![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Schematic reasoning
|
the process of reasoning by which new information is interpreted according to a memory structure, a schema, which contains a network of generic scripts, metaphors, and simplified characterizations of observed objects and phenomena.
|
|
|
Cognitive dissonance
|
the general psychological tendency to deny discrepancies between one's preexisting beliefs(cognitions) and new information.
|
|
|
Mirror Images
|
- the tendency of states and people in competitive interaction to perceive each other similarly
- to see others the same hostile way others see them. |
|
|
enduring rivalries
|
prolonged competition fueled by deep-seated mutual hatred that leads opposed actors to feud and fight over a long period of time without resolution of their conflict.
|
|
|
individual level of analysis
|
an analytical approach that emphasizes the psychological and perceptual variables motivating people, such as those who make foreign policy decisions on behalf of states and other global actors.
• Emphasizes individual leaders’: o Life experience o Perceptions o Beliefs and values o Political efficacy |
|
|
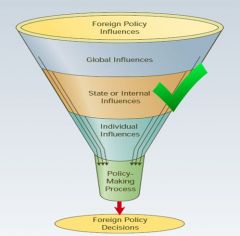
state level of analysis
|
an analytical approach that emphasizes how the internal attributes of states influence their foreign policy behaviors.
• Level of economic development and financial resources • Type of government democratic or authoritarian • Domestic politics including support for political leaders and their policies • SOP rules for reaching decisions about particular types of situations • Bureaucratic Politics- sees foreign policy choices as being based on bargaining and compromises among govt. agencies |
|
|
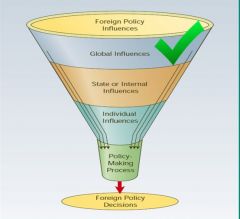
global level of analysis
|
an analytical approach that emphasizes the impact of worldwide conditions on foreign policy behavior and human welfare.
• Focuses on the worldwide conditions that shape interactions between global actors • Geopolitics • Relative Power • Governance |
|
|
State
(Modern State System) |
a legal entity that possesses:
- a permanent population - a well-defined territory - a government capable of exercising sovereignty |
|
|
Nation
(Modern State System) |
a group of people who feel a common identity due to a shred language, culture, and history
|
|
|
Nation-State
(Modern State System) |
- a convergence between territorial states and psychological identification of people with them
|
|
|
Birth of the modern state system
|
1. The peace of Westphalia (1648) ( started the modern state system)
- Secular leaders freed to choose the religious faith of their subjects - Contributed to the idea of state sovereignty • Expansion of the state system 2. Colonialism expanded the European state system globally |
|
|
Defining Characteristics of the state system
|
1. Sovereignty- sovereign states are the primary actors in international relations
o The exclusive rights of states to make enforce and adjudicate laws within their domains 2. Anarchy- states operate in a condition of anarchy o The absence of a higher authority with the legitimacy and coercive capability to make and enforce rules that bind states o No world government 3. Governance o Norms and rules that shape interactions between international actors ex: international law |
|
|
Sovereignty
|
sovereign states are the primary actors in international relations
- The exclusive rights of states to make enforce and adjudicate laws within their domains |
|
|
Anarchy
|
states operate in a condition of anarchy
- The absence of a higher authority with the legitimacy and coercive capability to make and enforce rules that bind states - No world government |
|
|
Governance
|
Norms and rules that shape interactions between international actors ex: international law
|
|
|
Levels of Analysis
|
• Individual
• State • Global/Systemic |
|
|
Geopolitics:
|
a state’s foreign policy is determined by its location, natural resources, physical environment
|
|
|
Relative Power
|
Global and regional distributions of military and economic power. A country's power relative to others
|
|
|
Geopolitics
|
Presence or absence of international institutions
|
|
|
Sovereignty
|
(Defining Characteristics of the state system)
sovereign states are the primary actors in international relations o The exclusive rights of states to make enforce and adjudicate laws within their domains |
|
|
Anarchy
|
(Defining Characteristics of the state system)
states operate in a condition of anarchy o The absence of a higher authority with the legitimacy and coercive capability to make and enforce rules that bind states o No world government |
|
|
Governance
|
(Defining Characteristics of the state system)
Norms and rules that shape interactions between international actors ex: international law |
|
|
Syria Individual level
|
Bashar Al Assad
-Father = dictator -Reaction to Arab Spring -Not original heir(Basil car crash), opthamologist kids graffiti |
|
|
Syria State Level
|
-Nations(colonial legacy): Alawites(Shia)12%,, Sunni(65%), Christian(10%)
-Not a Nation State -Bad Economy(50-80% gdp) -Multiple rebels: o ISIS- Alqueda(combine Syria w/ Iraq o Al Nusra- Alqueda(sharia law) o FSA(free syrian...)Sunni military defectors, want secular democracy o Kurds(Sunni)- Play both sides. hold onto what they have. - Authoritarian regime(2028 free elections) - Bureaucracy |
|
|
Syria Systemic/Global Level
|
UN:
-China/Russia veto power/weak structure - powerless, no authorization of force - Russia allied with Assad-weapons sales, only warm water port - Iran(shia) want Alawites to stay in power. Supp Hezbollah who transport arms through Syria. Rev Guard in Syria. - Saudi(Sunni), support rebels. F over Iraq and Iran - US-non mil aid to FSA o Assad joins chem weapon convention o Apprehension/unpopularity - Alqueda from Iraq - China concerned about overthrow of authoritarians - Hezbola- fight for Assad |
|
|
Political Advocacy
|
Self confidence
|
|
|
Liberalism (idealism)
-Questions -Assumptions -Recommendations |
o Central question: How to maintain Peace?
