![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Retroperitoneal structures |
GI - no mesentery Non-GI Injuries cause blood or gas accumulation in Retroperitoneal space |
|
|
|
RetroP structures list |
Suprarenal glands = adrenal Aorta + IVC Duodenum - 2nd to 4th Pancreas - except tail Ureters Colon - asc and desc Kidneys Esophagus - lower 2/3 Rectum - partially |
SAD PUCKER |
|
|
Falciform L |
Liver to ant ab wall Derivative of ventral mesentery Contains ligamentum teres hepatis = derivative of fetal umbilical vein |
|
|
|
Hepatoduodenal L |
Liver to duodenum Contains portal triad = proper hepatic A, portal vein, common bile duct Pringle maneuver = ligament may be compressed between thumb and index finger placed in omental foramen to control bleeding Borders omental foramen |
|
|
|
Gastrohepatic L |
Liver to lesser curvature of stomach Contains gastric arteries Separates greater and lesser sacs on R May be cut in surgery to access lesser sac |
|
|
|
Gastrocolic L |
Greater curvature to transverse colon Contains gastroepiploic A Part of greater omentum |
|
|
|
Gastrosplenic L |
Greater curvature and spleen Contains short gastrics, left gastroepiploic vessels Separates greater and lesser sacs on L |
|
|
|
Splenorenal L |
Spleen to posterior ab wall Contains splenic A and V, tail of pancreas |
|
|
|
Layers of gut wall |
Mucosa Sub mucosa Muscularis externa Serosa |
|
|
|
Mucosa |
Epithelium - absorption Lamina propria - support Muscularis mucosa - motility Erosions in mucosa only |
|
|
|
Submucosa |
Includes Meissner plexus |
|
|
|
Muscularis externa |
Includes myenteric nerve plexus = Auerbach |
|
|
|
Serosa |
Called serosa when intraperitoneal Called adventitia when Retroperitoneal |
|
|
|
Basal electric rhythm |
Stomach - 3/min Duodenum - 12/min Ileum - 8-9/min |
|
|
|
Esophagus |
Nonkeratinised Stratified Squamous epithelium |
|
|
|
Stomach |
Gastric glands |
|
|
|
Duodenum |
Villi + microvilli - increase absorptive surface Brunner glands - Submucosa Crypts of Lieberkuhn |
|
|
|
Jejunum |
Plicae circulares Crypts of Lieberkuhn |
|
|
|
Ileum |
Peyer patches - lamina propria, Submucosa Plicae circulares - in proximal ileum Crypts of Lieberkuhn Largest no of goblet cells in SI |
|
|
|
SMA syndrome |
Occurs when transverse portion/3rd segment of duodenum is entrapped between SMA and aorta => intestinal obstruction |
|
|
|
Abdominal aorta branches |
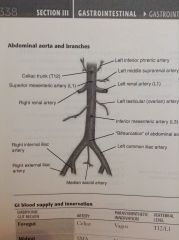
Supplying GI = branch anteriorly Non-GI = branch laterally |
|
|
|
Foregut supply |
Celiac A Vagus paraS T12/L1 Pharynx to duodenum Liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen |
|
|
|
Midgut supply |
SMA Vagus paras L1 |
|
|
|
Hindgut |
IMA Pelvic paraS L3 Splenic flexure = watershed region |
|
|
|
Celiac trunk branches |
Common hepatic Splenic Left gastric Main BS of stomach |
|
|
|
Collateral arterial circulation |
Compensate when abdominal aorta blocked Superior epigastric + inf epigastric Sup pancreaticduodenal + inf PD Middle colic + left colic Superior rectal + middle and inf rectal |
|
|
|
Pectinate line |
Where endoderm of Hindgut meets ectoderm |
|
|
|
Above pectinate line |
AdenoCa Internal haemorrhoids - not painful due to visceral innervation Superior rectal A <- IMA Superior rectal vein -> inf mesenteric vein -> portal system Deep LN |
|
|
|
Below pectinate line |
External haemorrhoids - painful - somatic innervation Anal fissures - tear in mucosa - pain on excretion, blood on paper, posteriorly, poorly perfused area SCC Inf rectal A <- internal pudendal A Inf rectal V -> int pudendal V -> int iliac V -> IVC |
|
|
|
Femoral region organisation |
Lateral to medial Nerve Artery Vein Empty space Lymphatics |
NAVEL |
|
|
Femoral triangle |
Femoral A, V, nerve |
|
|
|
Femoral sheath |
Fascial tube - 3/4 cm below inguinal L Femoral V, A, canal - deep LN NOT FEMORAL NERVE |
|
|
|
Diaphragmatic hernia |
Ab structures enter thorax Infants - detective development of pleuroperitoneal membrane Hiatal most common - stomach herniates up through esophageal hiatus of D Sliding hiatal H = gastroesophageal Jxn displaced up - hourglass stomach Paraesophageal H = gastroE Jxn normal - fundus protrudes through thorax |
|
|
|
Indirect inguinal hernia |
Goes thro internal/deep inguinal ring, external/superficial inguinal ring Into scrotum Enters inguinal ring lateral to epigastric A Infants - failure of processus vaginalis to close More common in males Follows path of testes descent Covered by all 3 layers of spermatic fascia |
|
|
|
Direct inguinal hernia |
Through inguinal triangle = Hesselbach Directly through ab wall medial to inf epigastric A Trough external/superficial ring only Covered by external spermatic fascia Older men |
Medial to inf epiG A - direct Lateral - indirect |
|
|
Femoral H |
Below inguinal L through femoral canal Below and lateral to public tubercle Females Leading cause of bowel incarceration |
|
|
|
Hesselbach triangle |
Inguinal triangle Inf epigastric vessels Lateral border of rectus abdominis Inguinal L |
|

