![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the objective of Governmental & NFP organization financial reporting?
|
To demonstrate the accountability of each organization for the stewardship of the resources in their care.
|
|
|
What is the difference between Accountability for Privately owned enterprises & Governmental & NFP organizations?
|
1- Accountability for privately owned enterprises may be clearly measured in either the NI of the entity or the increased wealth of its shareholders,
2- Accountability for Governmental & NFP organizations are focused on providing efficient & effective delivery of services with either public resources or private resources shielded from taxation. |
|
|
Note
|
Identifying & displaying the accountability objectives of governmental & NFP organizations is INTEGRAL to this type of financial reporting & related accounting.
|
|
|
Note
|
1- Governmental entities often derive their revenues from taxes or answer to public authorities
2- NFP entities often derive their income from contributions or fees which are not taxable. 3- Commercial entities usually derive their income from sales or fees which are generally taxable. |
|
|
Note
|
In accounting for public funds, both governments & NFP organizations seek to demonstrate their operational accountability for:
1- The entity taken as a whole, &, 2- The fiscal accountability for specific funding. |
|
|
Note
|
Foundational to governmental & NFP organization accounting is the concept of fund accounting.
|
|
|
What is the purpose beyond Fund accounting & reporting?
|
Fund accounting enables service & mission-driven organizations to easily monitor & report compliance with:
1- Spending purposes (fund restrictions), 2- Spending limits (budget), 3- Other fiscal accountability objectives. |
|
|
Note
|
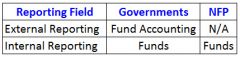
External fund reporting is only allowed for governmental units.
|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|
Governmental, NFP, & commercial accounting are applied to entities consistent with their basis of organization & their funding sources, not their industries.
|
|
|
Note
|
The Governmental Accounting standards Board (GASB), which is the governmental counterpart of the FASB , establishes accounting & reporting standards for governments.
|
|
|
Who established the authoritative literature hierarchy of GAAP relates to governments?
|
GASB
|
|
|
What is the authoritative literature hierarchy of GAAP relates to governments?
|
1- GASB Statements & Interpretations
2- GASB Technical Bulletins, AICPA Industry Audit Guides, & AICPA Statements of Position 3- AICPA Practice Bulletins 4- GASB Implementation Guides |
|
|
Note
|
The Governmental Finance Officers Association (GFOA), which is the professional trade organization for governmental officers (i.e., similar to the AICPA for public accountants), provides optional & non-authoritative guidance.
|
|
|
Who establishes Accounting Principles & standards for NFP Organizations?
|
1- Financial Accounting standards Board (FASB)
2- Audit & Accounting Guides 3- Industry-specific literature |
|
|
What is the "Government Accountability Office GAO"?
|
It is the audit, evaluation, & investigative arm of the United States Congress.
|
|
|
Note
|
The GAO establishes "government auditing standards" (Yellow Book standards) for audits of governmental organizations & federal assistance programs, activities, & functions.
|
|
|
Note
|
Federal financial assistance is primarily awarded to governments & NFP organizations, & is frequently subject to audits under the Single Audit Act (based on the level of expenditures of federal funds).
|
|
|
Note
|
Single audits require compliance with:
1- Government auditing standards 2- Specific single audit rules |
|
|
Note
|
Governmental accounting generally revolves around three themes that make it different from commercial & even NFP accounting,
1- Fund Structure 2- Fund Accounting 3- External Reporting |
|
|
What is the definition of a "Fund"?
|
A fund is a sum of money or other resource segregated for the purpose of carrying on a specific activity or attaining certain objectives in accordance with specific regulations, restrictions, or limitations, constituting an independent fiscal & accounting entity.
|
|
|
Note
|
Each fund is a self-balancing set of accounts.
|
|
|
Note
|
Fund classifications within the fund structure defined by the GASB impact the basis of accounting & the measurement focus principles associated with each fund category.
