![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Meaning of these on peripheral smear? 1. Microcytosis, anisocytosis 2. Spherocytes 3. Macrocytes or macroovalocytes 4. Target cells (codocytes) 5. Schistocytes 6. Nucleated erythrocytes |
1. Iron deficiency
2. Hereditary spherocytosis, warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
3. Cobalamin or folate deficiency; myelodysplasia, use of antimetabolites
4. Hemoglobinopathy, liver disease, splenectomy
5. Microangiopathy (TTP, HUS, DIC)
6. Marrow stress (hemolysis, hypoxia) |
|
|
Meaning of these on peripheral smear?
1. Teardrop cells (dacryocytes) 2. Bite cells 3. Rouleaux 4. Burr cells (echinocytes) 5. Spur cells (acanthocytes) |
1. Fibrosis, marrow granuloma, marrow infiltration
2. G6PD deficiency
3. Paraproteinemia (myeloma)
4. Kidney disease
5. Severe liver disease |
|
|
=== ANEMIA === |
=== ANEMIA === |
|
|
Iron deficiency and Hepcidin? |
- Hepcidin causes decreased iron absorption from enterocytes and decreased iron release by macrophages through internalization and proteolysis of the membrane protein ferroportin. - iron deficiency is characterized by low hepcidin levels |
|
|
i. Iron is absorbed predominantly in the
ii. how soon after starting iron can you check the results? |
i. proximal small bowelii. retic count will go up in 5 days
|
|
|
test for folate deficiency? |
Serum homocysteine levels increase in folate deficiency, whereas BOTH homocysteine and methylmalonic acid levels are increased in cobalamin deficiency. - Measuring serum folate levels is typically unreliable |
|
|
target hgb in anemia of CKD |
Current guidelines recommend the use of supplemental erythropoiesis-stimulating agents to achieve target hemoglobin values of 11 to 12 g/dL (110-120 g/L) in patients receiving dialysis. |
|
|
basic findings in hemolytic anemia |
An increased reticulocyte count, increased indirect bilirubin increased LDH levels, decreased haptoglobin level morphologic changes in erythrocytes |
|
|
Hemolytic anemia, in addition to correcting underlying condition, what to give pt? |
Folic acid 1 mg / day |
|
|
hereditary spherocytosis tx? |
asymptomatic: none symptomatic: splenectomy |
|
|
alpha thal trait (-α/-α or --/αα), how to tell from iron deficiency? |
Presents similarly, but IDA has increased RDW, alpha thal has normal RDW |
|
|
Beta - thal trait findings |
mild anemia, microcytosis, hypochromia, target cells, and increased hemoglobin A2 (α2δ2) and, at times, hemoglobin F (α2γ2) on electrophoresis. |
|
|
Sickle trait (AS) hgb findings, clinical features? |
NORMAL: Hgb, MCV, smear Hb S < 50%, rest HbA Can have splenic sequestration and hematuria Crisis with severe hypoxia |
|
|
Sickle cell SC electrophoresis finding, clinical features? |
Hgb 10-15, HbS 50% MCV 75-normal Avascular necrosis retinal infarcts |
|
|
Sickle cell HbSS electrophoresis findings, clinical features? |
Hb 6-8, > 90% HbS Vasocclusive crises, functional asplenia |
|
|
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia , dx? |
- The direct Coombs (antiglobulin) test is used - typically positive for IgG and negative or only weakly positive for complement (C3) in warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia, whereas it is positive for only complement (C3) in cold agglutinin disease |
|
|
Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia , tx? |
- steroids - Splenectomy if non responsive - refractory: azithioprine, cyclo(phos/sporin) |
|
|
Cold Agglutinin Disease, dx / tx? |
peripheral blood smear in CAD may show clumping, which leads to a falsely elevated MCV - direct Coombs test is typically negative for IgG and strongly positive for complement TX: cold avoidance, plasmapheresis if acute |
|
|
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia, description? |
refers to the disruption, fragmentation, and subsequent lysis of erythrocytes during travel through the vascular system |
|
|
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia, smear and lab findings? |
- Erythrocyte fragmentation leads to the smear finding of schistocytes or helmet cells - Lab: intravascular hemolysis with low haptoglobin levels, hemoglobinuria, and elevated serum LDH |
|
|
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia causes? |
Macrovascular: turbulen flow around mech valves, pumps, etc Microvascular: TTP / HUS |
|
|
PNH, consider in pt with __? |
hemolytic anemia, pancytopenia, or unprovoked atypical thrombosis. |
|
|
PNH caused by? dx? |
- Mutations in the PIG-A gene -> absence of glycosylphosphatidylinositol - absence of decay-accelerating factor (CD55) and membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (CD59) DX: flow cytometry with CD55 and CD59 deficiency |
|
|
PNH, tx? |
* Eculizumab (c5 compl Ab) has resulted in decreased transfusion requirements, improved quality of life, and potentially decreased thrombosis in transfusion-dependent patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. |
|
|
infectious causes of hemolysis? |
- Malaria (most common) - Babesiosis: NE USA - Clostridial sepsis (alpha toxin) - Bartonellosis (s. america, sand fly)
Brown recluse spider, bee sting, snake bite |
|
|
tx for secondary iron overload? |
Deferasirox PO (can cause agranulo / AKI) - deferoxamine IV |
|
|
==== TRANSFUSION === |
==== TRANSFUSION === |
|
|
FFP indications? |
- Multiple clotting deficiencies with active bleeding (e.g., DIC, liver disease) - TTP - Reversal of warfarin in patients with intracranial bleeding - Factor replacement when specific factor concentrates not available - Massive transfusion of packed red blood cells to avoid dilutional coagulopathy |
|
|
Indication for plt transfusion as prophylaxis? |
<10,000/µL in patients with leukemia with no other bleeding risk factors <50,000/µL and planned surgery <100,000/µL and planned intracranial surgery |
|
|
Indication for plt transfusion as treatment? |
Active bleeding with platelet count <50,000-100,000/µL (50-100 × 109/L) Active bleeding with dysfunctional platelets |
|
|
cryoprecipitate, contents and indication? |
- contains a concentrated source of factor VIII, von Willebrand factor, factor XIII, fibronectin, and fibrinogen - treatment of choice in bleeding patients with hypofibrinogenemia from liver disease, thrombolytic therapy, or DIC |
|
|
Product of choice to reverse warfarin in life-threatening bleeding? |
IV vitamin K + Prothrombin Complex Concentrate |
|
|
Transfusion-related Acute Lung Injury, presentation? tx? |
- hypoxia and dyspnea resembling noncardiac pulmonary edema during or within 6 hours of a transfusion. - Fever and hypotension, b/l infiltrates with pulmonary edema on CXR.
