![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
113 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bronchopneumonia showing patchy areas of consolidation
|

.
|
|
|
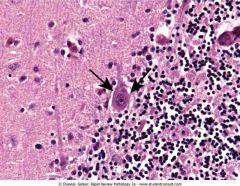
Cerebellum in a patient with rabies showing Purkinje cells with intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions (arrows) called Negri bodies
|
.
|
|
|
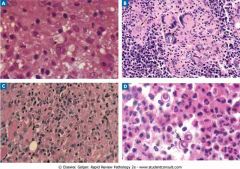
Common systemic fungal infections. The yeast form of Cryptococcus neoformans (A) produces a narrow-based bud (arrow). Coccidioides immitis (B) has spherules containing endospores (arrows). Multinucleated giant cells
|
.
|
|
|
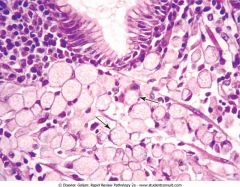
Diffuse type of gastric adenocarcinoma with signet-ring carcinoma cells (arrows)
|
.
|
|
|
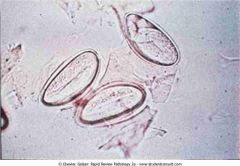
Embryonated eggs of Enterobius vermicularis
|
.
|
|
|
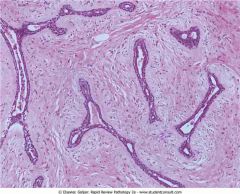
Fibroadenoma
|
.
|
|
|
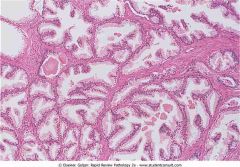
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
|
.
|
|
|
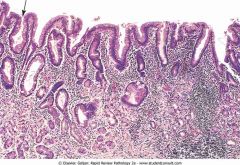
Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric mucosal epithelium in chronic gastritis
|
.
|
|
|
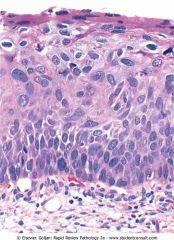
Squamous dysplasia of the cervix, a precursor of squamous cell carcinoma.
|
.
|
|
|
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) showing a pale infarction of the posterior wall of the left ventricle (bottom left)
|
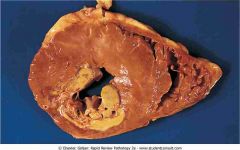
.
|
|
|
Signs of acute inflammation. The patient has erysipelas of the face due to group A streptococcus. Signs of acute inflammation that are present in the photograph include redness (rubor) and swelling (tumor)
|
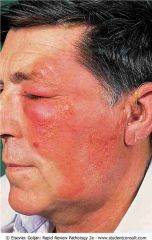
.
|
|
|
Fibrinous inflammation. The epicardial surface of the heart is covered by a shaggy layer of fibrin material
|
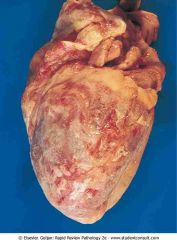
.
|
|
|
Pseudomembranous inflammation. There is necrosis and a yellow-colored exudate covering the mucosal surface of the colon due to a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile.
|
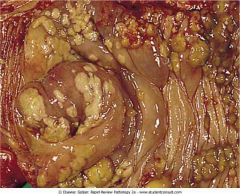
.
|
|
|
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
|
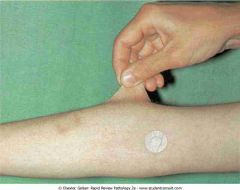
.
|
|
|
Absolute leukocytosis with left shift. Arrows point to band (stab) neutrophils, which exhibit prominence of the azurophilic granules (toxic granulation). Vacuoles in the cytoplasm represent phagolysosomes
|
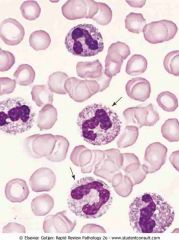
.
|
|
|
Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV. Skin lesions are raised, red, and nonpruritic
|
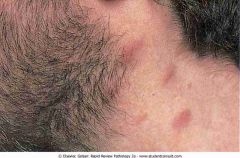
.
|
|
|
Prader-Willi syndrome
|
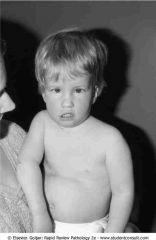
.