|
|
|
Note
|
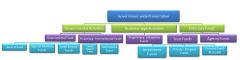
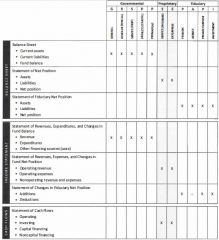
GASB 34 defines a fund structure for governments, which consists of Eleven fund types classified in the following three generic categories:
1- Governmental funds 2- Proprietary funds 3- Fiduciary funds |
|
|
Note
|
Fund FSs should be separately presented for governmental, proprietary & fiduciary funds to report additional & detailed information about the primary government.
|
|
|
Note
|
GASB 34 (as amended) establishes minimum reporting requirements to be in compliance with GAAP.
|
|
|
What are the GASB 34 minimum external reporting requirements?
|
1- Fund-based & GW presentations supported by notes to the FSs & a variety of required supplementary information.
2- Presentation of a reconciliation of fund FSs to GWFSs to fully integrate reporting objectives. |
|
|
Note
|
GWFSs convert disaggregated fund-based FSs using multiple measurement focuses & basis of accounting to a single consolidated set of FSs which use:
1- Full accrual accounting (basis of accounting) 2- Economic resources measurement focus |
|
|
Note
|
Financial activity of the primary government is classified in the following two ways:
1- Governmental activities 2- Business-type activities |
|
|
Note
|
Major funds are presented using the basis of accounting & measurement focus unique to each category of fund.
|
|
|
Note
|
Only major funds (as defined by the GASB) are presented.
|
|
|
Note
|
Non-major funds are displayed in the aggregate.
|
|
|
Note
|
Governmental fund FSs are reconciled to the governmental activities section of the GW presentation.
|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|
FSs are presented with appropriate note disclosures & required (& optional) supplementary information.
|
|
|
What are examples on Supplementary information presented?
|
1- Budget versus actual data,
2- MD&A 3- Presentation of non-major funds 4- Modified approaches to presentation of infrastructure |
|
|
Note
|
A governmental entity, although a single entity, consists of a number of separate funds.
|
|
|
Note
|
Funds are generally classified into three generic categories:
1- Governmental funds 2- Proprietary funds 3- Fiduciary funds |
|
|
Note
|
Governmental funds are accounted for using:
1- The Modified accrual basis of accounting 2- Current financial resources measurement focus |
|
|
Note
|
The source, use, & balance of the government's current financial resources & the related current liabilities are accounted for through the use of governmental funds.
|
|
|
Note
|
Governmental funds often have a budgetary focus, & seek to measure financial position & the changes therein.
|
|
|
Note
|
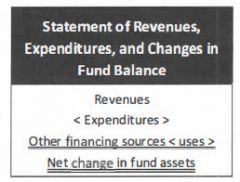
The main FS for the Governmental funds is the statement of revenues, expenditures, & changes in fund balance.
|
|
|
Note
|
The statement of revenues, expenditures, & changes in fund balance is used by the Governmental funds to demonstrate compliance with laws, rules, & regulations.
|
|
|
What are Governmental Fund types?
|
1- General Fund
2- Special Revenue Funds 3- Debt Service Funds 4- Capital Projects Funds 5- Permanent Fund GRaSPP |
|
|
What is the purpose of the General Fund?
|
It is set up to account for the ordinary operations of a governmental unit which is financed from taxes & other general revenues.
|
|
|
Note
|
All transactions not accounted for in other funds are accounted for in General Fund
|
|
|
Note
|
All accounts in the General Fund are of a "current" nature, thus this fund contains no fixed-asset or long-term debt accounts.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Special Revenue Funds?
|
They are set up to account for revenues from specific taxes or other earmarked sources that are restricted or committed to finance particular activities of government.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Debt Service Funds?
|
They are set up to account for the accumulation of resources & the payment of interest & principal on all "general obligation debt," other than that serviced by enterprise funds or by special assessments in another fund.
|
|
|
Note
|
Resources of the "Debt Service Fund" are restricted, committed or assigned to debt service expenditures.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Capital Projects Funds?
|
They are set up to account for resources restricted, committed or assigned for the acquisition or construction of major capital assets by a governmental unit, except those projects financed by an enterprise fund or by a special assessment.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Permanent Funds?