o Assumptions Humans are reasonable and capable of cooperation Peace in the natural state of affairs Recommendations o Establish international organizations to manage disputes and provide collective security Collective security: a security regime based on the principle that an act of aggression by any state will be met by a collective response from the rest o Strengthen global governance through international laws(genocide, Kellog Pact-war illegal) o Arms control and disarmament o Promote free trade o Promote Democratic Forms of Government o Democratic peace- although democratic states sometimes wage wars against other states they don’t fight each other o Protect Human Rights(R2P Doctrine) WWII blamed, BUT:Isolationism, league of nations failure, trade wars, Great Depression, Dictators, Colonialism. |
|
|
Realism (pragmatism)
-Questions -Assumptions -Recommendations |
o Central question: How to protect the security of the state
o Assumptions Humans have an inherent lust for power that leads to conflict in society • Self help: in a condition of anarchy each state must provide for its own security o Security of the state must be the primary objective of any state leader o Recommendations States should seek to increase their relative power, particularly military power If all countries seek to maximize power, stability will result by maintaining a balance of power |
|
|
Marxism (Radical Critique)
|
Ind Rev. Bourgeois exploit Proletariat.
o Central question: how has global capitalism structured domestic and international society o Assumptions Global capitalism creates an exploitative relationship between developed and developing countries • Recommendations o Change the existing economic system to promote greater equality(20% pop, controls most wealth) |
|
|
Constructivism
|
o Central question- how does the Social construction of knowledge influence how international actors perceive the world and act in it
o Recommendations New ideas values and norms can be promoted as a mechanism for changing international relations |
|
|
Obama Doctrine
|
• U.S. Reserves the right to use military force unilaterally when its security is directly threatened
• U.S may also take military action for other purposes, including the protection of human rights • In such situation, military force should be used only as a last resort • U.S. will act only with the participation of other countries |
|
|
Great Powers
|
o Military Power
o Economic Power o Soft Power- the ability of a country to get what it wants in international affairs through the attractiveness fo its culture, political ideals, and policies |
|
|
Polarity
|
o The degree to which military and economic capabilities are concentrated among the major powers in the state system
o Multipolar: three or more great powers Pre-WWII o Bipolar: two great powers Cold War o Unipolar: one great power U.S. after cold war Hegemon: a single, overwhelmingly powerful state that exercises predominate influence over the global system |
|
|
• Why focus on Great Powers?
|
o Great powers strongly influence patterns of global governance
o To understand patterns of global war and peace |
|
|
• Long-Cycle Theory
|
o Pattern of great power war is tied to the rise and decline of hegemonic states
o Following each great power war, a new hegemon emerges o The hegemon establishes and maintains global governance institutions o Maintaining the global order imposes a cost on the hegemon. Over time, the power of the hegemon declines o One or more states will rise up to challenge the power and authority of the hegemon(power Transition) leading to conflict and war |
|
|
The Cold War (1949-1991)
|
o Truman Doctrine (1947): established a containment policy the U.S would support countries threatened internally or externally by communism(Realism)
o Soviets test their first atomic bomb ( August 1949) |
|
|
Causes of the Cold War
|
Systemic
• Power Transition: narrowing the gap in power capabilities between potential great power rivals(Russ nukes, rivalries) State • Ideological incompatibility o Democracy- political leaders chosen in free elections o Authoritarian- political power controlled by communist party o Capitalism- free market economic system with limited govt. role and private property ownership o Socialism- govt. run economic system with little or no private property ownership Individual Level • Misperceptions created “self-fulfilling prophecy |
|
|
Characteristics of the Cold War
|
A No direct conflict
1 Two sides didn’t fight in a direct military conflict 2 Proxy Wars- two countries fought indirectly through third- parties Korea, Vietnam, Afghanistan B. Arms Race- competition to acquire more and better weapons, including nuclear weapons C Ideological completion o Each side attempted to portray its political and economic system as superior D Confrontation/détente o Alternated periods of confrontation with periods of detente ( relaxed tensions) E Unexpected end of the Cold War o Mikhail Gorbachev- became leader of the soviet union in 1985 ---Key to end ---Not commy hardliner, supported reforms Para stroika, reduced mil spending, started talks. a. 1989, Protests for solidarity, capitalism, democracy in Hungary, Chech, Poland. Mikhail allowed protests and for auth. gov't to fall. ---Nov 11, 1989- fall of Berlin Wall ---1991- fall of Sov Union(US Hegemony) |
|
|
• Imperial Overstretch
|
o The historical tendency of Hegemons to weaken themselves through costly foreign pursuits that drain their resources
|
|
|
US Decline?