tx: Intubation may be required, supportive, improve in few days, ban blood donor
|
|
|
Febrile Nonhemolytic Transfusion Reaction, management? |
- stop trf - rule out AHTR - resume with close monitoring - Pretransfusion antipyretics or leukoreduction of cellular blood products may prevent recurrence. |
|
|
Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (T-GVHD) - who is at risk? - ppx? |
- HSCT recipients, recipients of blood transfusion from first-degree relatives, and pt with immunosuppression associated with hematologic malignancies
- ppx with gamma irradiation of blood prdcts |
|
|
severe anaphylactic rxn from RBC trf usually associated with:_____ Management? |
IgA def pt with anti-IgA Ab Give washed cells |
|
|
Apheresis i. What is it? ii. indications? iii. monitor for iv. withhold these before elective procedure: |
i. separation of whole blood into components, tx and return ii. sickle cell ACS, malaria, babesia iii. hypocalcemia iv. ACE Inhibitor |
|
|
===== BLEEDING DISORDERS ==== |
===== BLEEDING DISORDERS ==== |
|
|
Clotting Cascade |
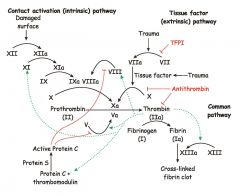
|
|
|
primary hemostasis? |
injured blood vessel constricts and platelets adhere to TF–bearing cells through interactions between glycoprotein Ib/IX/V and (vWF). - platelets secrete their granular contents - Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa undergoes a conformational change, allowing it to bind fibrinogen, which then cross-links platelets |
|
|
secondary hemostasis? |
- phospholipid scaffold is formed in primary hemo - prothrombin -> thrombin - fibrinogen -> fibrin - 13a X-links fibrin to meshwork
|
|
|
A history of bleeding into muscles and joints is characteristic of ? |
disorders of humoral clotting factors |
|
|
mucosal bleeding occurs more commonly in ? |
disorders of primary hemostasis thrombocytopenia qualitative platelet defects |
|
|
Bleeding associations: i) enlarged tongue, carpal tunnel syndrome, and periorbital purpura ii) A harsh systolic murmur iii) Splenomegaly
|
i) may indicate amyloidosis, which is associated with an acquired deficiency of clotting proteins, especially factor X. ii) may indicate severe AS, which can cause an acquired type 2 vWD. iii) can be associated with thrombocytopenia and may indicate underlying cirrhosis. |
|
|
In general, (i) a prolonged PT is most commonly due to ____ (ii) An isolated prolonged aPTT is most commonly due to __
|
i) an acquired deficiency of factor VII, from vitamin K deficiency, liver disease, DIC, or warfarin use ii) a lupus inhibitor, but hemophilia is also a concern |
|
|
hemophilia A/B are from? tx? |
Factor 8 and 9 deficiency respectively
tx with concentrates, desmopression for mild Hemo A. No ASA or NSAID |
|
|
normal PTT with i. giant platelets ii. abnormal platelet aggregation |
i. Bernard-Soulier dz ii. Glanzmann's dz |
|
|
vWD dx, tx? |
dx: decreased Ristocetin cofactor assay
tx: mild type 1: desmopressin severe type 1 or bleeding type 2/3 - vWF-containing factor 8 concentrate |
|
|
acquired hemophilia: lab findings? Assoc with? |
i) bleeding with an isolated aPTT prolongation, factor 8 low, mixing study won't correct ii) postpartum state, malignancy, or autoimmune conditions, but 50% of cases are idiopathic |
|
|
acquired hemophilia, tx? |
if factor 8 inhibitor titre low: factor 8 concentrate
titre high: factor 7a, PTC to activate factor X, immunosuppresion |
|
|
coagulopathy of liver dz, tx? |
FFP + vitamin K |
|
|
DIC, lab findings, tx? |
Low platelet levels, a prolonged PT, a low or decreasing fibrinogen level, and an elevated D-dimer level are diagnostic - tx: underlying cause + supportive plasma, cryoprecip, plt transfusions |
|
|
Hemophilia A, mild, scheduled for dental extraction, wtd |
Desmopression spray +/- aminocaproid acid / tranexamic acid |
|
|
Hemophilia A + trauma to head, wtd |
Give factor 8 concentrate, keep level > 50% |