|
|
|
Angelman syndrome
|

.
|
|
|
Testicular feminization. The patient is genotypically male, but phenotypically female
|
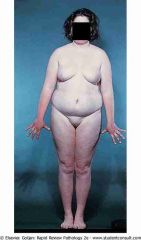
.
|
|
|
Adenocarcinoma. Irregular glands infiltrate the stroma
|
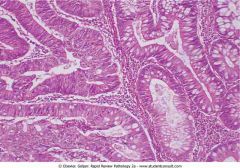
.
|
|
|
Osteogenic sarcoma of the distal femur. The light-colored mass of tumor in the metaphysis abuts the epiphyseal plate (arrow)
|
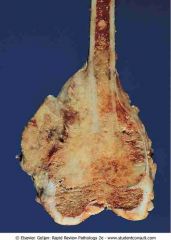
.
|
|
|
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
|
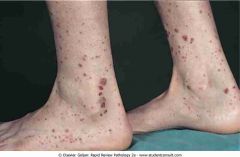
.
|
|
|
Acute myocardial infarction (day 7) in the posterior wall of the left ventricle
|
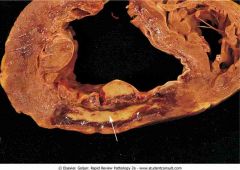
.
|
|
|
Fibrinous pericarditis. The surface of the heart is covered by a shaggy, fibrinous exudate
|
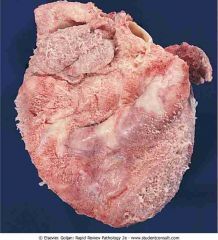
.
|
|
|
Acute rheumatic fever. Uniform, verrucoid-appearing sterile vegetations appear along the line of closure of the mitral valve
|
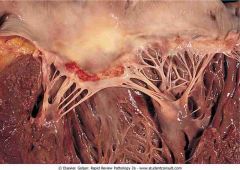
.
|
|
|
Mitral valve prolapse. The arrow shows prolapse of the posterior mitral leaflet into the left atrium
|
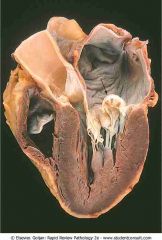
.
|
|
|
Aortic stenosis
|

.
|
|
|
Acute bacterial endocarditis
|
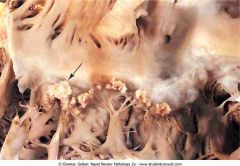
.
|
|
|
Myocarditis. The biopsy shows a lymphocytic infiltrate with dissolution of myocardial fibers
|
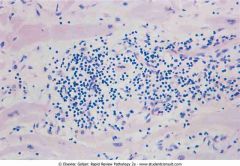
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood reticulocytes with supravital stain (new methylene blue). Red blood cells with thread-like material in the cytosol represent residual RNA filaments and protein (arrow)
|
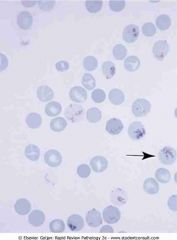
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood with coarse basophilic stippling of RBCs in lead poisoning. Note the mature RBC containing numerous dots representing ribosomes (arrow)
|
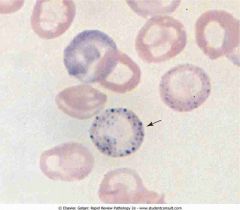
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood with sickle cells and target cells, showing the dense, boat-shaped sickle cells. Cells with a bull's-eye appearance are target cells (arrows), which have excess RBC membrane that bulges
|
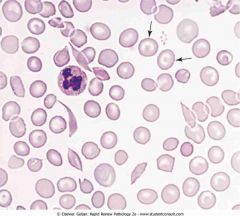
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood with sickle cells and Howell-Jolly bodies. The three dense boat-shaped sickle cells and the two cells containing a single dark, round inclusion (arrows) represent nuclear remnants. Howel
|
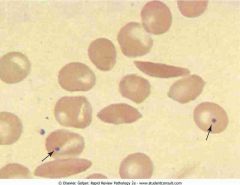
.
|
|
|
Plasmodium falciparum ring forms in red blood cells (RBCs). This RBC has two ring forms. Multiple infestation of an RBC is characteristic of P. falciparum malaria
|
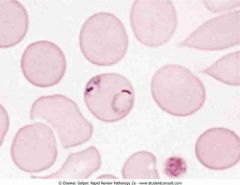
.
|
|
|
Leukoerythroblastic reaction. Numerous bone marrow reticulocytes with a blue discoloration
|
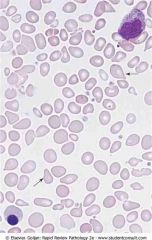
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood in CML.
