![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A 8‐year‐old female presents with swelling around her right eye
and abdominal pain. Blood work and radiographic imaging reveal Chagas’ disease and megacolon, respectively. Which component of the colon wall is most likely to be involved with this condition? |
Myenteric plexus
|
|
|
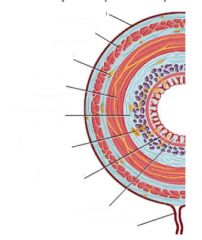
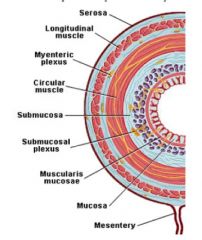
What are the four layers comprising the wall of G.I. Organs?
|
– mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and outer covering
|
|
|
What can be found in the submucosa of the GI tract?
|
– Submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus, maybe glands
|
|
|
What is found between the muscular layers of the muscularis externa?
|
– Myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus
|
|
|
What types of epithelium are found in the GI tract?
|
– Simple columnar OR stratified squamous
|
|
|
What are the components of the mucosa?
|
– epithelium, lamina propria, & muscularis mucosa
|
|
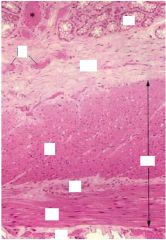
|
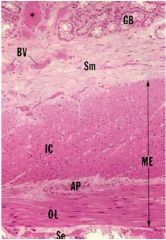
muscularis externa
AP- auerbach's nerve plexus OL- outer longitudinal IC- inner circular BV- blood vessels SE serosa |
|
|
|
|
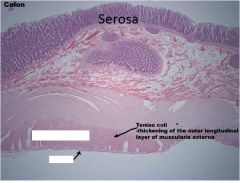
Label the serosa
|
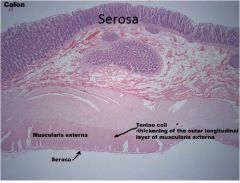
|
|
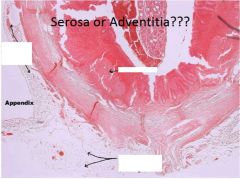
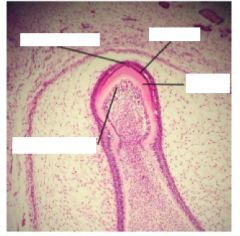
Label arrowed areas
|
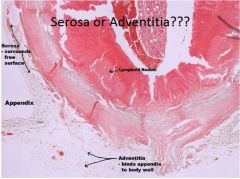
|
|
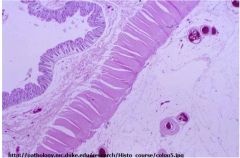
Label the four layers of the GI
|
left is mucosa, submucosa, intercircular, muscularis externa, outer longitudinal, adventitia
|
|
|
name the 4 types of papilla on the tongue
|
1. Filiform
2. Fungiform 3. Foliate 4. CIRCUMVALLATE OR VALLATE (L., AROUND |
|
|
Deciduous vs permanent teeth?
#'s when should you have each? |
1. Deciduous (primary or milk) teeth:
– 10 per jaw (20) – Usually complete by two years of age 2. Permanent (secondary) teeth: 16 per jaw (32) 18Y-22Y – Usually complete by midteens, except third molars (“wisdom teeth”) |
|
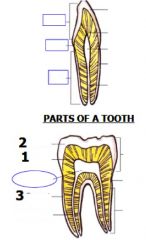
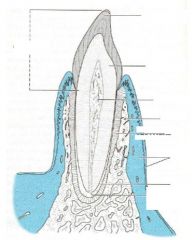
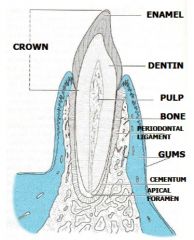
What are the three parts of the tooth?