|
Decline:
- GDP vs Debt - Interest on Debt - China Lending - Trade deficits - Guantanamo, Drones, Debt crisis, Iraq, Snowden... Not Declining: - world currency(60% of currency) - 1/3 int'l companies |
|
|
President of China
|
Xi Jinping
-3rd most powerful in the world -Cracked down on dissent. (microblogs, arrested critics of govt) |
|
|
China's Economy
|
GDP to overtake US in 15 years
GDP per capita very low 2 Chinas, coastal vs rural areas A bubble? Cause of Recent stock market drop? Similar to Japan in 80s Authoritarian Capitalism- illusion of capitalism |
|
|
China
Cost of growth Military Soft Power |
Environmental
25% of water polluted Polluted air Largest military(dated tech) Distant Second Olympics, News |
|
|
China Politics
|
Authoritarian Political system- comm party chooses officials.
Authoritarian Capitalism- illusion of capitalism- soviet failed -Gov't runs bank -Dong Pong Ching incorporated capitalism in 80s |
|
|
Global South/North/East
|
Developing countries
advanced industrial countries China & India 80% has only 17% wealth |
|
|
Gross domestic product
|
total value of goods and services produced within a country during a year.
|
|
|
Gross National Income
|
GDP + net income earned from a country's companies and citizens from outside the country.
|
|
|
Purchasing Power Parity
|
Value of GDP or GNI adjusted to reflect the cost of living in a country.
|
|
|
Human Development Index
|
Used to indicate QUALITY OF LIFE within a country
-UN development program -electricity, hunger, life expectancy |
|
|
Semi-Periphery
|
parts of the global south that are doing well
1. Oil Exporting Countries(OPEC) 2. Newly Industrialized Countries(NIC) --Export manufactured goods to the North --Eg. Global East(China, Singapore, Malaysia, S. Korea) |
|
|
Least Developed Countries
|
*Majority in Sub Saharan Africa
-49, 34-African, 9-Asia, 5-Pacific, 1-Carribean |
|
|
(Explanations for Poverty & Inequality)
Millenium Development Goals -Goals? |
-Adopted in 2000 at the UN Millenium Summit
Goals: 1. Eradicate Poverty and Hunger-reduce by half the number of people living on less than 1.25$ a day 2. Achieve UNIVERSAL Primary Education(K-6) 3. Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women-in education and employment. 4. Reduce Chiled Mortality-by 2/3 5. Improve Maternal Health-reduce maternal mortality by 3/4 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Other Diseases-halt and begin to reverse the spread of AIDS and malaria |
|
|
Millenium Development Goals
-Already achieved? -Least progress |
1. Eradicate Poverty and Hunger
-ALREADY achieved -Better in E Asia than Sub Saharan Africa 2. Achieve UNIVERSAL Primary Education(K-6)-Not Yet 3. Promote Gender Equality and Empower Women-Not Yet 4. Reduce Chiled Mortality-Not Yet 5. Improve Maternal Health-Not Yet 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Other Diseases-ALREADY |
|
|
OFficial Development Assistance(ODA)
|
grants or loans to countries from other countries
-0.7% GNI goal |
|
|
Intergovernmental Organizations
|
Institutions created and joined by STATES' governments.
