resources
- Large data centers can be operated more efficiently (cooling, power, ...) - Hardware is used at the right load, no under- or over-privisioning - Load balancing over many customers, higher server utilization |
|
|
Now, what is Green in ICT all about?
|
- Energy efficiency
- Main focus: Data centers - Use metrics to measure progress - Reduce hardware / increase utilization - Use energy efficient data centers to lower footprint - Better user behavior is most important |
|
|
Basic model of economic development
|
Shareholders have an ownership of an enterprise. This enterprise is controlled by management.
Principals maximize shareholder value and maximize enterprise's efficiency. Agents maximize bonuses and increase size of enterprise. |
|
|
Agency theory and its problems
|
??? Beschreibung Agency Theory ???
Problems: - Unlikely to maximize enterprise value to shareholders by ignoring interests of other stakeholders - Generating long-term value is determined by enterprise's relationship to critical stakeholders - Stakeholder theory arises from rejection of the idea that enterprises should maximize benefit of single stakeholder or shareholders, resp. |
|
|
Stakeholder Theory
|
Stakeholder in an organization is a group/individual who can affect or is affected by the achievement of organization's objectives. (employees, owners, customers, society, suppliers, ...)
Their stakes: Wages / income growth / beneficial products / taxes, jobs, ecological aspects / technology transfer, steady sales source |
|
|
What is "value"?
|
Capacity of a good, service or activity to satisfy a need or provide a benefit to person/legal entity.
|
|
|
Value dimensions
|
Value can be either financial, non-financial or time (which can be of speed of access to benefit, provided time savings or extension of time horizon)
|
|
|
Value Creation and Destruction for Shareholders
|
Financial
- Create: profits/income/stock appreciation - Destroy: poorly managed enterprise, failing products, risk of losing investment Non-financial - Create: pride of ownership, autonomy, reliable source of income - Destroy: Stress created by uncertainties, bad product publicity (might destroy pride of ownership) Time - Create: Long-term financial security, investments (products, advance technology, quality, HR), long term strategic partnership with suppliers - Destroy: Short-term considerations might destroy long-term viability and enterprise's success |
|
|
Quadrants of Shareholder Value (Shareholder Value Matrix)
|
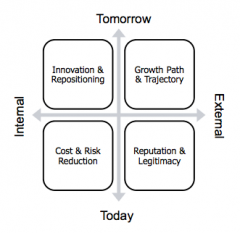
|
|
|
Five Stages Of Sustainable Development
|
???
|
|
|
Chrematistic vs. oikonomic organizations
|
???
|
|
|
How are resources the basis for profitability?
|
Things like Patents, Market share, Financial resources are basic resources that combine to an industry attractiveness.
Together with basics like process technology, low cost inputs (cost advantages) and brands, product technology and marketing (differentiation advantage) as a competitive advantage, this leads to the rate of profit in excess of the competitive level. |
|
|
What is a strategy?
|
Strategy is the match an organization makes between its internal resources and skills and the opportunities and risks created by its external environment.
|
|
|
What a Porter's five forces?
|
- The industry (jockeying for position among current competitors)
- Threat of new entrants (new entrants bring new capacity, desire to gain market share and often substantial resources) - Bargain power of suppliers (suppl. can raise prices, reduce quality -> squeeze profitability) - Bargain power of customers (force down prices, demand higher quality or more services and play competitors off against each other) - Thread of substitute products and services (?) |
|
|
What are the next steps according to Porter?
|
1) Position the enterprise so that its capabilities provide best defense against competitive forces
2) Influence forces in oder to improve firm's position 3) Exploit changes before opponents recognize imbalances |
|
|
What is a resource?
|
All assets, organizational process, firm attributes, information, knowledge etc. controlled by an enterprise that enables the firm to conceive of and implement strategies that improve its efficiency and effectiveness.
-> Physical, human, organizational and financial capital |
|
|
What is an enterprise?
|
Unique bundle of resources that determines which external circumstances afford opportunities and which pose threats.
-> Only few resources are productive on their own (cooperation/coordination of resource bundles) - capability means capacity of a bundle to perform a task/activity. Resources -> Capability -> Competitive Advantage -> Competitive advantages = strenghts/weaknesses to create cost/differentiation (dis-)advantages in competitive markets |
|
|
What is a (sustained) competitive advantage?
|
A value creating strategy that is not implemented by another competitor at the same time.
Sustained when (see above) and other enterprises cannot duplicate benefits of strategy. |
|
|
What kinds of resources exist?
|
- Valuable
- Rare - Imperfectly imitable - Non-substitutable |
|
|
Valuable resources
|
Enable an enterprise to conceive of implement strategies that improve effectiveness/efficiency.
-> Exploit Opportunities, neutralize threats |
|
|
Rare resources
|
Not possessed by a large number of (potentially) competing business.
Combination of valuable and rare resources can be seen as describing first-mover advantages. |
|
|
Imperfectly imitable resources
|
Cannot be obtained by enterprises that don't possess them. (e.g. because they are unique historical, socially complex or causally ambiguous)
|
|
|
Non-substitutable resources
|
Cannot be replaced by similar or different resources.
|
|
|
Resource-based view
|
Resources (capitals) support capabilities (technology, design, production, distribution, service, procurement) which creates competitive advantage (cost differentiation, future position, preemption).
|
|
|
RBV vs. Stakeholder Management
|
??
|
|
|
How can sustainable strategies be applied to the four shareholder value quadrants?
|
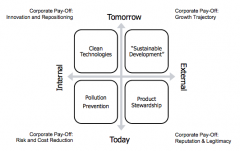
|
|
|
What are the sustainable development drivers?
|
Pollution/Consumption/Waste drives their prevention.