Marked leukocytosis shows neutrophils at different stages of development (segmented and band neutrophils, metamyelocytes and myelocytes) |
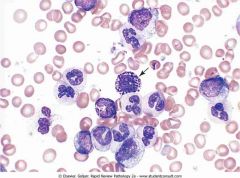
.
|
|
|
Peripheral blood in CLL.
|
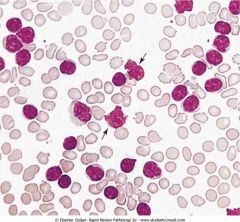
.
|
|
|
Gaucher disease
|
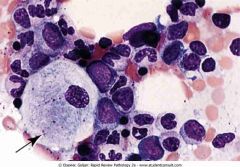
.
|
|
|
Niemann-Pick disease
|
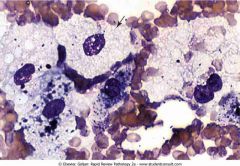
.
|
|
|
Senile purpura
|

.
|
|
|
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
|
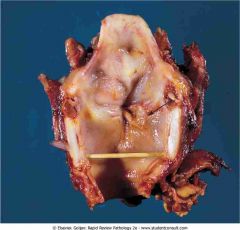
.
|
|
|
Asbestos ferruginous body
|
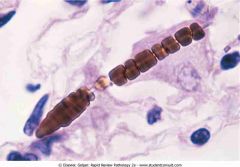
.
|
|
|
Malignant mesothelioma
|
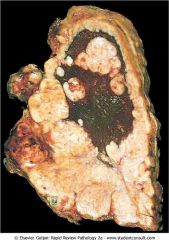
.
|
|
|
Sarcoid granuloma
|
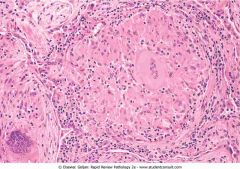
.
|
|
|
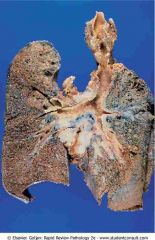
Primary lung cancer
|
.
|
|
|
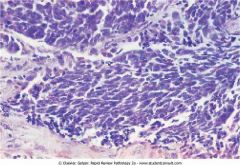
Small cell carcinoma of the lung
|
.
|
|
|
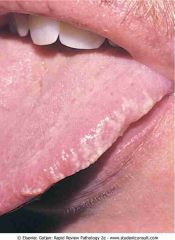
Hairy leukoplakia along the lateral.
|
.
|
|
|
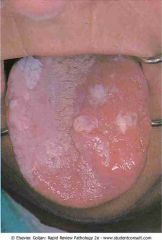
Leukoplakia of the tongue
|
.
|
|
|
.Barrett's esophagus
|
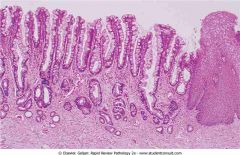
.
|
|
|
. Gastric adenocarcinoma
|
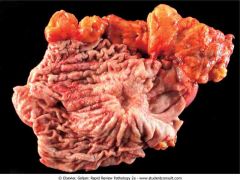
.
|
|
|
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites
|
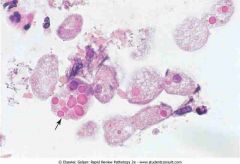
.
|
|
|
Celiac disease
|
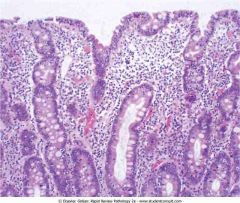
.
|
|
|
Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
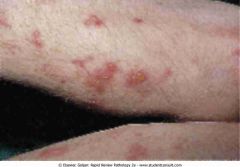
.
|
|
|
Sigmoid diverticulosis
|
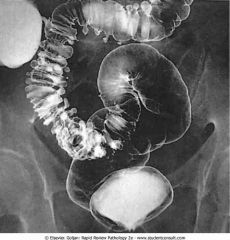
.
|
|
|
Crohn's disease
|
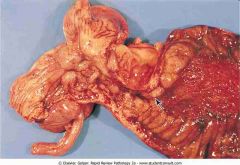
.