ex. UN |
|
|
United Nations: History
|
a. League of Nations(14pts)
b. Roosevelt and Churchill c. Dunbar Oaks 1944(SU, China, GB, France, US) d. UN Charter Signed in 1945 on Oct 24(effective) |
|
|
UN: Functions
|
All Liberal Ideologies
1. Maintain international peace and provide collective security 2. Promote cooperation in solving social and economic problems(more success) 3. Encourage respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms |
|
|
UN: Organizatial Structure
|
1. General Assembly
2. Security Council 3. Economic and Social Council(ECOSOC) 4. Secretariat 5. International Court of Justice |
|
|
UN: Org. Structure- General Assembly
|
1. Each UN member state gets a vote
2. Most decisions made by majority vote 3. Global South states have a significant majority(G77) 4. Resolutions passed are non-binding. It cannot req state to take action. 5. UN reg budget is determined by General Assembly *US contributes the most(22%) |
|
|
UN: Org. Structure- Security Council
|
1. Responsible for maintaining int'l peace and security
2. 5 *permanent members* with veto power(France, US, Russia, UK, China)Dunbar Oaks 3. Ten non-permanent members elected for 2 year terms by the general assembly 4. Decisions must be approved by 9 of 15 members with no veto(reason it hasn't worked well) |
|
|
UN: Org. Structure- Economic and Social Council(ECOSOC)
|
Coordinates the economic and social work of UN(Big umbrella group overseeing 14 specific programs ie Mill dev goals)
1. 54 member states elected by gen assem for 3 year terms 2. Funding is voluntary, hence wealthier countries are favored |
|
|
UN: Org. Structure- Secretariat
|
Carries out administrative work of UN
-Takes most money 1. Secretary General: Ban Ki Moon --traditionally not of 5 permanent members on UNSC --rotates country |
|
|
UN Secretary General
|
Ban Ki Moon(secretariat)
|
|
|
UN: Org. Structure- International Court of Justice
|
1. Can decide disputes between member state, but only if they agree to participate
2. Issues advisory legal opinions on other legal questions. |
|
|
Evaluating UN: Collective Security
|
Has rarely fullfilled its role of providing for collective security.
-Korean War- because SU was boycotting and Taiwan taking China's seat -1st Persian Gulf War |
|
|
Evaluating UN: Peace Keeping
|
The interposition of military forces from a third party between belligerents to prevent hostilities from escalating
-reduces civil fighting 60%, state/state 85% -Rwanda-failure |
|
|
Evaluating UN: Peace Keeping-Responsibility to Protect-
|
international community should intervene if a state is unable or unwilling to protect its citizens from human rights abuses 2005
-1st used in Libya, Mohmar Kadafi, no fly zone, military action --criticism-poor followup, AU collonialism, Rus+China -Syria- abuses on both sides, syria is stronger. |
|
|
Evaluating UN: Promoting Cooperation
|
Most of the effective work of the UN has been with non-security issues(UNICEF, Dev Prog, WTO, WFP)
|
|
|
Evaluating UN: Agenda Setting
|
Bringing an issue to the attention of political decision makers and he public.
|
|
|
European Union
|
Regional IGO
28 Countries Nobel Peace Prize Speculation- new state system(Hegemon) |
|
|
European Union: Origins
|
1. European Coal and Steel Community 1951
2. Treaties of Rome 1957 3. European Communities(EC) 4. Single European Act 5. Maastricht Treaty 1992 6. Lisbon Treaty 2007, 2009 |
|
|
European Coal and Steel Community
European Union Origins |
1951
1. France and Germany(Italy, Lux, Bel, Neth) 2. Established a common market for trade in coal and steel(Liberalism) |
|
|
Treaties of Rome
European Union Origins |
1957
1. Created 2 institutions: i. European Economic Community-established a common market for a wide range of goods. ii. European Atomic Energy Community-created to promote cooperation in the development of nuclear energy(EURATOM) -became European Communities(EC) |
|
|
Single European Act
European Union Origins |
1. Established the goal of completing the common market by Jan 1, 1993.
2. Provided for free movement of goods, services, capital and *people* |
|
|
Maastricht Treaty *
|
************1992
1. Shift toward political integration** 2. Name changed to European Union 3. Created EU citizenship 4. Pooled Sovereignty-states gives up some of their sovereignty to an IGO. i. For some policy areas, EU is given authority to make decisions that are binding to its member states. eg. Environmental, education, healthcare. 5. Eurozone- Some of the EU countries replaced their state currency with the Euro. 6. European Central Bank-established to manate monetary policy and the euro for Europeans. |
|
|
Lisbon Treaty*
|
2007, 2009
*Like a constitution 1. Expanded Pooled Sovereignty to include new policy areas eg. agriculture, criminal law, immigration. 2. New Position: President of European Council -2.5 year term **Herman Van Rompuy- 1st and current(former PM of Belgium) 3. Allows states to leave the EU |
|
|
Sovereign Debt
|
debt issued or guaranteed by a government
(PIGG) |
|
|
Fiscal Stability Treaty
|
EU
1. If a member state's total debt is greater than 60% of GDP, it must be reduced by a certain percentage each year. 2. Annual budget must be balannced or in surplus. 3. Failure to comply results in financial penalty(0.1% of GDP) *i. UK and Check Republic did not sign *ii. Pattern of varying levels of membership |
|
|
Nongovernmental Organizations
(NGOs) |
Members are *private citizens* from two or more states. Rise due to the internet.
