![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
kinematics |
study of motion without consideration of forces |
|
|
statics |
study of systems where forces are in equilibrium |
|
|
dynamics |
study of relationship between motion and forces |
|
|
centripetal acceleration formula |
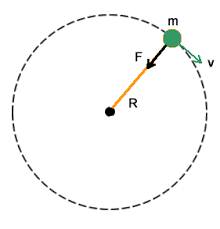
a = v^2 / r this acceleration produced by a force directed radially inwards (centripetal force). in gravitational orbital motion this is the force of gravity. |
|
|
Newton's law of gravitation formula |
F = G m M / r^2 the acceleration due to gravity derived by removing m from either side |
|
|
acceleration due to gravity formula |
g = G M / r^2 |
|
|
active force definition |
a force independent of other forces eg. weight |
|
|
passive force definition |
a force that adjusts ints magnitude / direction in response to other forces eg. tension, normal reaction |
|
|
inertial reference frame |
situations where the observer is not accelerating. Newton's laws apply here |
|
|
non-inertial reference frame |
situations where observer is accelerating eg spinning with the Earth. when Newton's laws apply we need to include 'pseudo" forces / "fictitious" forces eg. F = ma becomes F - ma = 0 ma is the pseudo force, 0 means no acceleration |
|
|
name the fictitious forces that occur when we use a frame of reference that rotates with the Earth |
Coriolis force, Centrifugal force |
|
|
Coriolis force details |
- acts perpendicular to direction of motion - turns motion to right in N hemisphere - turns motion to left in S hemisphere - means in N hem, winds turn anti-clockwise around low pressure systems |
|
|
centrifugal force formula |
F = m v^2 / r |
|
|
work formula |
W = F s cos θ |
|
|
change in gravitational potential energy formula, where g is constant |
U = mgh |
|
|
change in gravitational potential energy formula, where g is NOT constant |
U = -G m M / r U is equal to zero at large distances from Earth by convention and so negative everywhere. NOT VALID in interior of Earth. |