|
|
|
Normal glomerulus
|
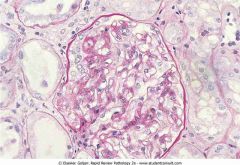
.
|
|
|
.Subepithelial immunocomplex
|
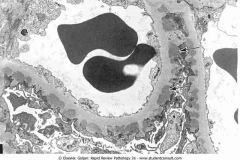
.
|
|
|
RBC cast in the urine
|
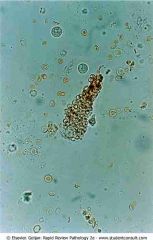
.
|
|
|
. Crescentic glomerulonephritis
|
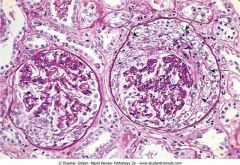
.
|
|
|
Fatty cast under polarization
|

.
|
|
|
.Acute pyelonephritis.
|
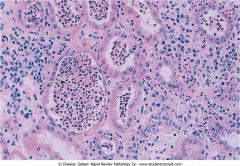
.
|
|
|
Benign nephrosclerosis
|
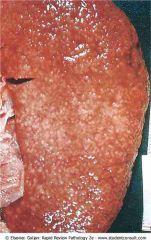
.
|
|
|
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
|
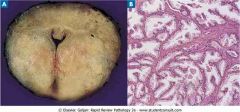
.
|
|
|
Prostate cancer. Arrow.
|
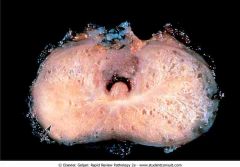
.
|
|
|
A, Candida.
B, Chlamydia trachomatis. C, Gardnerella vaginalis. D, Herpes type E, Herpes type 2. F, Human papillomavirus. |
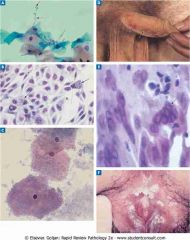
.
|
|
|
G, Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
H, Treponema pallidum. I, Treponema pallidum. J, Trichomonas vaginalis. |
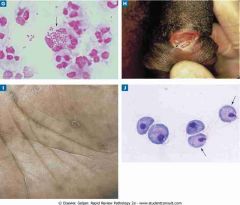
.
|
|
|
Extramammary Paget's disease
|
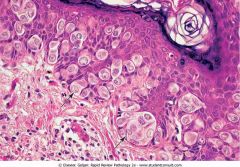
.
|
|
|
.Squamous cell carcinoma of cervix
|
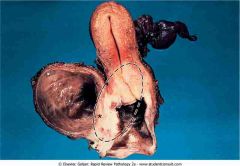
.
|
|
|
.Simple hyperplasia of endometria.jpg
|
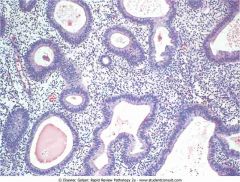
.
|
|
|
. Endometrial carcinoma
|
.
|
|
|
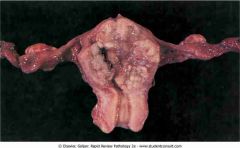
. Ruptured ectopic tubal pregnancy
|
.
|
|
|
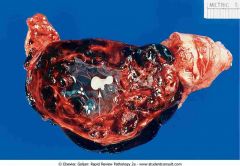
.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
|
.
|
|
|
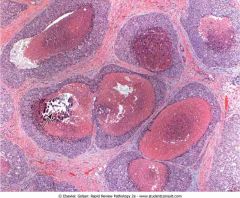
.Lobular carcinoma in situ
|
.
|
|
|
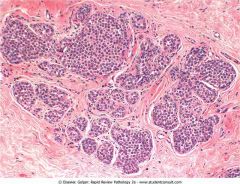
.Infiltrating ductal carcinoma.
|
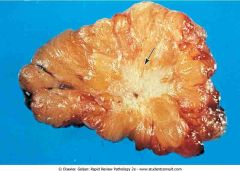
.
|
|
|
.Paget's disease of the breast
|
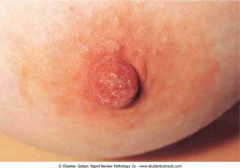
.
|
|
|
. Primary hypothyroidism
|
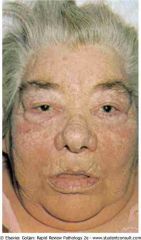
.