Types: 1. Issue Advocacy Gropus 2. Multinational Corporations 3. Cultural NGOs 4. Terrorist Groups |
|
|
Issue Advocacy Groups
Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) |
Transnational interest group organized to influence specific policy areas.
ex. Greenpeace, Amnesty Int'l, Global Fund For Women, IRC, Save the Children Functions: 1. Agenda Setting(ex. Greenpeace, KONY 2012) 2. Education- inform and influence how people view an issue. 3. Representation- Represent groups that cannot represent themselves. 4. Coalition Building- work with gov't leaders to reach int'l agreements. 5. Implementation- help with the implementation of global agreements and monitor compliance. |
|
|
Multinational Corporations
Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) |
Business enterprises headquartered in one state, that invest and operate extensively in other states.
|
|
|
Cultural NGOs
Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) |
Two Types:
1. Religious Movement- a politically active organization based on strong religious conviction. ex. *Catholic Church* Pope Francis* 1.2b members 2. Ethnopolitical Group- members share a common language, cultural tradition and kinship ties ex. Palestine Liberation Organization(PLO) |
|
|
Terrorist Groups
Nongovernmental Organizations (NGOs) |
Seek to further political objectives through the threat or use of violence.
1. Cultural Terrorist Groups- terrorist group whose members share a common cultural or religious identity. -Cultural NGOs and terrorist groups *Hezbolla- in Lebanon, Shia Islam 2. Ideological Terrorist Group- members share a common political ideology. - Earth Liberation Front (ELF) 3. Crime Syndicates - international drug cartels and mafias *Joaquin Guzman Loera, Sinaloa Drug Cartel, Mexico |
|
|
Dependency Theory
Explanations for Poverty and Inequality |
*Global capitalism* creates an unequal and exploitative international division of labor between Global North and Global South countries
1. Comes from Marxist theory 2. At global/systemic level. Look at structure of int'l econ system 3. Colonial origins, maintained through capitalism - GS is exploited for resources, cheap labor and imports manufactured products. 4. Significant changes to domestic and int'l economic institutions are necessary to achieve greater equality(socialist economic principles) -Hugo Chavez, Daniel Ortega, Raul Castro |
|
|
Modernization Theory
Explanations for Poverty and Inequality |
Developing states are impoverished due to their own *internal characteristics* that impede their economic development.
-State level of analysis 1. Social Characteristics- high illiteracy and low levels of education. 2. Political Characteristics: a. Political instability and conflict b. Corrupt and authoritarian gov't 3. Economic Characeristics: a. Lack of Investment Capital b. Lack of infrastructure and technology c. Lack of ecological resources Solution: Global North can provide the missing components of development, especially *investment capital* -Washington Consensus(strings attached)- Economic growth in the Global South can be best achieved through democracy, free market capitalism, and fiscal discipline(Royal Bank, IMF) |
|
|
Global South Soln's (Poverty/Inequality)
|
1. Commodity Cartel
2. Export-Led Industrialization 3. Regional Trade Regime 4. Micro-finance 5. International Organizations |
|
|
Commodity Cartel
Global South Soln's (Poverty/Inequality) |
“. . . an organization of the producers of a commodity that seeks to regulate the pricing and production of that commodity to increase revenue” (p. 295).
*Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)-only truly successful example |
|
|
Export-Led Industrialization
Global South Soln's (Poverty/Inequality) |
Economic strategy that promotes the export of manufactured goods.
Global East- China, India, Taiwan, Singapore |
|
|
Regional Trade Regime
Global South Soln's (Poverty/Inequality) |
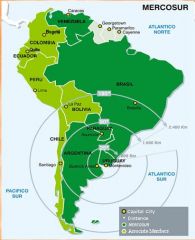
Promote trade between member states by reducing trade barriers (e.g. tariffs).
*Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) *MERCOSUR |
|
|
Microfinance
Global South Soln's (Poverty/Inequality) |

Providing small loans to the poor to help start or expand a small business.
|
|
|
International Organizations
|
Use numerical advantage in international organizations to promote issues important to the developing world.
Group of 77: coalition of Global South countries in the UN General Assembly |

