![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
|
Melanin Pigmentation of the lips and oral mucosa
|
|
|
|
Sulfur granules in pus contain gram + brnaching filamentous bacteria
|
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
|
|
Peritonsillar abscess, pharyngitis, and scarlet fever caused by
|
Strep Pyogenese
|
Erythrogenic toxin (super antigen) --> rash on skin an tongue
can cause acute rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis |
|
|
Hairy leukoplakia (glossitis associated with bilateral white, hairy excrewscences on lateral border of tongue caused by
|
EBV
|
|
|
|
Mumps is caused by
|
Paramyxovirus
|
Bilateral parotitis with increased serum amylase, can lead to meningoencephalitis, unilateral orchitis or oophoritis, pancreatitis.
|
|
|
Ddx for melanin pigmentation in oral mucosa
|
Addison's disease, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
|
|
|
|
Ameloblastoma
|
most common odontogenic tumor
Arise from enamel organ epithelium. Located in the mandible, produces a radiolucency in bone. |
|
|
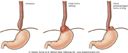
|
Hiatal hernia
|
|
|
|
Common infectious agents for infectious esophgitis
|
HSV, CMV, and candida
|
HSV: multi nucleated squamous cells with intranuclear inclusions
CMV: basophillic intranuclear inclusions Candida: yeast and pseudohyphae |
|
|
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
|
Mucosal tear in the proximal stomach and distal esophagus leading to hematemesis
|
Due to severe retching in alcoholics and bulimia
|
|
|
Boerhaave's syndrome
|
Rupture of the distal esophagus
|
|
|
|
Chagas's disease
|
destruction of ganglion cells by leishmanial forms
|
|
|
|
Most common esophageal cancer in US
|
distal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
|
Barrett's esophagus is most common predisposing cause
|
|
|
Most common esophageal cancer in developing countries
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|
smoking cigarettes most common cause
|
|
|
Most common cause of hematemesis and melena
|
PUD (peptic ulcer disease)
|
|
|
|
An infant 2-4 weeks vomiting of non-bile-stained fluid... Think of
|
Congenital pyloric stenosis
|
|
|
|
Erosions vs. Ulcer
|
Erosions: breach in the epithelium of the mucosa
Ulcer: breach in the mucosa with extension into the submucosa or deeper |
|
|
|
Most common cause of hemorrhagic gastritis
|
NSAIDs
|
|
|
|
Type AChronic atrophic gastritis
|
Fundus and body of stomach, most often due to pernicious anemia
|
Complications:
Achlorhydria with hypergastrinemia Macrocytic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency Increased risk for adenocarcinoma |
|
|
3 main diseases associated with H pylori
|
1. Duodenal and gastric ulcers
2. Type B antral chronic atrophic gastritis 3. Gastric adenocarcinoma and low-grade B-cell malignant lymphoma |
|
|
|
Menetrier's disease
|
Hypertrophic gastropathy --> giant rugal folds due to hyperplasia of mucus-secreting cells
|
Causes hypoproteinemia (protein-losing enteropathy)
Atrophy of parietal cells (achlorhydria) which increases risk for adenocarcinoma |
|
|
T/F Duodenal ulcers are never malignant
|
True
|
|
|
|
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome:
|
maligant islet cell tumor secreting gastrin
|
|
|
|
Hartnup disease
|
Cannot absorb neutral amino acids
|
|
|
|
T/F Gastric hyperplastic polyps have high malignant potential
|
False
|
|
|
|
2 types of gastric polyps
|
1. Hyperplastic polyp
2. Adenomatous polyp |
Adenomatous polyps have potential for malignant transformation
|
|
|
Most common benign tumor in the GI tract
|
Leiomyoma
|
|
|
|
Most common gastric carcinoma
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
|
Precursor lesion for gastric adenocarcinoma
|
Intestinal metaplasia
|
|
|
|
Krukenberg tumors
|
A type of diffuse gastric adenocarcinoma --> hematogenous spread of signet-ring cells to both ovaries
|
|
|
|
Clinical findings of gastric adenocarcinoma
|
1. Weight loss (most common), epigastric pain with vomiting
2. Metastasis to left supraclavicular node 3. Paraneoplastic skin lesions 4. Metastasis to umbilicus |
|
|
|
Most common site for extranodal malignant lymphoma
|
Stomach
|
|
|
|
2 types of primary gastric malignant lymphoma
|
1. Low grade B-cell lymphoma
H. pylori related MALToma 2. High-grade B-or T-cell lymphomas |
|
|
|
Hematochezia
|
Massive loss of whole blood per rectum
|
Sigmoid divericulosis or angiodysplasia
|
|
|
T/F Invasive diarrhea is low-volume
|
True
|
|
|
|
3 main causes of malabsorption
|
Pancreatic insufficiency, bile salt deficiency, small bowel disease
|
|
|
|
Cholangiocarcinoma is associated with what bugs in the developing countries?
|
Clonorchis sinensis (liver fluke)
|
|
|
|
Most common cause of adult gastroenteritis
|
Norwalk virus
|
|
|
|
Most common cause of childhood diarrhea
|
Rotavirus
|
Rotazyme test on stool establishes diagnosis.
|