|
|
|
Papillary carcinoma of thyroid.
|
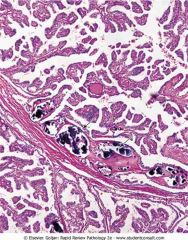
.
|
|
|
.Tophi (arrows)
|
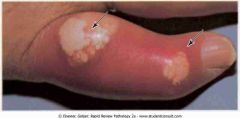
.
|
|
|
.Erythema chronicum migrans
|
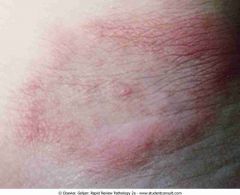
.
|
|
|
.Erythema infectiosum
|
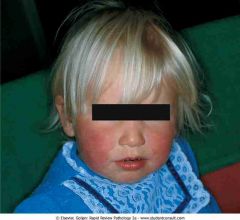
.
|
|
|
. Tinea versicolor.
|
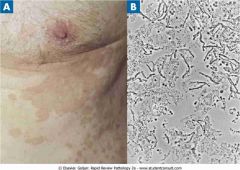
.
|
|
|
. Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis
|
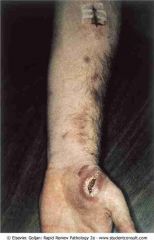
.
|
|
|
.Contact dermatitis.
|
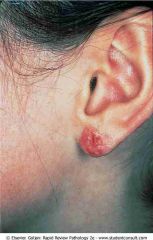
.
|
|
|
.Nail changes in psoriasis
|
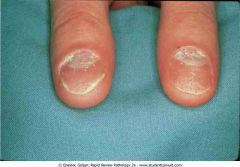
.
|
|
|
. Erythema multiforme
|
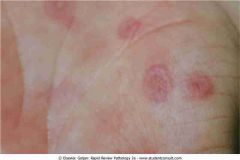
.
|
|
|
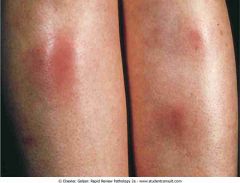
. Erythema nodosum
|
.
|
|
|
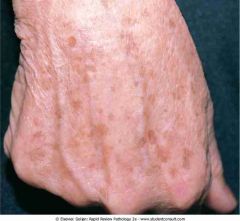
.Solar lentigo
|
.
|
|
|
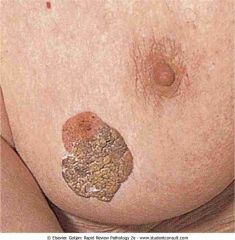
. Seborrheic keratosis on the breast
|
.
|
|
|
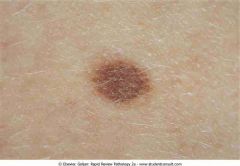
. Compound nevus
|
.
|
|
|
.Lentigo maligna melanoma
|
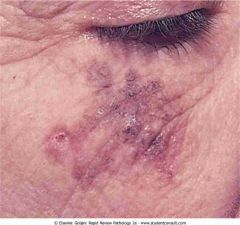
.
|
|
|
.Epidural hematoma
|
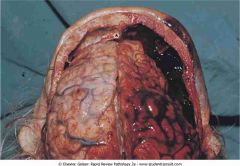
.
|
|
|
.Subdural hematoma
|
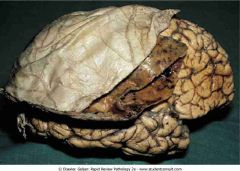
.
|
|
|
.Atherosclerotic stroke.
|
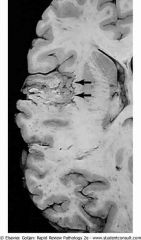
.
|
|
|
.Embolic stroke
|
.
|
|
|
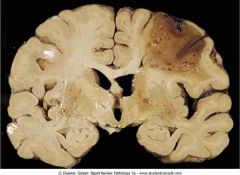
. Intracerebral hemorrhage
|
.
|
|
|
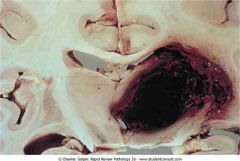
.Granular immunofluorescence. Granular irregular deposits in the capillaries are caused by immunocomplex deposition (e.g., poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
|
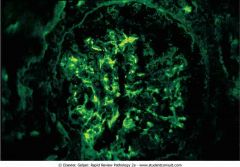
.