|
They are used to report resources that are legally restricted to the extent that only earnings, & NOT principal, may be used for purposes supporting the reporting government's programs(i.e., for the benefit of the public).
|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|
Proprietary funds are accounted for using:
1- The Full accrual basis of accounting 2- Economic resources measurement focus |
|
|
Note
|
Proprietary funds account for business-type activities & their accounting is similar to commercial accounting.
|
|
|
What does Proprietary Funds include?
|
1- Internal Service Funds
2- Enterprise Funds SE |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Internal Service Funds?
|
They are set up to account for goods & services provided by designated departments on a fee basis to other departments & agencies within a single governmental unit or to other governmental units. Ex. Print shops
|
|
|
Note
|
Customers of the internal service fund are primarily internal.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Enterprise Funds?
|
They are set up to account for the acquisition & operation of governmental facilities & services that are intended to be primarily (over 50%) self-supported by user charges. Ex. Water, Sewer, Airports & Transmit systems
|
|
|
Note
|
Customers of the enterprise fund are primarily external.
|
|
|
What are the criteria that if ONE of them exist, Enterprise Funds would be required?
|
1- Activity is financed with debt that is secured solely by a pledge of the net revenues from fees & charges of that activity,
2- Laws or regulations require that the activity’s cost of providing services be recovered with fees & charges, rather than from taxes or similar revenues, 3- Pricing policies of the activity establish fees & charges designed to cover its costs including capital costs (e.g., depreciation & debt service). |
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
Fiduciary (Trust) funds are accounted for using:
1- The Full accrual basis of accounting 2- Economic resources measurement focus Except for certain pension liabilities & post-employment health care plans. |
|
|
Note
|
Fiduciary funds account for assets received where the government acts in the capacity of a trust or agency fund.
|
|
|
What does Fiduciary Funds include?
|
1- Pension (& Other Employee Benefit) Trust Funds
2- Agency Funds 3- Private Purpose Trust Funds 4- Investment Trust Funds PAPI |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Pension Trust Funds?
|
It account for resources of:
1- Defined benefit plans, 2- Defined contribution plans 3- Post-employment benefit plans, 4- Other long-term employee benefit plans. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the Agency Funds?
|
It account for resources in the temporary custody of a governmental unit (e.g., taxes collected for another governmental entity).
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Private Purpose Trust Funds?
|
They are the designated funds for all other trust fund arrangements under which principal & income are for the benefit of specific individuals, private organizations, or other governments.
|
|
|
Note
|
Often, the government will need to record escheat property (i.e., property that has been forfeited as a result of the passage of time or process of law) in a private purpose trust fund.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Investment Trust Funds?
|
It accounts for resources held for investment on behalf of other governments in an investment pool.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
1- The modified accrual basis of accounting is used to accomplish the current financial resources measurement focus.
2- The accrual basis of accounting is used to complement the economic resources measurement focus. |
|
|
Note
|
The use of a measurement focus & basis of accounting in governmental funds different from those used in the GWFSs are the source of the reconciling items between their respective FSs.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of understanding the measurement focus of the fund?
|
Measurement focus refers to how to recognize transactions in the FSs, it governs where the transactions appear
|
|
|
Note
|
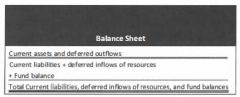
The current financial resources measurement focus seeks to measure only the current financial resources available, spendable or appropriable to the governmental entity.
|
|
|
Note
|
Although governmental funds might also report deferred outflows or deferred inflows of resources (generally within 60 days after year-end) only current assets & liabilities are included on the balance sheet.
|
|
|
Note
|
Adding fixed assets excluded from governmental fund FSs & subtracting noncurrent liabilities also excluded are two of the most significant reconciling items between governmental funds & GWFSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
The economic resources measurement focus & accrual basis of accounting is a method similar to accounting for commercial enterprises.
|
|
|
Note
|
The economic resources measurement focus seeks to determine the costs of services & the efficiency & effectiveness with which invested capital has been used.
|
|
|
Note
|
In the economic resources measurement focus FSs Net position is analyzed & reported in three components:
1- Net investment in capital assets 2- Restricted 3- Unrestricted |
|
|
Note
|
The basis of accounting relates to the timing of the measurements made.