Society/Transparency/Connectivity drives product stewardship. Population poverty/inequity drives sust. dev. Disruption/footprint/clean technology drives clean technologies (wtf?) |
|
|
Definition "Pollution prevention"
|
New product or process that allowed for pollutant source reductions or that involved in-process recycling.
|
|
|
Pollution prevention vs. control
|
Poll. control: Emissions/effluents are trapped, stored, treated or being disposed of. Entails expensive, non-productive equipment and diminishing returns.
Poll. prevention: E/e are reduced, changed or prevented. Requires employee involvement -> reduces pollution during manufacturing process while producing scalable goods. |
|
|
Benefits of pollution prevention
|
- Cost-savings (less/no pollution control devices)
- Increased productivity/efficiency - Cut emissions -> Significant savings resulting in cost advantage |
|
|
Product stewardship (SCM for sustainable products)
|
??
|
|
|
Benefits of product stewardship
|
- Reduce material waste/energy consumption, impact of existing product design to reduce liability
- Exit environmental hazardous businesses - Develop new products with lower life cycle costs - Gain preferred or exclusive access to important, limited resources - Establish rules, regulation or standards that are uniquely tailored to the firm's capabilities |
|
|
Role of ICT in product stewardship
|
Idenfity and optimize patterns in inventory/transportation
Data gathering combined with product development process -> Case studies -> Simulations -> Intelligence to handle complex web of information |
|
|
Clean Technologies
|
Product stewardship leads to clean technologies.
- Improve existing products - Create new products/services |
|
|
Sustainable Development
|
Plan/invest into future's technologies (balancing all aspects of sustainable development, economic/environmental/social) and create productive forces by improving capital/labor/resource usage in development countries.
|
|
|
Sustainable Development Vision
|
Roadmap to the future showing necessary for products/services evolvement and corresponding new capabilities.
Enterprise-specific, cannot be copied easily. |
|
|
Sustainable Development Considerations
|
??
|
|
|
Competitive advantage and transparency
|
??
|
|
|
Substituting services for products
|
??
|
|
|
Competitive advantages of natural-resource-based view
|
Lower cost by adjustments: Minimize emissions, effluents & waste (continuous improvements needed)
Preempt competitors by reorientation: Minimize life cycle costs of products (stakeholder integration needed) Secure future position by growth: Minimize environmental burden of firm growth and development (shared vision needed) |
|
|
Balanced scorecard
|
- Helps to translate vision into set of performance measures. Their success can be measured in four categories: Financial, internal business, innovation and learning & customer perspective.
- Management tool that supports successful implementation of corporate strategies |
|
|
Breaking down a vision into initiatives
|
1. Develop a vision
2. Develop strategy to implement vision 3. Develop strategic objects to realize strategy 4. Translate strategic obj. into tangible goals/actions 5. Transform vision/strategy into the BSC's 4 sets of performance measures. |
|
|
What are generic measures for the 4 BSC categories?
|
Financial: ROI / economic value added
Customer: Satisfaction / retention / market / account share Internal business: Quality / response time / cost / new product introductions Innovation/learning: Employee satisfaction / information system availability |
|
|
Lag and Leading Indicators
|
Lag indicators: Outcome measures (e.g. loss ratio, claims frequency, claims severity)
Lead indicators: Performance drivers (e.g. underwriting/claims quality audit) |
|
|
Incorporating sustainability
|
Enhance existing perspectives vs. add non-market perspective
Sustainability is not directly strategically relevant (in traditional sense) -> the 4 BSC perspectives are equipped with "sustainability questions" and a non-market perspective is added |
|
|
Sustainability aspects in BSC perspectives
|
Financial: financial cost reduction by Green IT
Customer: satisfy Green Customers Internal business: Manage material/energy most eco-efficiently Innovation/learning: Create a sustainability valuing culture Non-market: How can Green IT initiatives help to improve partnership with local comm./NGOs? |
|
|
Steps to create a (sustainable) BSC
|
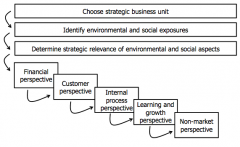
|
|
|
Generic lag/leading indicators
|
s. Folien
|
|
|
Strategy map
|
Strategic elements in the four perspectives are linked (hypothetical cause-and-effect-relationships) (e.g. improved eco-efficiency of products leads to improved value for green customers)
Strategy map unique for enterprise, but design patterns can be used as reference models and be customized/refined. |
|
|
Eco-efficiency analysis
|
= Product or service value / environm. influence
Achieved by serving Competitively-priced and human needs satisfying goods/services while reducing ecological impacts. Used to evaluate and communicate progress of environmental initiatives. |
|
|
Eco-efficiency categories
|
Broad areas of environmental influences or business value:
- Product/service value - Env. influence (creation) - Env. influence (use) |
|
|
Eco-efficiency aspects
|
General types of information related to a category – describe what is to be measured.
Product/service value: Volume/mass, monetary, function Env. influence (creation): Energy/materials/nat. resources consumption Env. influence (use): Packaging waste, energy consumption, disposal emissions |
|
|
Eco-efficiency indicators
|
Specific measures of an aspect to track/demonstrate performance. Some are generally applicable, some are business specific (e.g. all indicators for aspects in cat. "Env. influence (use)")
|
|
|
(Business Specific) Indicators - Principles
|
- Relevant/meaningful with respect to env. protection
- support benchmarking/monitoring over time - clearly defined, measurable, transparent, verifiable - understandable/meaningful to stakeholders - (...) |
|
|
Using eco-efficiency ratios
|
Two adjustments to be made:
- scope of eco-efficiency extended from product to "value creation" - focus on ratios where env. impact is denominator A decision can either have a positive or negative effect -> (1) economic value creation or (2) environmental impact added |