|
|
|
.Huntington disease. Coronal section (A) shows a dilated lateral ventricle and atrophy of the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus when compared with a normal coronal section (B)
|
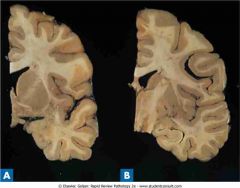
.
|
|
|
. Giardia lamblia with two nuclei
|
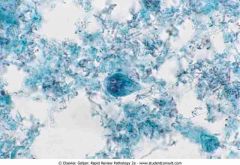
.
|
|
|
.Keratoacanthoma
|
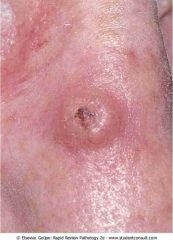
.
|
|
|
.Liver biopsy stained with Prussian blue in a patient with hereditary hemochromatosis
|
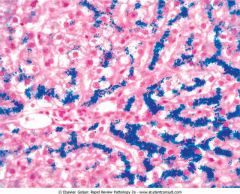
.
|
|
|
.Lung biopsy stained with Gomori methenamine-silver showing septated hyphae and fruiting body (inset) of Aspergillus fumigatus
|

.
|
|
|
.Multiple sclerosis showing multiple areas of demyelinated white matter (arrows pointing to brown plaques)
|
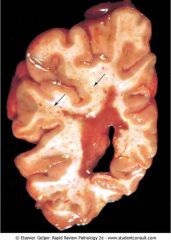
.
|
|
|
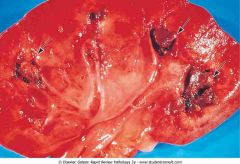
analgesic nephropathy showing multiple brownish necrotic papillae (arrows)
|
.
|
|
|
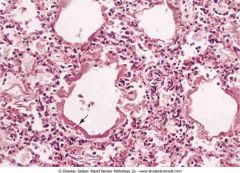
.Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
|
.
|
|
|
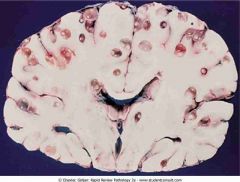
.Neurocysticercosis showing multiple cysts between the gray and white matter
|
.
|
|
|
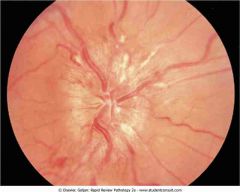
.Optic disk with papilledema showing loss of the disk margin and hard exudates (white streaks
|
.
|
|
|
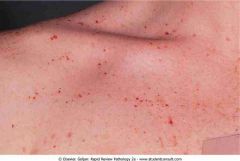
.Petechiae in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura showing pinpoint hemorrhages, a sign of platelet dysfunction
|
.
|
|
|
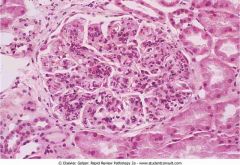
.Poststreptococcal diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
|
.
|
|
|
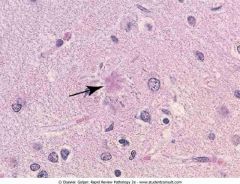
.Senile plaque (arrow) shows an eosinophilic center with peripherally located distended neuronal processes (neurites).
|
.
|
|
|
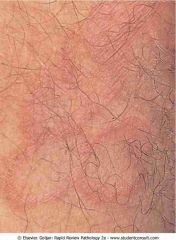
.Tinea corporis showing annular lesions with erythematous margins and clear centers
|
.
|
|
|
.subnuclear vacuoles (arrows) containing mucin push the nuclei of the endometrial cells toward the apex of the cell
|
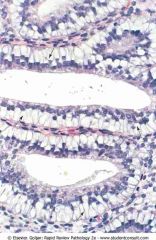
.
|
|
|
Wernicke's encephalopathy showing hemorrhage and discoloration of mamillary bodies and the wall of the third ventricle
|
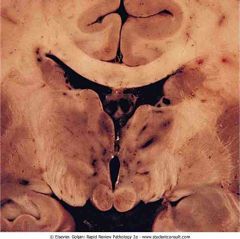
.
|
|
|
Wilson's disease showing cavitary necrosis of the putamen on both sides of the brain
|
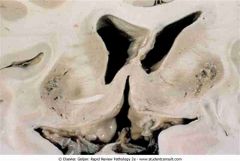
.
|