|
|
|
Note
|
The modified accrual basis of accounting is a blend of accrual & cash basis accounting concepts.
|
|
|
Note
|
The only difference between the timing of revenue recognition under the modified accrual & full accrual basis of accounting is the manner in which each basis defines the word "available."
|
|
|
Note
|
Available, under modified accrual, means collectible within the current period or soon enough thereafter to be used to pay liabilities in the current period (generally within 60 days after year-end).
|
|
|
Note
|
Measurable, under modified accrual, means quantifiable in monetary terms.
|
|
|
Note
|
Expenditures, under modified accrual, are generally recorded when the related fund liability is incurred, with some exceptions.
|
|
|
Under Modified accrual basis of accounting in Governmental funds, what is the exception for the "Expenditures" recognition GR?
|
Exception: Unmatured interest on long-term debt is not accrued, it is only recorded when legally due.
|
|
|
Note
|
Addition of accrual basis revenues in excess of modified accrual revenues a long with subtraction of accrued debt related expenses not recognized in governmental FSs are frequent reconciling items between the governmental fund FSs & the GWFSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
In full accrual basis of Accounting
1- Revenue is recognized when earned. 2- Expenses are recognized when incurred. |
|
|
Note
|
The economic resources measurement focus & full accrual basis of accounting is used for:
1- GWFSs 2- Proprietary funds 3- Fiduciary funds |
|
|
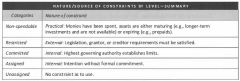
What are the Governmental fund balances 5 categories?
|
1- Non-spendable Fund Balance
2- Restricted Fund Balance 3- Committed Fund Balance 4- Assigned Fund Balance 5- Unassigned Fund Balance NU CAR |
|
|
What is the Non-spendable fund balance?
|
It is a governmental fund balance that is represented by current assets but can't be spent (Ex. pre-paid expenses, inventories, etc.)
|
|
|
What is the Restricted fund balance?
|
It is a governmental fund balance that include amounts that are restricted to specific purposes when constraints placed upon the resources are externally imposed by creditors, contributors, or laws or regulations of other governments.
|
|
|
What is the Committed fund balance?
|
It is a governmental fund balance that can only be used for specific purposes pursuant to constraints imposed by formal action of the government’s highest level of decision-making authority (e.g., resolutions, encumbered appropriations, etc.).
|
|
|
What is the Assigned fund balance?
|
It is a governmental fund balance that includes amounts that are constrained by the government’s INTENT to be used for specific purposes but are neither restricted nor committed.
|
|
|
Note
|
Assigned fund balance also includes any remaining positive amounts that are reported in governmental funds, other than the general fund, that are not classified as nonspendable, restricted, or committed & amounts in the general fund that are intended to be used for a specific purpose.
|
|
|
Note
|
To be classified as assigned “intent” should be expressed by:
1- Governing body 2- A body (i.e., budget or finance committee) or official who has the authority to assign amounts to be used for specific purposes. |
|
|
What is the Unassigned fund balance?
|
It is a governmental fund balance that is associated with spendable assets neither restricted, committed nor assigned.
|
|
|
Note
|
Unassigned fund balance is the residual classification for the general fund, it represents the fund balance that has not been assigned to other funds & that has not been restricted, committed, or assigned to specific purposes within the general fund.
|
|
|
Note
|
Only the general fund should have a positive unassigned fund balance. Other governmental funds might have negative unassigned fund balances if expenditures incurred for specific purposes exceed the amounts restricted, committed, or assigned to those purposes.
|
|
|
Note
|
The B/S or the notes to the FSs should disclose the details of the items in each of the 5 fund balance classifications.
|
|
|
Note
|
GASB Statement No. 54 indicates that encumbrances are not a specific purpose & should not be displayed as a separate item on the B/S but should be included in the appropriate fund balance classification based on the definition & criteria for fund balance classifications.
|
|
|
Note
|
Significant encumbrances should be disclosed in the notes to the FSs in conjunction with disclosures of other significant commitments.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
Note
|

|