|
Each type of tooth has:
– Crown projects from gingiva (gum) – Neck (cervix) where crown and root meet – Root fixed in alveolus (bony socket) by periodontal membrane |
|
|
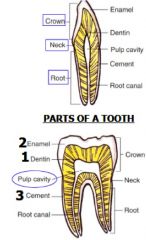
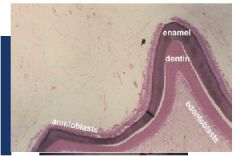
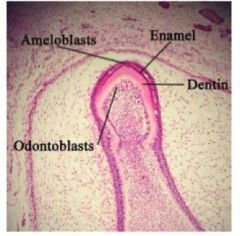
Entire tooth composed of three calcified (mineralized) substances... name them and their roles
|
Entire tooth composed of three
calcified (mineralized) substances: 1. Enamel covers crown portion PARTS OF A TOOTH 2. Cementum covers root portion 3. Dentin makes up bulk of tooth |
|
|
describe dentin and type of collagen
|
Second hardest substance in
body: (harder than bone) – ~70% calcium hydroxyapatite – ~30% organic material & water Type 1 collagen made from Odontoblasts which turn into dentin |
|
|
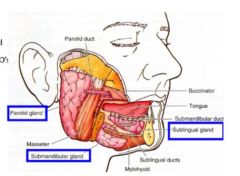
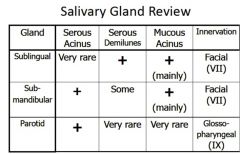
Describe the three main salivary glands
|
1. parotid- Almost exclusively serous secretion: largest,
2. submandibular- Mixed (serous & mucous) 3. sublingual gland- smallest salivary glad, mainly mucous |
|
|
what substances in the body are harder than bone?
|
– enamel and dentin
|
|
|
• what structure holds the tooth in place and acts as a shock absorber?
|
– Periodontal ligament
|
|
|
• Describe the structure of the tongue
, |
– str. Squamous epi, all skeletal muscle
|
|
|
what is unique about the skin of the lips/vermillion zone?
|
– thin Ker. Str sqamous epithelium with no sweat glands, hair follicles, nor sebaceous glands
|
|
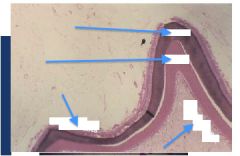
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
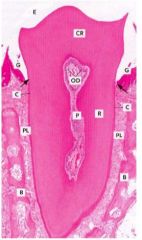
Periodontal ligament (PL)
P- pulp OD-odontoblasts CR- crown, C- cementum R- root Outer layer of the root(s) – Overlies dentin • Anchors periodontal ligament to root(s) of tooth • Approximately as hard as bone: proteoglycans & glycoproteins • Cementoblasts make cementum: – Become cementocytes (similar to osteocytes) |
|
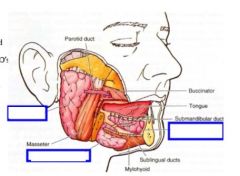
Identify the three main salivary glands
|
|
|
|
|
|
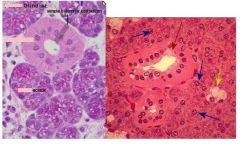
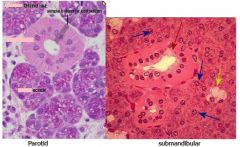
Distinguish whether these slides are parotid, submandibular or sublingual
|
|
|
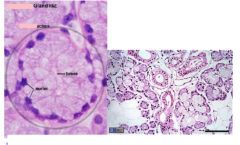
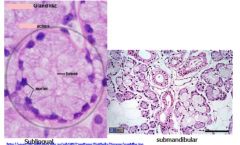
Identify the type of salivary gland shown
|
|
|
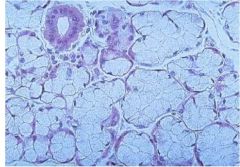
What type of gland is shown?
|
sublingual
|
|
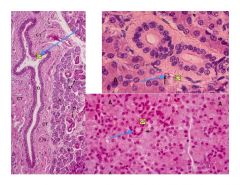
What is the blue arrow pointing to for each type of duct system in the salivary glands
|
Left- points to interlobular duct
Bottom right- points to intercalated duct Top Right- striated duct |
|
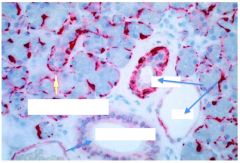
H and E stains muscle/myoepithelium red and this shows two ducts in your mouth... label them
|
|
|
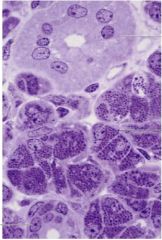
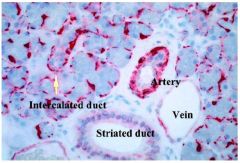
What salivary gland is this and what proves it?
|
Parotid gland see intercalated duct on bottom, striated duct on top and serous cells all over
Purely serous: – Serous cells stain dark – Rounded nuclei |
|
|
|
|
|
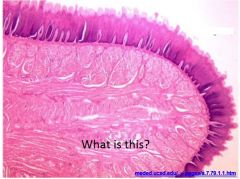
tongue slide
|

