![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Glacier |
slowly moving mass of dense ice, year-round ice |
|
|
Snow-line |
-lowest elevation where snow remains year round -high latitudes, high elevation |
|
|
Continental glacier |

ice sheet |
|
|
Alpine glacier |

ice cap, ice field |
|
|
Conversion of snow to ice |
loose snow -->firn(compacting snow)-->glacial ice |
|
|
Glacial mass balance |
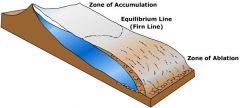
-accumulation: above equilibrium line, accumulates snow and exceeds ablation -ablation: refers to area of a glacier or ice sheet below equilibrium with loss in ice mass due to melting, evap, etc |
|
|
Glacier National Park |
-negative mass balance -150 glaciers 100 years ago; now 25 left -10-20 years - all are predicted to be gone |
|
|
Glacier movement |
-crevasses -glacial surge: faster velocity in center of glacier because less resistance from sides |
|
|
Abrasion |
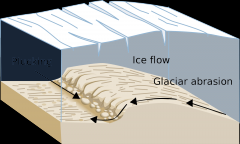
glacier grinds against bedrock, underneath |
|
|
Plucking |
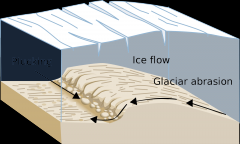
-water goes into bedrock and expands and breaks it -occurs in front |
|
|
Glacial debris/deposits |
-supra- top -en- middle -sub- bottom |
|
|
Till/Moraine |
contact with ice when deposited; usually unsorted |
|
|
Drift |
deposited directly or indirectly by a glacier; driftless area/region |
|
|
Moraine sections |
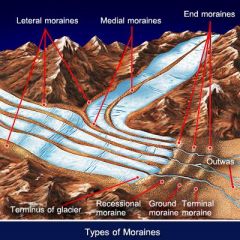
1. lateral: on the side 2. medial: 2 laterals come together 3. terminal: at the end of glacier 4. recessional: going back 5. ground: material below glacier |
|
|
Glaciofluvial deposits |
-meltwater with ice when deposited -usually sorted -wide range of deposits -wide range of sediment sizes -outwash plain, drumlins, eskers, kettle holes |
|
|
Drumlin |
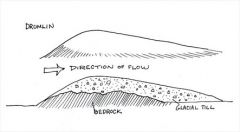
formed through sub glacier meltwater sediment filled |
|
|
Esker |

a long ridge of gravel and other sediment, typically having a winding course, deposited by meltwater from a retreating glacier or ice sheet. |
|
|
Outwash plain |
formed of glacial sediments deposited by meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier |
|
|
Kettle holes |

a shallow, sediment-filled body of water formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters. |
|
|
Antarctica |
-each year the continent approximately doubles in size due to the growth of the sea ice -max in October/min in February |
|
|
Quaternary glaciation |
-cycles of glaciation and deglaciation -multiple glaciations during last 2.58 my -interrupted by warmer periods-interglacials causes: earth wobbles, variation of tilt |
|
|
Glacial stages |
-Wisconsin (glacial) -when put heavy ice on land, it dips -Sangamonian (interglacial) -Pre Illinoian |
|
|
Glaciation |
-changed much of landscape -lowered sea levels and temperatures -much info from ice cores -paleoclimatology |

